SoftEther vs. OpenVPN: What Are the Differences?
The differences between SoftEther and OpenVPN include their approach to encryption, performance, and interoperability.
SoftEther is known for high speed performance, advanced encryption methods, and its ability to support multiple VPN protocols. OpenVPN stands out for a strong security model and its extensive support community.
What Is SoftEther?
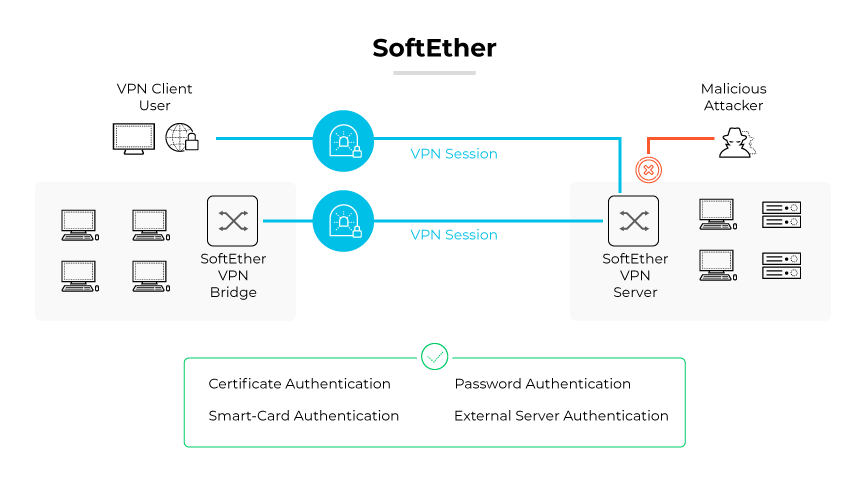
SoftEther, short for Software Ethernet, is an open source VPN protocol designed for creating secure network communications. The protocol uses robust encryption to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. SoftEther facilitates speedy and reliable client-to-server connections, making it suitable for a wide array of network configurations.
The SoftEther protocol differentiates itself by offering a versatile VPN server capable of supporting multiple protocols such as IPSec and L2TP. This flexibility is further enhanced by the protocol's user friendly management tools. These include a GUI for the SoftEther VPN Server and Bridge management, and a command line interface for advanced configuration.
SoftEther works by establishing secure channels through initiating a handshake between the client and server. Then the protocol forms an encrypted VPN tunnel through which data passes securely. Protective measures like AES-256 encryption and RSA-4096 bit keys are used to fortify connections against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
A notable feature of SoftEther is its compatibility with modern internet protocols, supporting both IPv4 and IPv6 stacks. This ensures the protocol's longevity and adaptability as networking technologies evolve. SoftEther's ability to integrate with different operating systems and VPN technologies makes it a comprehensive solution for establishing secure network environments.
The SoftEther protocol uses the OpenSSL library, which upholds stringent encryption and authentication standards. The protocol takes a meticulous approach to user authentication methods, strategic VPN packet filtering, and security policies.
The origin of SoftEther can be traced back to a university project which evolved into an open source network protocol. It was conceived at the University of Tsukuba in Japan as part of a master’s thesis in 2004. The project's goal was to develop a versatile and robust VPN solution that could navigate firewalls effortlessly.
What Is OpenVPN?
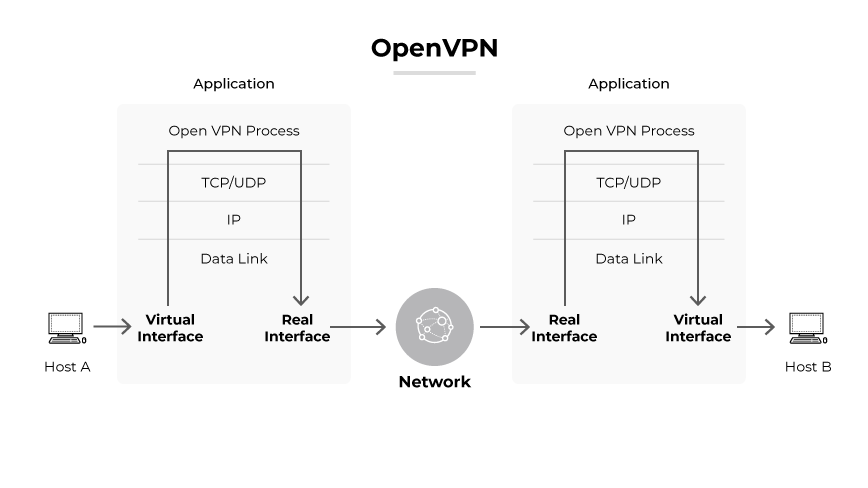
OpenVPN is an open source VPN software project, a VPN protocol, and the name of the company behind the two. OpenVPN facilitates secure internet connections by encrypting data traffic between devices. Renowned for robust security features, it enables encrypted VPN tunnels for data, safeguarding communications from potential eavesdropping. The protocol’s versatility is exemplified in its support for various network configurations, from individual remote access to site-wide VPN connections.
The protocol is distinguished by its dual mode operation, using both TCP and UDP to balance speed and reliability. TCP ensures ordered and complete data delivery. UDP offers speed, making it preferable for fast paced applications. OpenVPN's usage of the OpenSSL library for encryption and the SSL/TLS protocol for key exchange provides high grade security, characterized by up to 256-bit encryption with advanced cipher suites.
OpenVPN stands out for its open source nature, allowing for community driven development and third party audits. Its compatibility with IPv4 and IPv6 addresses future networking needs, ensuring longevity and adaptability. The protocol's administration interface simplifies VPN management, enabling businesses to configure servers, manage access, and direct traffic effectively.
Authentication options within OpenVPN are comprehensive, including pre-shared keys, certificates, and user credentials. Flexibility enables organizations to implement stringent security policies tailored to their needs. Its reputation for security is bolstered by the open source community's commitment to continuous improvement and the OpenSSL library's regular updates.
OpenVPN enables the integration of custom directives. These directives are useful for assigning fixed IP addresses to VPN clients or routing traffic via a proxy server post-establishment of the VPN connection.
OpenVPN works on Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris, QNX, Maemo, Synology NAS devices, ChromeOS, routers with firmware like DD-WRT; OpenWrt; and Tomato, and network appliances that use OPNSense and pfSense.
OpenVPN was co-founded by Francis Dinha and James Yonan. It started as a project to secure data over public networks. Today, OpenVPN is a widely used protocol, providing VPN solutions for users globally.
SoftEther vs. OpenVPN
| OpenVPN vs. SoftEther | |
|---|---|
| Client Support | SoftEther: Supports multiple VPN protocols with a user-friendly interface. OpenVPN: Provides strong encryption and customization, requires more setup effort. |
| Performance | SoftEther: Designed to minimize latency and maximize throughput. OpenVPN: Offers reliable performance with TCP and faster options with UDP. |
| Speed | SoftEther: Optimized for high-speed connections with full Ethernet frame utilization. OpenVPN: Speed varies with the chosen mode; UDP is faster, TCP is more reliable. |
| Security and Encryption | SoftEther: Employs RSA-4096 bit keys and AES-256 encryption, includes deep packet inspection and NAT traversal. OpenVPN: Utilizes the OpenSSL library for up to 256-bit encryption with advanced cipher suites. |
| Interoperability and Flexibility | SoftEther: Compatible with many protocols and operating systems, integrates well with existing infrastructure. OpenVPN: Broad platform support with a management UI for easier VPN administration. |
Comparing SoftEther and OpenVPN protocols involves examining various aspects of their operation and features to understand suitability in various settings.
While both SoftEther and OpenVPN protocols offer distinct advantages, the choice between them depends on specific needs, IT infrastructure, and desired balance between performance, security, and ease of management.
SoftEther VPN Client vs. OpenVPN
SoftEther offers a robust VPN client that supports a multitude of VPN protocols, enhancing adaptability for different network configurations. It's recognized for a user friendly interface that simplifies VPN connections across diverse operating systems. OpenVPN clients focus on a secure, open source framework that provides strong encryption and customization for users, but with a slightly steeper learning curve for setup and management.
SoftEther vs. OpenVPN Performance
When it comes to performance, SoftEther is engineered to minimize latency and maximize throughput, which is critical for enterprises with bandwidth intensive tasks. SoftEther architecture allows for rapid data transmission and efficient network traffic handling. OpenVPN also offers commendable performance, with the choice of TCP for reliability or UDP for speed, catering to different operational demands.
SoftEther vs. OpenVPN Speed
Speed is a vital factor in VPN protocols. SoftEther is designed for high speed connection scenarios, using like full Ethernet frame utilization to ensure swift data exchange. OpenVPN's speed is influenced by its mode of operation. While its UDP mode offers higher speeds suitable for streaming and real time communication, TCP mode focuses on reliability, which can impact speed.
SoftEther vs. OpenVPN Security and Encryption
Both SoftEther and OpenVPN place a high emphasis on security. SoftEther uses RSA-4096 bit keys and AES-256 encryption, offering a high level of security against potential intrusions. It also includes features like deep packet inspection and NAT traversal. OpenVPN is known for its strong security model using the OpenSSL library and supports up to 256-bit encryption with advanced cipher suites, ensuring robust data protection.
SoftEther vs. OpenVPN Interoperability and Flexibility
Interoperability is key for any enterprise VPN solution. SoftEther is compatible with multiple protocols and operating systems, coupled with its ability to integrate with existing infrastructure. OpenVPN also stands out for its broad platform support and its admin web UI, which facilitates VPN management.
SoftEther VPN vs. OpenVPN Solutions
When comparing SoftEther VPN and OpenVPN as VPN solutions rather than protocols, several key differences emerge across implementation, management, and scalability within enterprise environments.
SoftEther VPN provides a comprehensive suite that is lauded for its flexibility and ability to support a broad range of protocols, including SSL-VPN and L2TP/IPsec. The multiprotocol support makes SoftEther VPN highly adaptable to various network configurations and user needs. The solution is also noted for its ability to establish secure VPN connections rapidly, which is critical for organizations requiring efficient and reliable communication.
OpenVPN is recognized for its strong security measures and open source platform, which allows enterprises to customize and adapt the solution to fit their unique requirements. Its administrative interface provides a streamlined approach to VPN management, making it accessible for network administrators to control settings and monitor performance.
Both VPN solutions offer robust security features, including advanced encryption and multiple authentication methods. However, SoftEther VPN stands out for its performance, offering low-latency connections and high throughput, which can be advantageous for bandwidth heavy tasks.
OpenVPN's open source nature implies a continuous process of community driven improvements and updates. This may be beneficial for organizations looking for a solution that evolves with the changing landscape of cybersecurity threats.
In terms of deployment and ongoing management, SoftEther VPN's interface is designed to simplify these processes, but it may present a steeper learning curve. OpenVPN, while robust, can require additional third-party software for installation on most platforms, potentially introducing complexity to the setup process.
How to Choose Between SoftEther and OpenVPN
The choice between SoftEther and OpenVPN should involve considering factors like existing network infrastructure, technical expertise, and specific use cases.
While both protocols offer high levels of security, the decision may come down to whether an organization values SoftEther's high throughput and low latency, or OpenVPN's widespread adoption and strong community support.
It is entirely possible that neither SoftEther nor OpenVPN fully meets the complex, diverse needs of a business. Enterprises may require more sophisticated VPN solutions that offer not just encryption and secure data transit, but also advanced threat protection, network access control, and seamless integration with a broader security ecosystem.
These solutions often come with professional support and service level agreements (SLAs) that are critical for businesses requiring guaranteed uptime and quick resolutions to issues. As a result, many organizations might look beyond SoftEther and OpenVPN to more enterprise focused VPN protocols that align with strategic IT goals and offer a more integrated approach to network security.