SASE vs. Firewall: What Is the Difference?
The difference between SASE and firewalls is that SASE combines networking and security functions into a single service, while firewalls monitor and control network traffic.
SASE extends protection and connectivity to all points of access within a network for distributed and mobile workforces. Firewalls are also crucial for security but operate as a distinct barrier without the integrated network and security management capabilities of SASE.
What Is SASE?
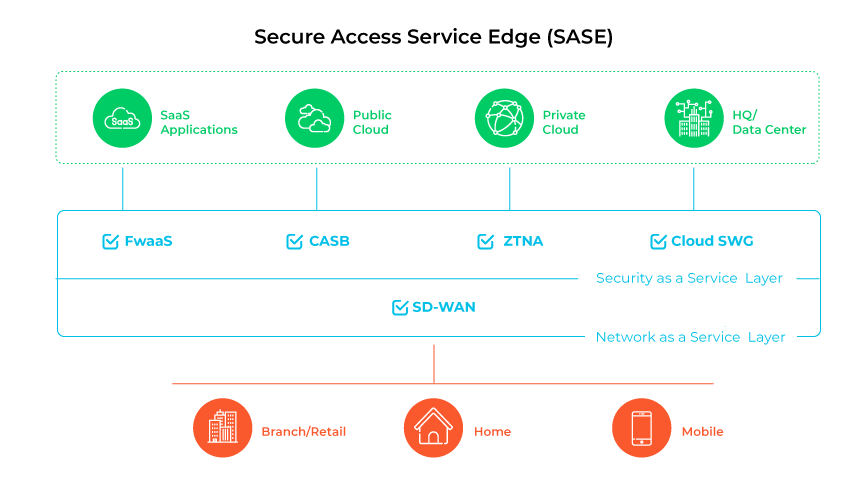
Secure access service edge (SASE) combines software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) and multiple security solutions like secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and zero trust network access (ZTNA) within a single cloud-delivered platform. Orchestrating various security and networking elements, SASE secures connections, streamlines security management, and supports a business's evolving network demands.
Addressing modern secure connectivity needs, SASE broadens the network perimeter to all points of entry, facilitating safe, effective cloud engagement for users everywhere.
SASE channels traffic via a cloud-centric service platform, integrating security and networking functions. Positioned at the edge, these services reduce latency, enhance performance, and centralize the enforcement of security policies. This streamlines operations throughout the organization.
What Is a Firewall?
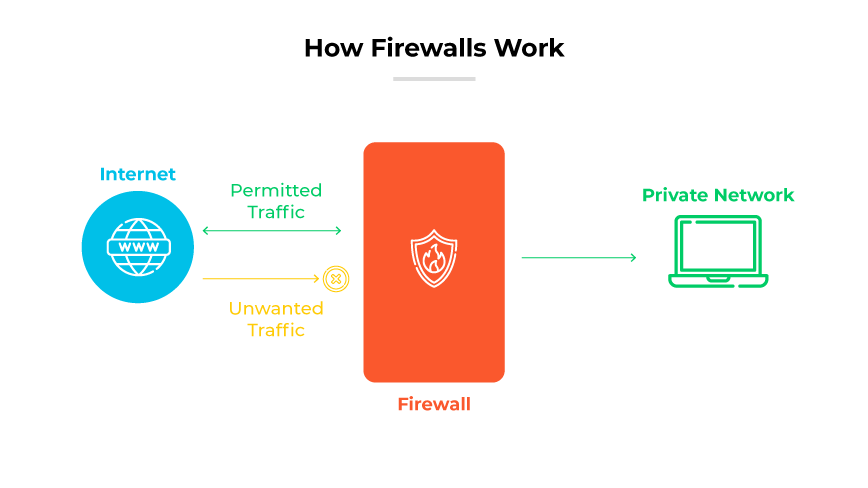
A firewall is a network security device that inspects and directs incoming and outgoing data traffic based on predetermined security standards to permit, block, or discard data packets.
Firewalls serve as a defensive mechanism between private networks and external sources, evaluating and filtering the flow of data using established security protocols. Their decisions to permit, deny, or discard traffic help ensure network integrity. Available in hardware, software, or a combination, firewalls are crucial in safeguarding network environments.
Firewalls are essential for protecting network hosts, which are devices such as computers that engage in data exchange within or across networks. They provide the initial defense line by monitoring network traffic, protecting against security risks and safeguarding an organization's digital resources.
Firewalls examine data packets against defined rules, rejecting those that do not conform. These packets, the basic units of data transfer over the internet, carry essential information and metadata required for successful communication.
What Are the Differences Between SASE and Firewalls?
| What Is the Difference Between SASE and Firewalls? | ||
|---|---|---|
| SASE | Firewalls | |
| Scope and Functionality | Combines SD-WAN with security in the cloud. | Regulates perimeter traffic based on rules. |
| Deployment and Configuration | Cloud-native with uniform policies for all users. | Configured per segment, typically on-premises. |
| Architecture Integration | Integrates various security services flexibly. | Standalone barrier, not cloud-integrated. |
| Adaptability to Modern Workspaces | Designed for remote and distributed workforces. | Limited flexibility for modern workspace needs. |
| Network Performance Optimization | Includes SD-WAN for optimizing performance. | Focused on security without network optimization. |
| Policy Management and Visibility | Centralized control over the entire network. | Visibility limited to network edge or perimeter. |
Scope and Functionality
SASE is an integrated network architecture that unifies SD-WAN and security solutions within a cloud-based platform. Firewall solutions, in contrast, are security devices or software focused on monitoring and controlling network traffic at the perimeter, based on set security rules.
Deployment and Configuration
SASE provides a global, cloud-native service that ensures consistent security policies and access across all users and devices, from mobile devices to laptops. Firewalls typically require on-premises or virtual deployment and protect specific network segments.
Architecture Integration
SASE represents a convergence of comprehensive security services. Firewalls traditionally serve as a standalone network barrier against unauthorized access and do not offer an inherent design catered to integrated, cloud-delivered security, though some next-generation firewalls (NGFW) offer this capability.
Adaptability to Modern Workspaces
SASE focuses on distributed and remote workforce requirements, offering seamless connectivity and security. Traditional firewall solutions, while adaptable to some extent, do not have the flexibility and scalability that cloud-native SASE architectures offer for modern digital environments.
Network Performance Optimization
Beyond security, SASE incorporates SD-WAN, which optimizes network performance and access to cloud applications, a feature not within the typical remit of firewall capabilities. Firewalls are primarily concerned with security, not network routing optimization.
Policy Management and Visibility
SASE facilitates centralized policy management and visibility across an entire organization’s network, while firewalls traditionally provide visibility and control at the network edge or perimeter without an integrated view of the entire network landscape.
What Are the Similarities Between SASE and Firewalls
| What Are the Similarities Between SASE and Firewalls? | |
|---|---|
|
Central Role in Cybersecurity
Both SASE and firewalls are pivotal in the cybersecurity infrastructure of an organization. They serve as key components in the protection of digital assets, with each system designed to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard data.
Traffic Inspection and Control
SASE and firewalls both inspect and regulate the flow of network traffic. They scrutinize data packets, using predefined security rules to manage access and ensure that only safe, legitimate traffic passes through.
Policy Enforcement
Policy enforcement is a core function of both SASE and firewalls. They implement security policies that control network access and user activities, contributing to the overall security posture of an organization.
Integration of Security Services
SASE architectures include FWaaS. highlighting the integration of firewall functionality within their broader suite of security services. This demonstrates a shared commitment to versatile and robust network protection.
Support for Remote and Hybrid Environments
SASE and firewalls both facilitate secure access for dispersed workforces. This is SASE’s inherent purpose. Firewalls have evolved to support remote workers and hybrid environments through advancements in technology and deployment strategies.