- What Is WireGuard?
- What Is a VPN Tunnel?
- What Is a Business VPN? Understand Its Uses and Limitations
- What Is Network Segmentation?
- Ivanti VPN Vulnerability: What You Need to Know
-
Replacing Legacy VPN and NAC Solutions with a Next-Generation Network Security Client for Endpoints
- VPN Security: Are VPNs Safe and Secure?
- What Is SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)?
- What is Remote Access?
- What Is PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)?
- What Is L2TP (Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol)?
- What Is IPsec?
- What Is IKE (Internet Key Exchange)? | IKE Meaning
- What Is an SSL VPN?
- What Is a Remote Access VPN?
- What Is a Cloud VPN?
-
Secure Remote Access | Protect Remote Employees from Cyberthreats
- IPsec vs. OpenVPN: What Are the Differences?
- What is Quality of Service?
- What is a Data Center?
- How to Set Up a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
- How Does a VPN Work?
-
What Is the History of VPN?
- 1960s–1970s: The Dawn of ARPANET and the Need for Connectivity Across Different Networks
- 1980s: TCP/IP and the Public's Introduction to the Internet
- 1990s: The Rise of the Web and Emergence of Early VPN Technologies
- 2000s: VPNs Evolve Alongside Cybersecurity Challenges
- 2010s: A Decade of Digital Transformation
- 2019–Present: The Response to Remote Work and Limitations of VPNs
- VPN History FAQs
- SoftEther vs. OpenVPN: What Are the Differences?
- What Are the Different Types of VPN?
- What Are the Different Types of VPN Protocols?
- VPN Alternatives for Remote Access
- VPC vs. VPN vs. VPS: What Are the Differences?
- What Is a Double VPN?
- What Is a Site-to-Site VPN?
-
What Is a VPN Concentrator?
- How Does a VPN Concentrator Work?
- Why Use a VPN Concentrator?
- VPN Concentrator Benefits
- VPN Concentrator Disadvantages
- VPN Concentrator Encryption Protocol Types
- VPN Concentrator vs. VPN Router
- VPN Concentrator vs. Site-to-Site VPN
- VPN Concentrator vs. IPsec Encryption
- VPN Concentrator vs. VPN Client
- VPN Concentrator FAQs
- What Is a VPN Gateway?
- What Is IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2)?
- What Is OpenVPN?
-
What Is SoftEther (Software Ethernet)?
- How Does the SoftEther VPN Protocol Work?
- What Is a SoftEther VPN?
- SoftEther VPN Architecture
- How Secure Is the SoftEther VPN Protocol?
- Pros and Cons of SoftEther
- How to Use SoftEther VPN
- Comparing SoftEther with Other Protocols
- The History of SoftEther
- Does SoftEther Work In Enterprise Environments?
- SoftEther FAQs
- WireGuard vs. OpenVPN | What Are the Differences?
SSL VPN vs. IPSec: What Are the Differences?
The difference between SSL and IPsec VPNs is that SSL VPNs secure individual web sessions, while IPsec encrypts entire network traffic.
SSL VPNs are generally used for secure web application access and are easier to use because they do not require dedicated VPN client software. IPsec VPNs are used for full network access, requiring a VPN client. They are considered more robust and secure for site-to-site connections.
What Is IPsec?
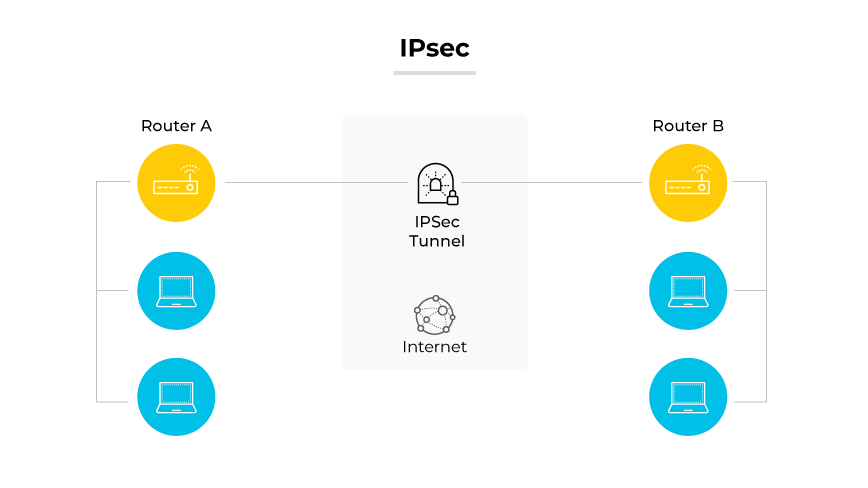
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is a suite of protocols used to authenticate and encrypt each IP packet in a network conversation. The suite is critical for setting up authenticated connections and exchanging cryptographic keys at the start of a session. Commonly implemented in VPN environments, IPsec facilitates the safe transfer of data across open networks by forming secure, encrypted channels among devices.
What Is SSL?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol developed for securing internet communications, providing privacy and data integrity by encrypting the data sent over the internet. SSL ensures the data exchanged between users and websites cannot be intercepted and read by others. It facilitates an authentication process to confirm the identities of parties communicating. Although SSL was succeeded by Transport Layer Security (TLS) in 1999, its principles remain foundational to secure internet communication, as evidenced by the 'HTTPS' prefix in web URLs.
What Are the Differences Between IPsec and SSL?
IPsec and SSL are both protocols used to secure data over the internet, but they operate differently and serve different purposes within a network infrastructure.
IPsec is a suite of protocols designed to secure internet communications at the network layer. It works by authenticating and encrypting each packet of a communication session, ensuring the entire data flow between two points on the internet is secure. IPsec is effective for creating virtual private networks (VPNs) because it can encrypt data transferred between multiple network nodes. IPsec is often used to establish secure connections between fixed ip addresses, ensuring all transmitted data is protected from point to point.
SSL secures data at the application layer, focusing on the encryption of data transmitted over the internet to prevent eavesdropping. It is most commonly recognized by its presence in HTTPS, the secure version of HTTP, which is used for secure transactions on the web. SSL, and its successor TLS, establish an encrypted link between a web server and a browser, ensuring all data passed between them remains private and integral. SSL is commonly used to secure transactions on websites, such as online banking or shopping, and it also forms the basis for SSL VPNs, which allow remote users secure access to web applications.
The key differences are use cases and implementation. IPsec secures all data traffic within an IP network, suitable for site-to-site connectivity. SSL secures individual web sessions, typically used for secure remote access to specific applications via the internet. IPsec is implemented in the network infrastructure and requires client software to be set up on a user’s device, while SSL is implemented on the server side and can be accessed with standard web browsers without additional client software.
What Is an IPSec VPN?
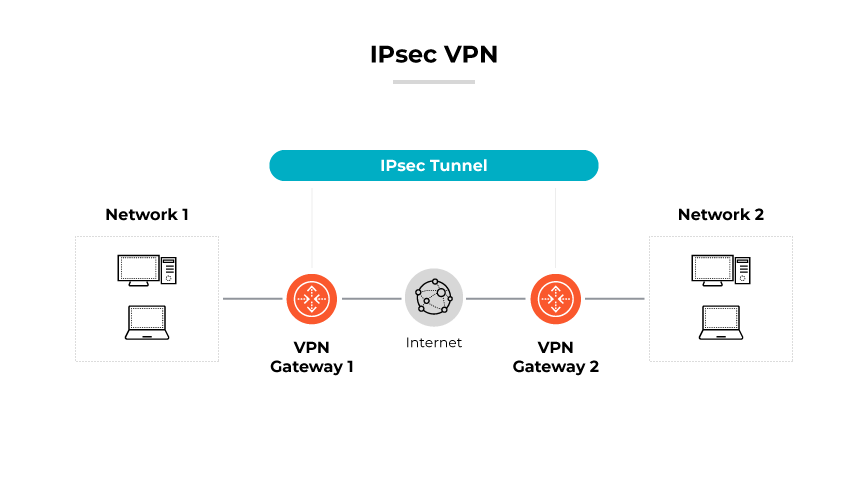
IPSec VPNs are known for their strong encryption capabilities, which protect the data integrity and privacy of communications. They are designed to authenticate data packets during their journey across the network, verifying that the information comes from a trusted source and has not been tampered with.
IPSec VPNs are compatible with various devices and network configurations. Their ability to work at the network layer allows for a seamless, secure integration of multiple network segments, facilitating a unified communication stream across an organization's global infrastructure.
Deploying an IPSec VPN typically involves setting up dedicated software on user devices. This setup secures not just individual applications but the entire data path from the user to the corporate network.
IPSec VPNs provide an encrypted conduit for all network traffic, ensuring end-to-end security. They are especially beneficial for organizations looking for a reliable, secure way to extend the corporate network across geographically dispersed locations, offering a balance between high level security and network performance.
How Does an IPsec VPN Work?
An IPsec VPN functions by creating a secure network tunnel that facilitates encrypted communications between devices across the internet.
IPsec VPN operations can be broken down into several key components. Initially, the VPN establishes a mutual authentication between devices at the start of a connection. This phase involves the exchange of cryptographic keys that will be used to encrypt and decrypt the data. Once authentication is complete, the devices can start transmitting data securely.
During data transmission, IPsec VPNs encapsulate the data packets, effectively hiding the original data and protecting it from unauthorized access. This encapsulation process includes both encryption of the data and the addition of an IPsec header. Encapsulation ensures data can only be decrypted by the receiving device that has the correct cryptographic key.
Since IPsec VPNs can be used across various hardware and software configurations, they are suitable for securely connecting disparate network segments. IPsec VPNs create a secure, reliable method of communication which creates a user experience similar to being directly connected to the enterprise network.
What Is an SSL VPN?
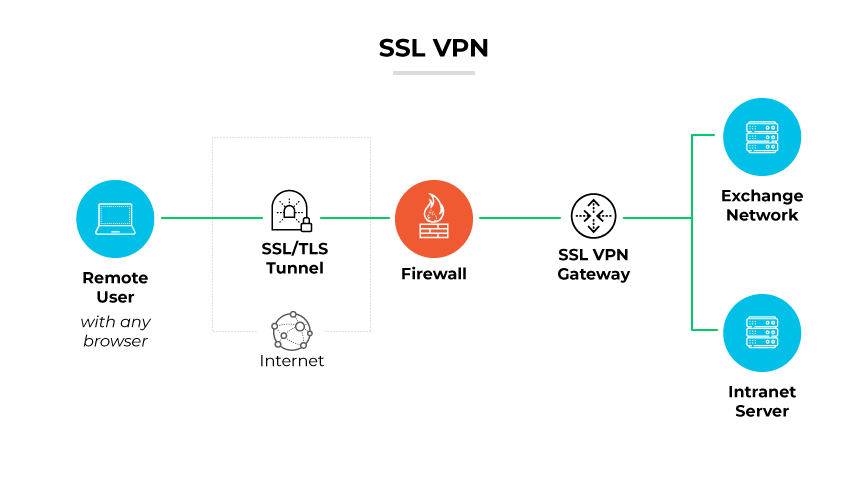
An SSL VPN uses the SSL protocol. The SSL protocol is traditionally used to secure transactions on the internet or provide remote users with secure access to an organization's internal networks and services. This type of VPN is web based, so it can be accessed through a standard internet browser without the need for additional client software installation.
SSL VPNs offer a versatile, user friendly means of establishing remote network connections. They are particularly beneficial for organizations looking to enable remote work securely. By creating an encrypted link between the user's web browser and the VPN server, SSL VPNs ensure sensitive data remains confidential and protected from potential interception.
The encryption used in SSL VPNs typically operates with the TLS protocol, ensuring the data passed between the browser and the VPN is not accessible to unauthorized parties. This mechanism is essential in maintaining the privacy of communications and safeguarding the integrity of transmitted information. The use of TLS also means that security measures are automatically updated with browser or operating system upgrades, relieving users of the responsibility to manage encryption protocols manually.
SSL VPNs are useful for providing secure access to applications, files, and services that are typically available only within an organization's internal network. This technology allows employees to access corporate resources from any location securely, increasing productivity and flexibility without compromising security.
SSL VPNs help ensure that remote access to network resources does not become a vulnerability for the organization. With secure, authenticated pathways, SSL VPNs make network resources available to authorized users as if they were connected locally, regardless of geographical location.
How Does an SSL VPN Work?
An SSL VPN operates by establishing a secure communication channel over the internet, enabling remote users to access an organization's network. Unlike traditional VPNs that may require specific client software, an SSL VPN uses standard web browsers to initiate a secure connection.
The process begins when a user connects to the SSL VPN gateway via their web browser. The gateway presents a secure webpage where the user can authenticate themselves. Upon successful authentication, the SSL VPN establishes an encrypted link between the user’s device and the network. This link is made secure using the SSL or TLS protocol, ensuring the data transmitted is encrypted and thus inaccessible to any unauthorized entities.
Once the encrypted tunnel is established, the user can access applications, files, and services on the network securely.
IPsec vs. SSL VPNs: What Are the Differences?
When comparing IPsec and SSL VPNs, it's essential to consider the specific needs of the organization. This includes required security level, ease of deployment, and the type of access needed by users. Each protocol serves different purposes and offers distinct advantages and challenges in an enterprise environment.
| IPsec VPN vs. SSL VPN | ||
|---|---|---|
| OSI Layer | Network Layer | Application Layer |
| Data Encryption | Encrypts all network traffic | Encrypts web sessions specifically |
| Common Uses | Site-to-Site connections | Secure remote access to specific applications |
| User Authentication | Requires client software and complex setup | Accessed through web browsers, simpler setup |
| Security | Provides full network access with strong security | Offers ease of access with fundamental security |
| Deployment | Can be complex, requiring in-depth configuration | Easier to deploy with less client-side configuration |
| Management | Requires managing security for each device | Simplified management due to web-based access |
| Access Control | Authenticated device-based access | User-based access, often integrated with web authentication |
| Network Integration | Encapsulates data packets for secure transmission | Secures data at the point of entry or exit via the browser |
Network Layer vs. Application Layer
IPsec VPNs operate at the network layer of the OSI model. This allows them to secure all data transmitted across the network, not just specific applications or services. They create a secure tunnel that encapsulates data packets. IPsec is commonly used for site-to-site connections, effectively linking two segments of a private network over the internet.
SSL VPNs function at the application layer. They are designed to provide secure access to specific applications rather than the entire network. This approach is advantageous for providing users with access to web applications and services without exposing the entire network. SSL VPNs are particularly useful for remote workers who need to securely access corporate web applications and services from any device that supports a web browser.
User Authentication and Access Control
IPsec VPNs typically require a more complex setup involving client software installed on the user's device. This setup includes rigorous authentication processes to ensure that only authorized devices can establish a connection.
SSL VPNs offer a more straightforward user experience, as they can be accessed through standard web browsers without the need for specialized client software. Ease of access simplifies user authentication and may work for organizations looking to provide access to specific applications without the overhead of installing and maintaining client VPN software. The simplicity also requires careful management to ensure access controls are stringent enough to protect sensitive applications.
Deployment and Management
IPsec VPN deployment can be seen as more complex due to the requirement for client software and the need to manage security for each device individually. It often requires in depth configuration to navigate through network address translation (NAT) settings and firewalls. This complexity can lead to a more robust security posture but also requires more extensive management overhead.
SSL VPNs are generally considered easier to deploy and manage because they leverage standard web technologies and require less client side configuration. They can be quickly rolled out to users without significant changes to the existing network infrastructure. Because they are easier to deploy, it is vital to ensure that security is not compromised in favor of convenience.
