- 1. What Is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
- 2. What Is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
- 3. What Is a Virtual Private Server (VPS)?
- 4. What Are the Differences Between VPN, VPC, and VPS?
- 5. What Are the Similarities Between VPN, VPC, and VPS?
- 6. When to Choose VPN, VPC, and VPS
- 7. VPN vs. VPC vs. VPS FAQs
VPC vs. VPN vs. VPS: What Are the Differences?
VPN, VPC, and VPS differentiate in core functionality: secure network access, isolated cloud environments, and virtual server platforms, respectively.
VPNs encrypt internet connections for safe data transit, VPCs provide a segregated space within the cloud for dedicated resource use, and VPSs offer virtual servers with dedicated control and resources akin to physical servers. These technologies cater to specific needs: VPNs focus on security, VPCs on cloud resource isolation, and VPSs on server virtualization.
What Is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
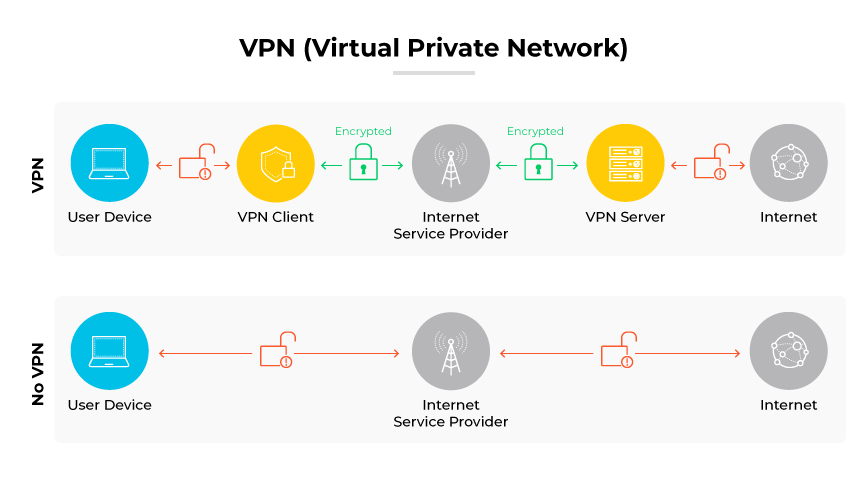
A VPN (virtual private network) establishes a secure and encrypted link, protecting data as it travels between devices across the internet. This secure channel acts as a shield for sensitive data against possible risks and breaches. VPNs are essential for providing protected remote connections to company assets, maintaining the privacy and protection of data.
A VPN establishes an encrypted pathway known as a tunnel through which a device's data is securely transmitted. When connected to a VPN, a device behaves as if it's on the same local network as the VPN, allowing for safe data exchange. The VPN provides a protected conduit for data to travel, offering remote internet users a secure means to connect to a corporate network and conduct online activity. Corporate VPNs are commonly used within remote home offices or even on public Wi-Fi.
With a VPN, information traverses the web within a protected tunneling framework, shielded through encryption to block unauthorized entry. VPNs use predominant encryption standards such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) to secure data. Encryption converts the data into a secure code decipherable only with a specific key. The data is then encapsulated with destination information, and upon verification of the user, access is granted, with the system monitoring the session's activities.
What Is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
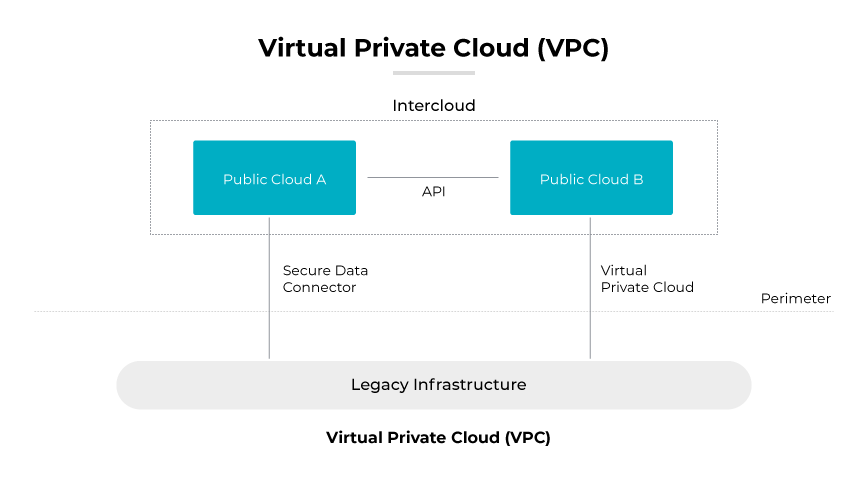
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are dedicated segments within a public cloud service infrastructure that provide a private network space to an enterprise. They offer control over virtual networking environment configurations, including selections of private IP address ranges, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. A VPC combines the scalability and efficiency of public cloud computing with the data isolation and security of a private cloud.
Enterprises utilize VPCs to deploy applications in a virtual network that resembles a traditional network experienced in an on-premises data center, but with the added benefit of the cloud's scalable infrastructure. In a VPC, resources like virtual servers, storage, and network components can be allocated and scaled according to business needs, offering a flexible and cost-efficient solution for companies looking to extend their data centers without investing in physical hardware.
The ability to establish secure connections from a VPC to an organization’s local network makes it an integral part of enterprise cloud strategies. These connections can be made via encrypted tunnels, ensuring secure data transfer, and allowing for a hybrid cloud environment where applications can leverage resources across both local and cloud networks seamlessly. This empowers businesses with a balance of control, security, and the competitive edge that cloud resources provide.
What Is a Virtual Private Server (VPS)?
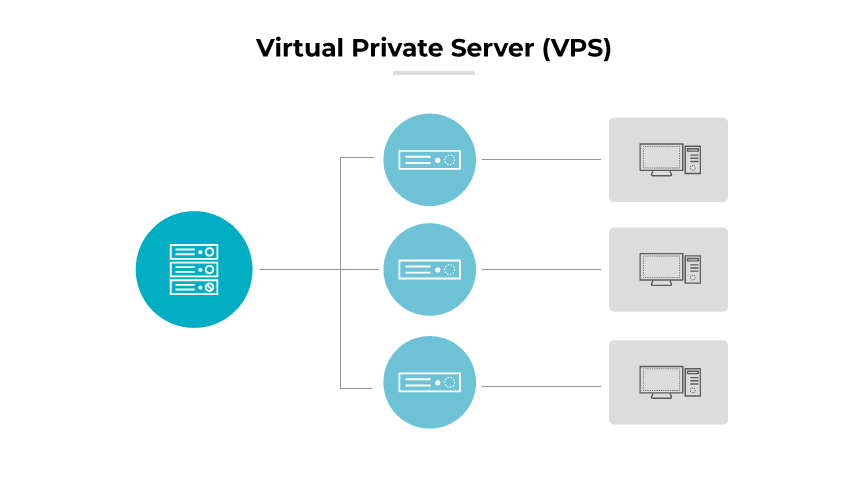
A virtual private server (VPS) works similarly to a partitioned space on a powerful server, where each partition operates independently as its own server. This virtual server provides businesses with dedicated resources, such as CPU and memory, without the investment in physical hardware. Virtual private servers are ideal for enterprises that require control over their hosting environment with the affordability of a shared resource. In a VPS, the operating system installed on it determines the execution environment for applications, including compatibility and available system resources.
In practice, a VPS offers the customization and control of a dedicated server while remaining cost-effective. Enterprises can install their choice of software, manage settings, and scale resources to match their demands. This scalability ensures that businesses only pay for what they use, optimizing their IT budget and resources.
The operational advantage of a VPS lies in its balance between autonomy and economy. It gives enterprises their own operational space in a shared server, reducing costs while maintaining a high level of performance and security. For growing businesses that need to manage web applications or services without the complexities of managing physical servers, a VPS is a strategic choice.
What Are the Differences Between VPN, VPC, and VPS?
Purpose and Functionality
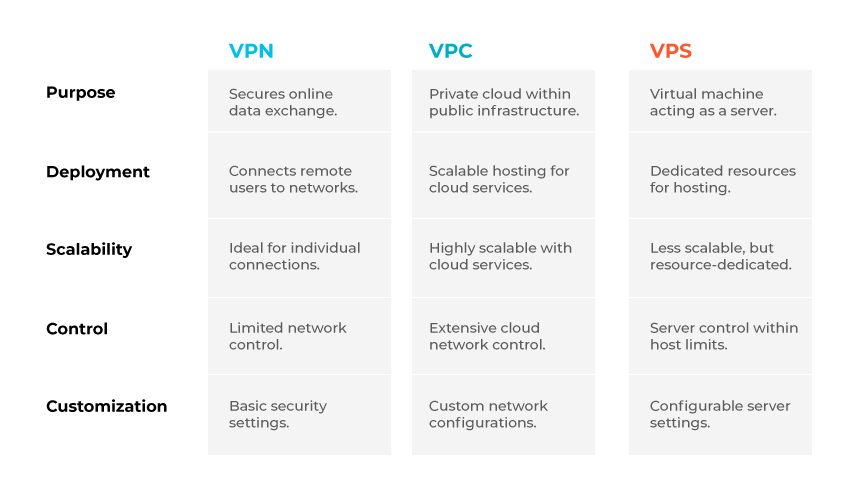
A VPN (virtual private network) creates a secure connection over the internet to protect data exchanges between a user and the network. A VPC (virtual private cloud), however, is a segment of a public cloud infrastructure that offers a private cloud environment. Lastly, a VPS (virtual private server) is a virtual machine provided by an internet hosting service, giving users the experience of a dedicated server.
Deployment and Scalability
VPNs are typically used to securely connect remote users to a corporate network, emphasizing privacy and data protection for individual connections. VPCs are cloud-based environments that offer scalable infrastructure solutions for hosting services and applications, aligning with the broader scalability of cloud services. VPSs stand out for their ability to provide dedicated server resources and environments for applications and services, though they are generally less scalable than VPCs.
Control and Customization
VPNs offer secure access but limited control over the networking infrastructure. In contrast, VPCs provide extensive control over network settings within a cloud provider's environment, allowing for detailed customization of the virtual networking components. VPSs offer a middle ground, with administrative access and customization capabilities for the server environment, though within the constraints of the hosting provider's platform.
What Are the Similarities Between VPN, VPC, and VPS?
Virtualization Foundation
Both VPN (virtual private network), VPC (virtual private cloud), and VPS (virtual private server) are built on the concept of virtualization. They utilize software to simulate hardware functionality and create dedicated resources from a shared physical infrastructure. This enables the creation of isolated, secure environments for networking, computing, and storage.
Security, Privacy, and Controlled Access
VPN, VPC, and VPS technologies are all geared toward enhancing security. They employ various mechanisms to safeguard data and communication. VPNs provide secure tunnels for data transmission, VPCs allow for the creation of segregated network spaces in the cloud, and VPSs offer a contained environment for running applications, all contributing to a heightened security posture.
Privacy is also a core characteristic shared by VPNs, VPCs, and VPSs. They are designed to ensure that access to the network, data, and computing resources is restricted to authorized users only. This exclusivity is established through authentication methods like cryptographic certificates or username and password combinations.
Support for Remote Connectivity
The ability to support remote connectivity is another similarity. VPNs facilitate secure connections from remote locations to the corporate network, VPCs enable the creation and management of network resources accessible over the internet, and VPSs can be managed and utilized remotely, providing flexibility and convenience for users and administrators alike.
When to Choose VPN, VPC, and VPS
Choosing between a VPN (virtual private network), VPC (Virtual Private Cloud), and VPS (Virtual Private Server) is not about selecting one over the others, but rather understanding when each technology is appropriate based on organizational needs. These technologies serve different purposes and are tools for specific scenarios in enterprise infrastructure.
A VPN is essential when secure, remote access to a network is required. Virtual private networks are the technology of choice for businesses that prioritize data protection while accessing resources over the internet or when connecting multiple business locations. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential even when transmitted over public networks.
For organizations looking to deploy services within a secure, isolated portion of a cloud provider's platform, a VPC is the right choice. It provides a simulated private cloud within a public cloud, offering the enterprise control over virtual networking environment components like IP addresses, subnets, and network gateways.
When the need arises for a dedicated server environment without the costs associated with physical hardware, a VPS stands out. A VPS is suitable for businesses seeking control over their hosting with the flexibility to install a wide range of software and manage settings, which would not be possible on shared hosting plans.
Each of these technologies plays a pivotal role in creating a network architecture that is secure, scalable, and optimized for various business requirements.
