How to Set Up a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
Setting up a virtual private network involves multiple steps, often including:
- Aligning essential VPN components
- Preparing the network
- Client installation
- Consulting configuration guidance
- Logging into the VPN
- Selecting the VPN protocol
- Troubleshooting
- Optimizing the connection
The VPN setup process can vary significantly based on the solution and platform. While the steps provided offer a very general overview on how to use VPNs, they may not apply universally to every enterprise service or platform. It is essential to consult specific guidance from the chosen provider to ensure a successful, efficient setup tailored to the particular environment in use.
Step 1: Align Essential VPN Components.
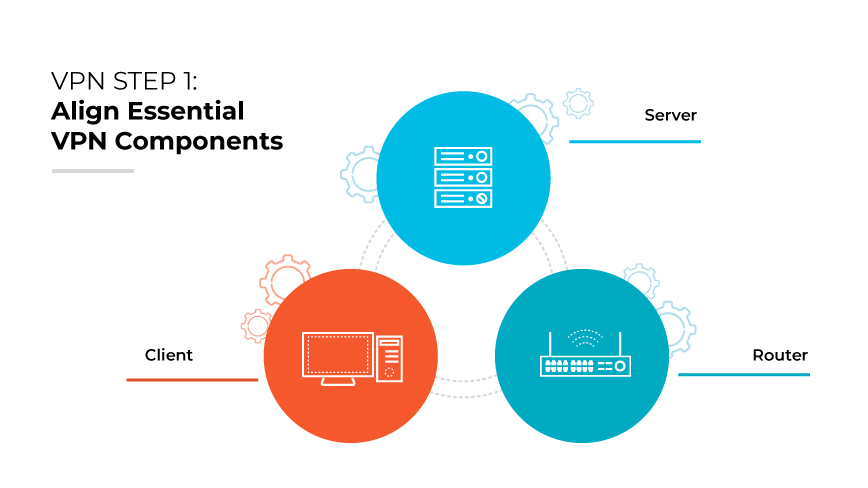
To establish a robust VPN, begin by securing a VPN client, server, and router. A VPN client serves as the bridge for users to connect to servers, enabling remote access to the network. Modern routers typically have VPN clients integrated, which simplifies setup. The server acts as a central hub that all encrypted communications pass through, ensuring secure access to enterprise resources.
The VPN's effectiveness is dependent on the integration of these components within the existing network infrastructure. This step should be executed with careful consideration of network zones, routing protocols, and security policies to ensure a secure yet flexible VPN operation that aligns with technical and security standards.
Step 2: Prepare the Network.
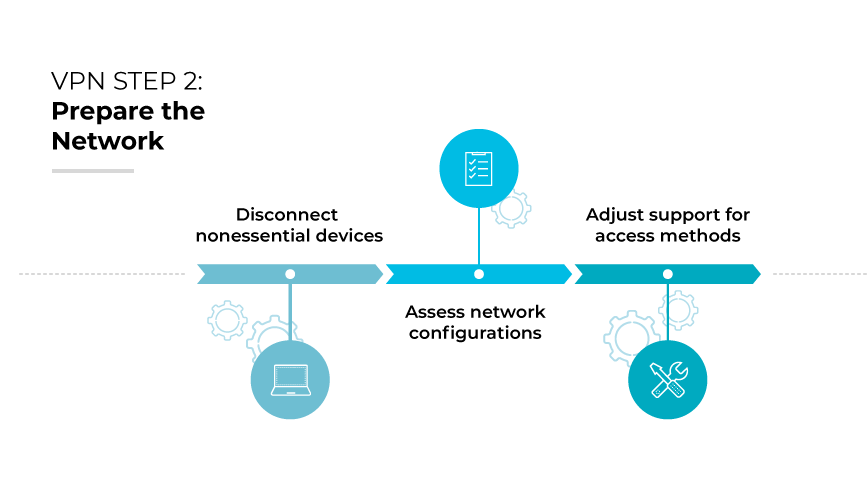
Prior to deployment, remove redundant VPN client software and disconnect nonessential devices that could cause conflicts or security breaches. This process is critical in preparing the network for a secure, efficient VPN implementation. It is also the time to assess network configurations and make necessary adjustments to support a variety of access methods, including wired and wireless connections, without compromising on security or performance.
Step 3: Initiate Client Installation.
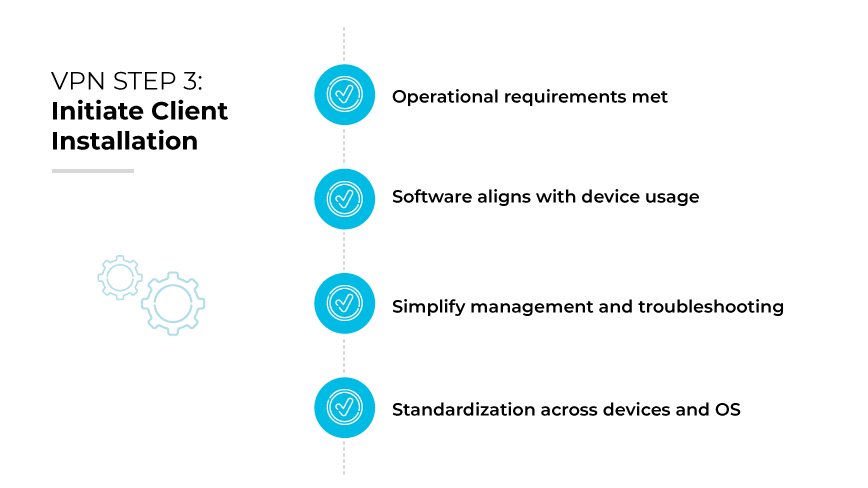
Installing the client software provided by your VPN service is the next critical step. It is crucial to focus on immediate operational requirements, selecting client versions that match hardware specifications and operating systems. Ensure the software aligns with the devices most utilized within your enterprise, including mobile devices, for seamless integration and deployment.
Once the appropriate software is identified, proceed with installation on all necessary devices. During this phase, maintain a consistent approach across all platforms to simplify management and troubleshooting. Standardization is key to establishing a reliable VPN connection across different devices and operating systems, laying the groundwork for secure, remote network access.


If the VPN service lacks device specific software, consult the vendor for setup manuals. This guidance should provide detailed instructions for how to add VPN configuration, ensuring the connection is secure and stable across various devices. It is essential to adapt general instructions to fit the specific infrastructure and security requirements of your organization's network.
Additionally, seek best practices for network configurations that support VPN use, such as setting up firewalls, adjusting network routes, and ensuring proper tunneling protocols are in place.

Post client installation, input the necessary login details. Upon login, the VPN typically connects to the nearest available server. It is imperative for network administrators to ensure access credentials are securely managed and distributed. The process should use enterprise grade authentication methods to validate user identities and maintain robust security.
Once connected, users should verify the integrity of the connection, whether on mobile devices or traditional computing platforms. It is recommended to check the secured IP address and conduct a brief network test. These actions validate the effectiveness of the VPN and confirm that the user's data is routed through the VPN's encrypted tunnel.

Choosing a VPN protocol properly is pivotal to balancing the network’s speed and security. Protocols such as OpenVPN and L2TP/IPSec provide robust security and are ideal for organizations that prioritize data protection. Meanwhile, options like SSTP and PPTP may offer increased speeds suitable for less sensitive data transmission.
Administrators should evaluate the nature of the data traffic and the security requirements of their organization to select the most appropriate protocol. It is essential to configure the VPN service to use a protocol that aligns with the organization's specific needs for encryption, authentication, and speed. This step is crucial in ensuring a secure, efficient VPN setup that supports the company's operations without compromising on performance or security.
Step 7: Troubleshoot Potential Issues.
When connection troubles emerge, a systematic approach is essential. Begin by restarting the VPN client or device to reset the connection. Ensure there are no conflicts with other VPN services. It is also wise to check and update VPN software drivers, as outdated components often cause instability.
If login issues persist, verify that the correct credentials are being used. If uncertainty remains, consult any provided documentation or support from the VPN provider. Exploring alternative servers or protocols can also overcome connectivity problems. Sometimes certain configurations yield better stability. Ensure that other software, like firewalls or security suites, isn't interrupting the VPN.
Step 8: Optimize the Connection.
Customize VPN settings to align with business operations. Determine auto-start behavior based on usage frequency. Set commonly used servers as defaults to expedite future connections.
Optimizing a VPN connection ensures seamless integration into daily operations. Consider automatic activation of VPN upon device startup for constant protection, particularly for remote or mobile workforces. Prioritize server selection, setting the most frequently accessed servers as the default. This proactive measure simplifies the process, reducing the time required to establish connections in subsequent sessions.
Assess network performance regularly and consider implementing Quality of Service (QoS) rules to prioritize VPN traffic, especially for critical business applications. This ensures that VPN traffic is not adversely affected during high bandwidth usage.
Remember, the optimal configuration is one that balances security, speed, and efficiency, tailored to the unique demands of the enterprise environment.
