SASE vs. CASB: What Is the Difference?
The difference between CASB and SASE is that CASB is a cloud services security tool, and SASE is a framework that integrates multiple security functions, including CASB, into one platform.
CASB focuses on cloud visibility and compliance. As part of SASE, it plays a crucial role in extending security policies to cloud-based resources. SASE integrates networking and security into a cloud-based service model for comprehensive protection.
What Is SASE?
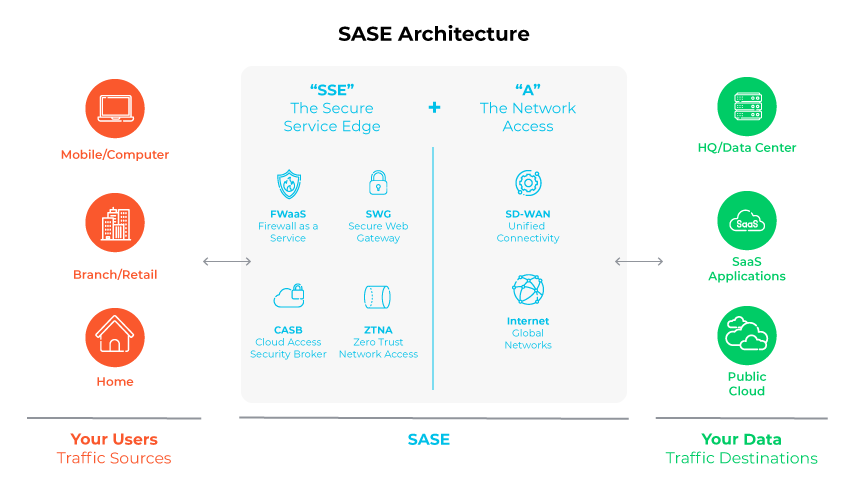
Secure access service edge (SASE) is a security architecture model based in the cloud which combines software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN), secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and zero trust network access (ZTNA) capabilities into one platform. Within the SASE framework, various elements synergize to maintain secure network connectivity, manage multiple security services, enhance administrative efficiency, and provide an agile network setup that adjusts to the fluctuating needs of a business.
This architecture caters to the evolving, secure connectivity requirements of modern enterprises. By expanding the conventional network boundary to encompass all access points, SASE strives to deliver both secure and rapid cloud engagement for all users, irrespective of their physical location.
The functionality of SASE involves routing data through a cloud-native service that combines multiple security and networking functionalities. Operating these services at the edge of the network, close to users and device connection points, helps reduce lag and increase network throughput. It guarantees uniform policy application and protection throughout the organization and centralizes oversight.
What Is CASB?
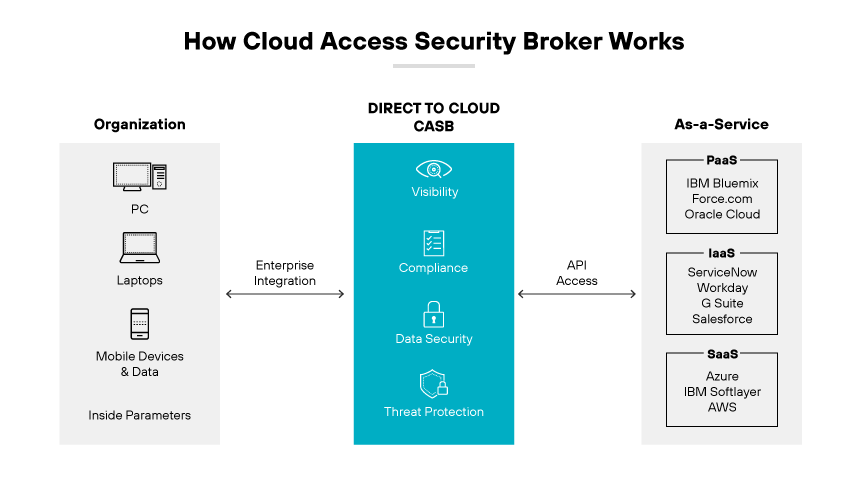
A cloud access security broker (CASB) serves as a security mediator between users and cloud service providers. It enables security policy adherence by implementing and integrating protective measures. A CASB is essential to manage cloud-based risks, apply security policies, and meet regulatory requirements.
Four fundamental functions define CASBs:
Visibility
CASBs offer insight and command over both utilized and non-utilized cloud services. This allows IT departments to regulate user activities and data within these services. In this way, organizations can identify active cloud services, assess cloud expenditures, and eliminate service redundancies and excess licensing fees.
Compliance
CASBs support organizations in upholding cloud compliance, helping to align with standards such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Data Security
CASBs implement advanced data protection strategies, such as document fingerprinting, to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized cloud transfer. They enable security personnel to redirect potential policy breaches to local systems for deeper investigation and to intervene malicious activities promptly.
Threat Protection
CASBs protect against cloud-based threats and malicious software, preventing employees from spreading or introducing these hazards via cloud services. They monitor and block unauthorized attempts to access cloud services and data. CASBs also provide detailed threat analysis to preempt potential cloud-originated risks.
What Are the Differences Between SASE and CASB?
| What Are the Differences Between SASE and CASB? | ||
|---|---|---|
| SASE | CASB | |
| Purpose | A comprehensive security architecture merging security with WAN capabilities for secure access across organizational environments. | Focuses on securing cloud services and ensuring compliance with data security policies. |
| Implementation | Offers an integrated approach combining various network security functions delivered through a cloud service. | Acts as a specific point of control for cloud applications. |
| Scope | Has a broader scope, securing network access and performance for services, users, and devices everywhere. | Targets cloud applications specifically for detailed oversight and control. |
| Network Design Role | Evolution in network design with a cloud-native approach, supporting modern, distributed workforces. | Fits within traditional network architecture, securing the use of cloud-based resources. |
| Security Policy Management | Centralizes and streamlines security policy management across networks and services. | More focused on policy enforcement for cloud platforms and applications. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Provides a scalable and flexible architecture that adapts to business needs and network demands. | May require more effort to scale and integrate with other tools in a diverse IT ecosystem. |
Purpose
SASE is a comprehensive framework that merges security with wide-area network (WAN) capabilities to provide secure access across organizational environments. CASB, on the other hand, secures cloud services and ensures compliance with data security policies.
Implementation and Integration
CASB acts as a specific point of control for cloud applications, while SASE offers a more integrated approach. SASE combines various network security functions and delivers them through a cloud service, aiming to simplify the security infrastructure.
Scope
CASB solutions target cloud applications specifically. SASE has a broader scope, ensuring secure network access and optimized performance for all cloud services, users, and devices, regardless of location.
Network Design Role
SASE represents an evolution in network design, focusing on a cloud-native approach that supports the needs of modern, distributed workforces. In contrast, while CASB is a SASE component, it can fit within the traditional network architecture, focusing on the secure use of cloud-based resources.
Security Policy Management
SASE centralizes and streamlines security policy management across networks and services, while CASB is more focused on policy enforcement for cloud platforms and applications.
Scalability and Flexibility
SASE provides a scalable and flexible architecture that adapts to changing business needs and growing network demands. Independent CASB solutions may require more effort to scale and integrate with other security tools within a diverse IT ecosystem.
What Are the Similarities Between SASE and CASB?
| What Are the Similarities Between SASE and CASB? | |
|---|---|
|
Cloud Security Enhancement
Both SASE and CASB enhance security for cloud-based services. They implement measures to safeguard sensitive data within cloud environments and manage data access and use.
Threat Prevention and Monitoring
SASE and CASB both offer capabilities to identify and mitigate threats. They monitor network and user activity to detect potential security breaches, unauthorized access, or malicious activities.
Compliance Support
Each framework supports regulatory compliance by offering tools and features that help organizations adhere to various data protection standards and regulations.
IT and Security Infrastructure Integration
SASE and CASB contribute to a unified security posture for organizations, enabling better management and oversight of security policies across different platforms and services. Both SASE and CASB integrate with existing IT infrastructure, providing enhanced security without the need for entirely new systems or disrupting current operations.
Support for Remote Workforces
With the increase in remote work, both technologies are relevant for providing secure access to corporate resources. They cater to the security needs of dispersed workforces by enabling secure and compliant access to organizational data and applications.
Risk Control and Management
CASB and SASE assist in risk management by offering solutions to control and reduce risks associated with cloud storage and data transmission, particularly in ensuring only authorized users have access to sensitive information. SASE and CASB focus on protecting critical business assets, whether hosted on-premises or in the cloud, by ensuring users access assets securely and in compliance with policy.
The Role of CASB in SASE
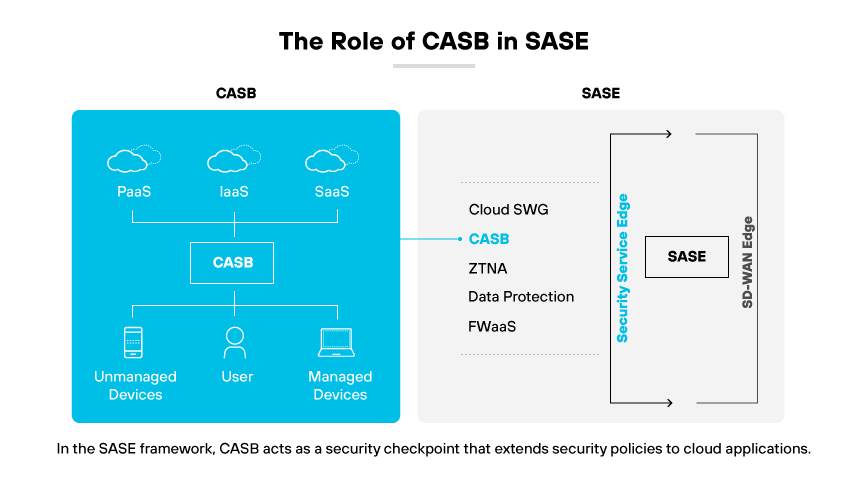
Within the secure access service edge framework, a cloud access security broker is a critical security component. It primarily handles security for cloud applications, extending the organization's data protection policies to cloud environments where traditional IT perimeter defenses may not reach. The inclusion of CASB within SASE allows for the enforcement of consistent security policies across both on-premises and cloud applications, addressing the security management needs of increasingly hybrid IT infrastructures.
CASB in SASE is responsible for identifying and mitigating risks associated with cloud service usage. It monitors and controls access to cloud applications, ensuring only authorized users can interact with sensitive data. This helps with maintaining compliance with industry regulations. CASB’s role in SASE is essential for organizations that use a variety of SaaS applications and whose employees access these tools from multiple locations, including unsecured networks.
The integration of CASB within SASE offers a streamlined approach to securing cloud access, which is a foundational element in a comprehensive SASE strategy. By providing visibility into cloud application usage, CASB helps to uncover shadow IT, manage risks, and secure data against breaches and leaks. As part of a SASE solution, CASB ensures cloud security is not a siloed effort but an integral part of the unified network security strategy.
ZTNA vs. SASE vs. CASB
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) is a security framework that mandates rigorous identity verification for every entity trying to access resources on a network. Unlike conventional security measures which trust entities within a network perimeter, ZTNA operates on a “never trust, always verify” principle. ZTNA centers around the concept of 'least privilege' and requires continuous credentials verification, often adapting to the user's context. ZTNA ensures only authenticated and authorized users and devices can access network applications and data.
SASE is an integrated framework that combines the functions of network and security solutions into a single, cloud-delivered service. SASE aims to provide secure and efficient network connectivity and security for all users, devices, and services, regardless of their location. As a holistic model, SASE facilitates a secure transition to cloud-based environments and the support of a distributed workforce.
A CASB manages the interaction between users and cloud services. As a standalone solution or part of SASE, CASB provides visibility into cloud application usage and controls over data security, compliance, threat protection, and data loss prevention. It ensures security policies apply consistently across all cloud services. While CASB is a component within SASE, it specifically targets cloud access security, whereas SASE offers a broader scope, including but not limited to cloud security.