-
What Is SASE (Secure Access Service Edge)? | A Starter Guide
- Why do businesses today need SASE?
- What is SASE architecture?
- What are the components of SASE?
- What are the use cases for SASE?
- What are the benefits of SASE?
- What are the potential SASE implementation challenges?
- How to choose a SASE provider and what to look for
- How to execute a successful SASE implementation in 6 steps
- What are the most common SASE myths?
- How SASE works with complementary technologies
- Comparing SASE with other security and technology solutions
- What is the history of SASE?
- SASE FAQs
- What Is SASE for the Cloud?
- What Is AI-Powered SASE?
- SASE vs. ZTE: What Is the Difference?
- What Are Managed SASE Services?
- SASE vs. CASB: What Is the Difference?
- What Is SSE? | Security Service Edge (SSE)
-
End User Experience Monitoring
- SD-WAN vs. SASE vs. SSE: What are the differences?
- SD-WAN vs. SASE: What’s the Difference?
-
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) Key Requirements
- SASE vs. SSE: What Is the Difference?
- SASE vs. Firewall: What Is the Difference?
-
Protecting Data with a SASE Solution
SASE vs. VPN: What Is the Difference?
The difference between SASE and VPNs is that SASE provides a cloud-native platform combining networking and security services, while VPNs primarily focus on creating secure data transmission tunnels.
SASE extends the traditional network perimeter by merging SD-WAN with SWG, CASB, FWaaS, and ZTNA, ensuring secure access regardless of user location. VPNs secure the connection between the user and the network, typically without the additional, integrated security features that SASE offers.
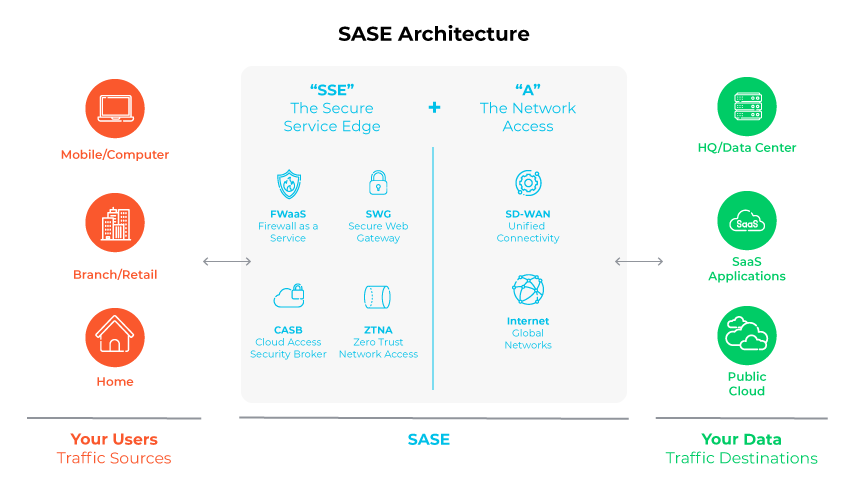
What Is SASE?
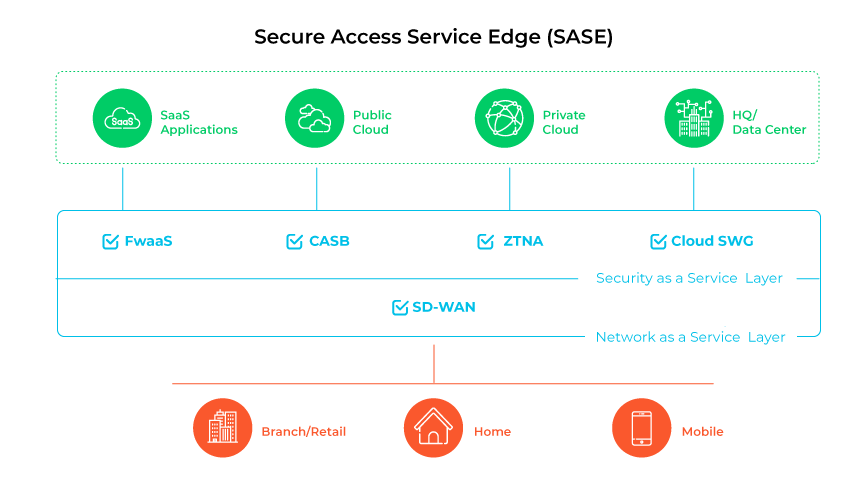
Secure access service edge (SASE) combines software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) and multiple security solutions like secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and zero trust network access (ZTNA) within a single cloud-delivered platform. Orchestrating various security and networking elements, SASE secures connections, streamlines security management, and supports a business's evolving network demands.
Addressing modern secure connectivity needs, SASE broadens the network perimeter to all points of entry, facilitating safe, effective cloud engagement for users everywhere.
SASE channels traffic via a cloud-centric service platform, integrating security and networking functions. Positioned at the edge, these services reduce latency, enhance performance, and centralize the enforcement of security policies. This streamlines operations throughout the organization.
What Is a VPN?
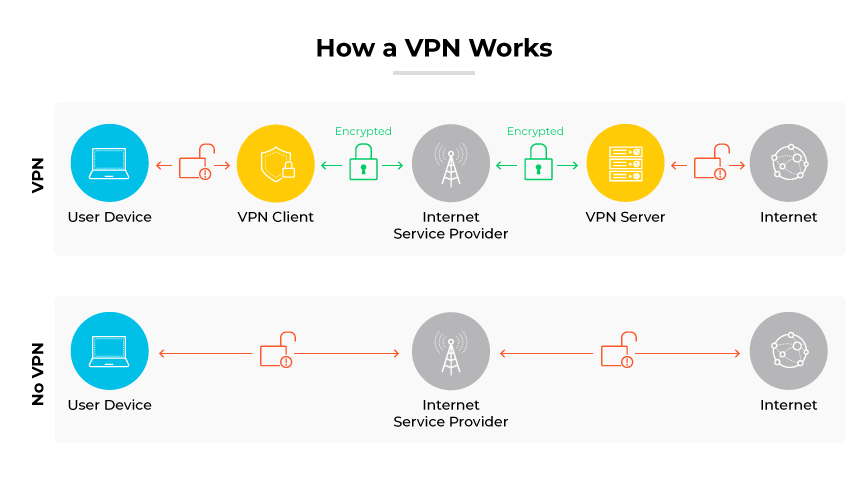
A virtual private network (VPN) creates a protected channel that encrypts data as it travels between computers across the web.
A VPN works by masking the genuine IP address of a device, rerouting its internet traffic through an alternate server. This process presents the device as operating from the location of the VPN server rather than its true physical location. This obscures the true connection source.
Encryption makes data inaccessible without the correct decryption key. VPNs rely on encryption standards like transport layer security (TLS) and internet protocol security (IPsec). These protocols envelop the data, ensuring only authorized users can access and interact with the network during a session.
A VPN provides an enhanced level of privacy and protection by concealing both the connection’s origin and the data exchanged.
What Are the Differences Between SASE and VPNs?
| VPN vs. SASE: What Are the Differences? | ||
|---|---|---|
| SASE | VPNs | |
| Architectural Design and Integration | Unified cloud-native solution integrating networking and security. | Secure tunnels for data transmission, separate from network management. |
| Security and Access Management | Zero Trust framework with a range of security functions like FWaaS and ZTNA. | Secured data channels, often without integrated advanced security features. |
| Performance and Scalability | Efficient network routing via SD-WAN, suitable for distributed workforces. | Potential latency issues, dependent on central server locations. |
| Network Complexity and Management | Reduces complexity by using cloud services, streamlining security management. | Adds a layer to existing networks, possibly increasing management needs. |
| Cost and Deployment | Potential long-term cost benefits from reduced infrastructure and maintenance. | Lower initial cost, with possible additional expenses for hardware and upkeep. |
Architectural Design and Integration
SASE is a cloud-native architecture that merges networking and security into a holistic service, providing a unified solution that extends beyond the capabilities of a VPN. VPNs primarily establish a secure tunnel for data transmission without inherently incorporating integrated network management and policy enforcement features.
Security and Access Management
The security model of SASE relies on the Zero Trust framework and incorporates a range of security functions, including FWaaS and ZTNA, for stringent access control and continuous verification. VPNs offer secure data transmission but lack the comprehensive, adaptive security features that SASE brings to an organization's network.
Performance and Scalability
SASE's SD-WAN component enhances network efficiency, reducing latency and improving bandwidth allocation, which is especially beneficial for geographically dispersed workforces. VPNs can introduce performance bottlenecks due to their reliance on a central server for rerouting traffic, which may not be ideal for modern enterprise environments that require rapid scalability.
Network Complexity and Management
SASE simplifies network complexity by consolidating multiple security services in the cloud, streamlining network management, and reducing the need for multiple point solutions. VPNs, by contrast, are typically another layer added to the existing network infrastructure and might require additional management and hardware.
Cost and Deployment
While VPNs may appear less expensive initially, especially for individual users or small enterprises, SASE can offer cost savings over time through reduced hardware dependence and maintenance. Businesses must consider both the short-term and long-term financial implications when choosing between SASE and VPN solutions.
What Are the Similarities Between SASE and VPNs?
| What Are the Similarities Between SASE and VPNs? | |
|---|---|
|
Secure Remote Access
Both SASE and VPNs provide secure remote access to organizational resources. VPNs ensure encryption for data transmitted across the internet, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity necessary for corporate security.
Encryption Protocols
SASE and VPNs utilize encryption to protect data. While SASE might use a variety of protocols and incorporate them into its architecture, VPNs commonly employ protocols like TLS and IPsec to create secure connections.
Enhancing Business Connectivity
SASE and VPNs enhance business connectivity by facilitating safe and efficient access to cloud resources and company networks. This is especially critical for supporting a remote or global workforce in accessing applications and services necessary for their daily operations.
Traffic Handling and User Authentication
Both technologies handle traffic securely and incorporate user authentication to verify and manage network access. Whether through SASE's cloud-native service platform or VPNs' secure tunnels, they provide mechanisms to ensure secure and reliable access to network resources.
Does SASE Make VPNs Obsolete?
SASE and VPNs serve a common goal of providing secure access to network resources. However, SASE's modern framework integrates extensive security functions, which may surpass the singular connectivity role of VPNs. With the rise of SASE, the notion that it could render VPNs obsolete has begun to circulate. This is primarily due to SASE's ability to provide secure, context-aware access directly in the cloud, potentially reducing reliance on traditional VPNs.
SASE's architecture offers a more dynamic and comprehensive solution, including ZTNA and FWaaS, which VPNs do not inherently provide. The transition to SASE can result in enhanced performance due to its cloud-native design. This optimizes connection routes, potentially eliminating the performance bottlenecks VPNs might face when routing through a central server.
Nevertheless, VPNs maintain their relevance for specific use cases, including individual consumer use for privacy or as a cost-effective option for organizations that do not require the full breadth of SASE's capabilities. SASE does not make VPNs completely obsolete but highlights a shift in the approach to secure access management in an increasingly cloud-reliant world.
Is SASE or VPNs More Secure?
Secure access service edge (SASE) integrates a broad set of security features directly into the network fabric. This offers a comprehensive, context-aware framework to provide enhanced security over traditional VPNs. SASE's model is identity-centric, employing Zero Trust principles, which verify and continually inspect each request. Zero Trust reduces the risks associated with perimeter-based security models that VPNs traditionally use. This granular approach to access and continuous security validation makes SASE stand out in safeguarding remote connections.

VPNs, while effective in creating secure tunnels for data transmission, typically operate by extending the network perimeter to remote workers. This potentially exposes the network once a user is authenticated. SASE's approach goes further by not only securing connections but also by implementing consistent security policies and access controls regardless of the user's location or device, thanks to its cloud-native and integrated nature.
How to Choose Between SASE and VPNs for Remote Access
When choosing between SASE and VPNs for remote access, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the organization. SASE offers a broad, integrated suite of networking and security services delivered from the cloud, designed to support the dynamic needs of businesses, particularly those with a substantial remote workforce.
VPNs, while traditionally used to secure connections from remote locations to the corporate network, can face challenges such as network latency and limited bandwidth, especially when a large number of users are connected. While VPNs effectively encrypt data in transit, they may not offer the same level of security features or performance optimization as SASE. However, VPNs could be suitable for smaller organizations who require secure access to a network without the additional features that SASE provides.
The decision to use SASE or VPNs depends on factors like the size of the remote workforce, level of data sensitivity, required security, and the existing network infrastructure. Businesses must weigh the enhanced security and performance capabilities of SASE against the simplicity and potentially lower initial costs of VPNs. Ultimately, the goal is to strike a balance between security, performance, and cost efficiency that aligns with the business's long-term strategy and operational requirements.