-
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)? | A Comprehensive Guide
- How does a secure web gateway work?
- Why are secure web gateways necessary for network security?
- What are the benefits of secure web gateways?
- What are the features of secure web gateways?
- What are the most common secure web gateway deployment challenges?
- How do secure web gateways enforce acceptable use policies?
- How do secure web gateways secure remote workforces and branch offices?
- What is the role of secure web gateways in SASE?
- How do secure web gateways relate to compliance?
- Comparing secure web gateways with other security technologies
- What is the history of secure web gateways?
- How are secure web gateways evolving for the future?
- How to choose the right secure web gateway for your business
- Secure web gateways FAQs
- What Is a Cloud Secure Web Gateway?
- Secure Web Gateway vs. CASB: What Is the Difference?
- What Are Secure Web Gateway Use Cases?
-
Secure Web Gateway vs. Proxy Server: What Is the Difference?
- What Is an SWG?
- What Is a Proxy Server?
- Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
- What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
- The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
- SWG vs. Proxy Server FAQs
- SASE and Secure Web Gateway: How Are They Related?
- Secure Web Gateway vs. WAF: What Is the Difference?
- What Is a Next-Generation Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
Secure Web Gateway vs. Firewall: What Is the Difference?
The difference between a secure web gateway (SWG) and a firewall is that an SWG primarily focuses on filtering and managing web traffic, while a firewall has a broader scope, enforcing security policies and examining network packets, not just web traffic, to protect against a wider range of threats.
SWGs filter internet traffic and enforce policy compliance, serving as intermediaries between users and the internet. Firewall positioning depends on network architecture and security requirements, ensuring only safe, legitimate traffic enters the network. Combining both technologies can enhance overall security by creating a layered defense against various types of threats.
What Is an SWG?
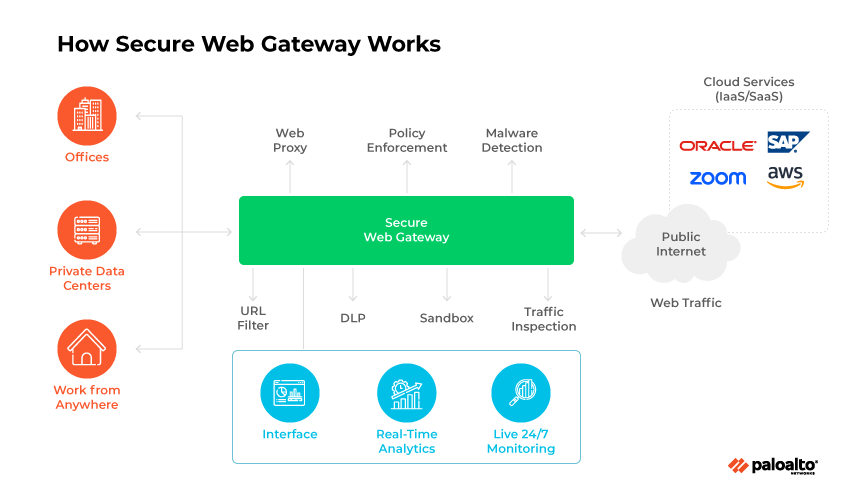
A secure web gateway is a cloud-delivered or on-premises network security solution that filters internet traffic and enforces regulatory and corporate policy compliance.
The SWG operates as an intermediary between a corporate network and the internet, applying filters to web traffic to uphold security protocols and usage policies. An SWG's primary function is to oversee and control data exchange between the internet and the network.
Key security features of an SWG include URL filtering, application control capabilities, and antimalware and threat prevention.
SWG deployment options include cloud-based virtual machines and services, software applications, and physical servers.
Secure web gateways scrutinize traffic originating from user devices that are requesting access to internet destinations. The SWG routes each web request made by a user, verifies the user's credentials, and evaluates the request for compliance with established usage policies. The SWG permits the request to pass only if it deems it appropriate and secure. Similarly, the system inspects inbound data before allowing it to reach the user.
SWGs provide a protective barrier against online threats while maintaining adherence to prescribed usage policies. A secure web gateway acts as an internet access gatekeeper that prevents the entry of hazardous web content and guards against potential data breaches.
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
What Is a Firewall?
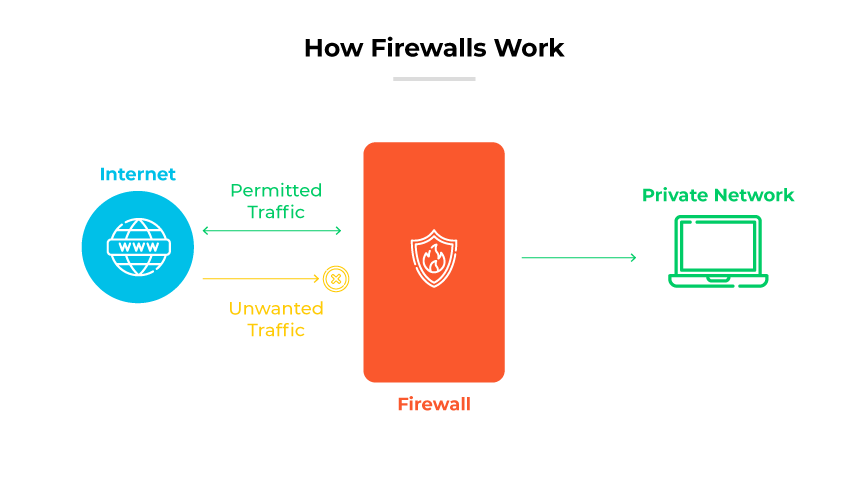
A firewall is a network security technology that monitors and controls traffic based on defined security rules and accepts, rejects, or drops traffic correspondingly.
Using security rules, firewalls decide if they should allow, block, or drop data to protect the network. Form factors can include software, hardware, or both. This process ensures only safe, legitimate traffic gains entry.
Crucial to this process is stateful packet inspection, where the firewall examines every data packet in relation to its original session, recording its route, source, and intended endpoint. This scrutiny ensures a thorough evaluation against security threats.
What Are the Differences Between SWG and Firewall?
| Secure Web Gateway vs. Next Generation Firewall: What Is the Difference? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Deployment and Architecture | Deployed on premises or cloud; filters internet traffic for web; manages data flow for web traffic. | Positioning depends on network architecture, security requirements, and threat mitigation strategy. |
| Traffic Inspection and Management | Inspects traffic, authenticates users, applies URL filtering, and anti-malware. | Examines all incoming/outgoing network packets; applies broader security rules for traffic flow. |
| Policy Enforcement | Enforces web security policies; uses URL filtering and application controls. | Enforces broader network security policies; blocks access that’s unauthorized, and attacks. |
| Threat Prevention | Prevents threats targeting web app vulnerabilities; uses threat prevention systems. | Employs packet inspection, stateful inspection; monitors active connections for threats. |
| Data Protection | Monitors data movement related to web access; prevents data loss via internet traffic. | May offer DLP; focus extends to all network data transfers, not just web. |
| Encrypted Traffic | Decrypts, inspects, re-encrypts HTTPS traffic; directly addresses security within encrypted web channels. | Inspects encrypted traffic; approach to encryption extends beyond web traffic. |
| Integration and Complexity | Deployment can introduce complexity due to detailed web security policies and user access control. | Challenges related to network segmentation, maintaining performance; requires balancing security and network throughput. |
Deployment and Architecture
Typically, organizations deploy an SWG either on premises or through the cloud. SWG architecture design enables internet traffic filtering and policy compliance enforcement. It sits between users and the internet, managing data flow specifically for web traffic. A firewall’s positioning, however, depends on the network architecture, the specific security requirements of the organization, and the types of threats they are looking to mitigate.
Traffic Inspection and Management
SWG focuses on inspecting web traffic from client devices, authenticating users, and ensuring that web requests adhere to acceptable use policies. This inspection includes detailed analysis like URL filtering and the application of antimalware. Firewalls examine all incoming and outgoing network packets, applying a broader set of security rules to control traffic flow and protect against network threats.
Policy Enforcement
The policy enforcement of an SWG centers on web security, utilizing URL filtering and application controls to manage access to web resources. Firewalls enforce a broader range of network security policies to prevent unauthorized access and attacks, such as blocking unsolicited incoming traffic that does not comply with the security policy.
Threat Prevention
SWGs prevent threats by targeting web application vulnerabilities, using capabilities like threat prevention systems that detect anomalous traffic patterns. Firewalls employ packet inspection and may use stateful inspection to monitor active connections and prevent network-level threats, including those that do not necessarily originate from web traffic.
Data Protection
Data loss prevention (DLP) in SWGs specifically monitors data movement related to web access, aiming to prevent sensitive information from escaping the network via internet traffic. Firewalls may offer DLP features, but their focus extends beyond the web to include all network data transfers.
Encrypted Traffic
SWGs decrypt, inspect, and re-encrypt HTTPS traffic, directly addressing security within encrypted web channels. Firewalls can also inspect encrypted traffic but their approach to encryption is not limited to web traffic and may include various forms of network encryption protocols.
Integration and Complexity
SWG deployment can introduce complexity due to the need for detailed web security policies and user access control. On the other hand, firewall deployment can involve challenges related to network segmentation and maintaining performance, requiring careful balancing of security and network throughput.
What Are the Similarities Between SWG and Firewall?
| Secure Web Gateway vs. NGFW: How Are They Similar? | |
|---|---|
|
|
Core Security Objective
Both secure web gateways (SWGs) and firewalls share the core objective of protecting networked systems from unauthorized access and cyberthreats. They are essential components in a security infrastructure that serves to safeguard digital assets.
Traffic Analysis
SWG and firewalls analyze network traffic, albeit with different scopes and mechanisms. They inspect the data packets or traffic flow to detect and prevent security risks, allowing only safe and authorized data.
Rule-Based Operation
Both technologies operate on a basis of rules defined by security policies. These rules dictate how to treat incoming and outgoing traffic, and they are crucial for maintaining an organization's security posture.
Security Policy Compliance
SWGs and firewalls are both instrumental in enforcing security policies that comply with corporate standards and regulatory requirements. They help organizations maintain the necessary level of compliance with various regulations.
Adaptability to Threats
The adaptability to evolving threats is a commonality between SWGs and firewalls. Both technologies must continually update their capabilities to counter new and emerging security threats.
Support for Secure Access
Providing secure access to network resources is a key similarity. Whether it’s remote workers needing secure internet access or internal users accessing the network, both SWGs and firewalls play a role in ensuring that this access is secure and controlled.
Integration within Security Frameworks
Organizations can integrate SWGs and firewalls within broader security frameworks to provide a cohesive defense strategy. They are often part of multilayered security approaches, such as a secure access service edge (SASE) framework, providing comprehensive protection.
Using an SWG and Firewall Together
Integrating web security gateways and firewalls can enhance network security and overall security services. Firewalls are adept at inspecting individual data packets, while SWGs focus on web traffic, complementing each other's capabilities. This combined approach provides a layered defense, bolstering protection against a wide range of cyberthreats and enhancing security for sensitive data.
By deploying SWG and firewall together, organizations can effectively filter traffic at both the packet and application levels. This dual-layered protection helps prevent malware infiltration, reduces the risk of human error leading to security breaches, and mitigates the impact of any malicious code that does manage to breach the network.
In fact, the evolving cybersecurity landscape is quickly leading to the development of platforms that offer integrated SWG and firewall defenses, indicating a growing trend toward combined security solutions.