-
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)? | A Comprehensive Guide
- How does a secure web gateway work?
- Why are secure web gateways necessary for network security?
- What are the benefits of secure web gateways?
- What are the features of secure web gateways?
- What are the most common secure web gateway deployment challenges?
- How do secure web gateways enforce acceptable use policies?
- How do secure web gateways secure remote workforces and branch offices?
- What is the role of secure web gateways in SASE?
- How do secure web gateways relate to compliance?
- Comparing secure web gateways with other security technologies
- What is the history of secure web gateways?
- How are secure web gateways evolving for the future?
- How to choose the right secure web gateway for your business
- Secure web gateways FAQs
- What Is a Cloud Secure Web Gateway?
- Secure Web Gateway vs. CASB: What Is the Difference?
- Secure Web Gateway vs. Firewall: What Is the Difference?
-
Secure Web Gateway vs. Proxy Server: What Is the Difference?
- What Is an SWG?
- What Is a Proxy Server?
- Is a Proxy and Secure Web Gateway the Same?
- What Are the Differences Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- What Are the Similarities Between SWGs and Proxy Servers?
- How to Choose Between SWG vs. Proxy Server
- The Roles of SWGs and Proxy Servers in SASE
- SWG vs. Proxy Server FAQs
- SASE and Secure Web Gateway: How Are They Related?
- Secure Web Gateway vs. WAF: What Is the Difference?
- What Is a Next-Generation Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
What Are Secure Web Gateway Use Cases?
The primary use cases for modern secure web gateways (SWG) are web filtering, malware and threat protection, data loss prevention (DLP), SSL/TLS inspection, and secure, flexible connection methods.
URL Filtering
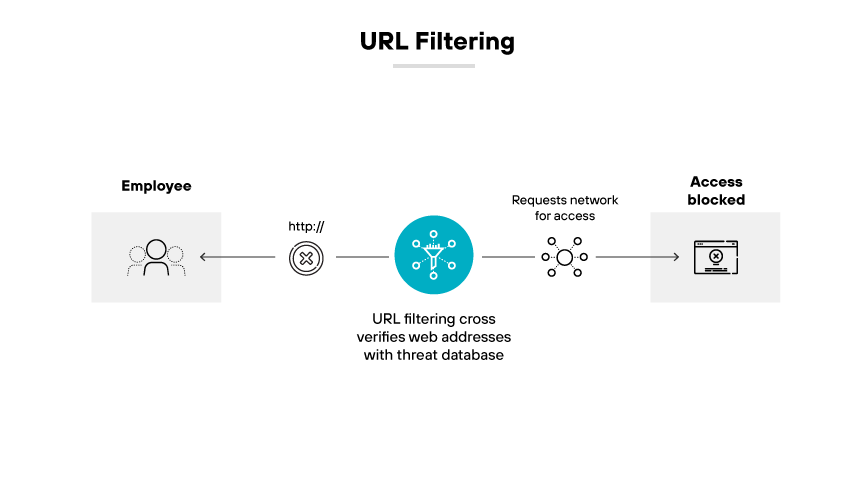
URL filtering is a process that allows organizations to control access to the internet by blocking or permitting web content based on specific URLs. URL filtering is a key use case for secure web gateways because it categorizes web traffic and enforces security policies. This categorization usually relies on the nature of content, user groups, or potential security risks to ensure accessibility to appropriate and safe material only.
The importance of URL filtering in SWGs is its ability to improve security and productivity. It reduces the risk of exposure to web based threats such as malware and phishing and helps maintain compliance with regulatory standards. With URL filtering, organizations can prevent access to harmful or inappropriate content, contributing to a secure and efficient online work environment.
Malware & Threat Protection
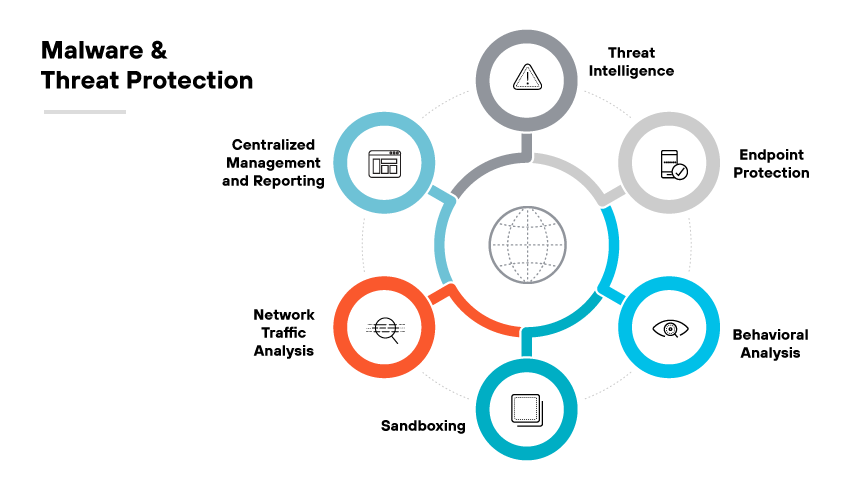
Malware and threat protection involves scanning internet traffic in real time to detect and block threats. It uses a combination of threat intelligence, URL reputation checks, and content analysis to prevent the execution of malicious website content.
The role of malware and threat protection as a core use case for SWG is critical, considering the complexity and volume of web based threats. As organizations increasingly move to cloud delivered operations and remote work, SWGs are essential for enforcing security policies that detect and manage these evolving threats. This proactive defense mechanism is crucial in maintaining the integrity of an organization’s data and the continuity of its operations.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
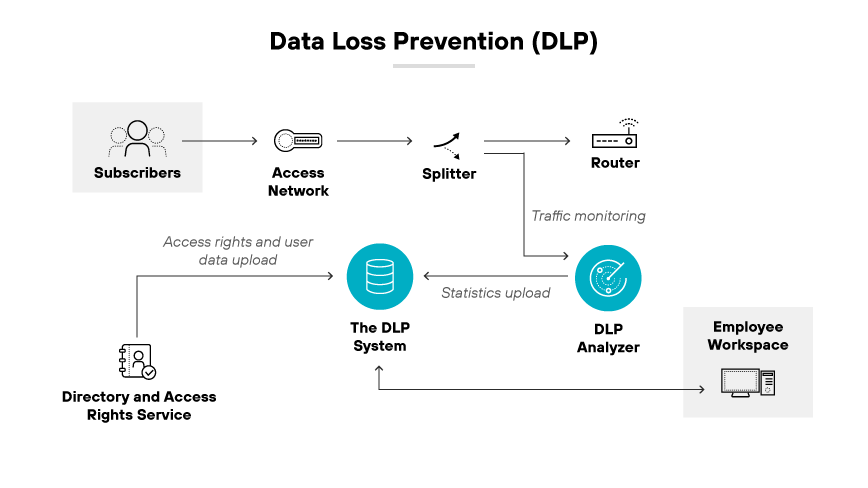
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a strategy for making sure sensitive or critical information does not leave the corporate network without authorization. DLP capabilities are crucial for SWGs, as they monitor and control data in transit to prevent unauthorized data transfer. This is particularly important as organizations operate in increasingly cloud centric and perimeterless environments.
DLP serves as a protective measure against both inadvertent and deliberate data breaches which can have severe financial and reputational repercussions for businesses. By implementing DLP policies, SWGs help organizations comply with regulatory requirements and protect intellectual property by inspecting data movement across the network and blocking potential leaks.
SSL/TLS Inspection
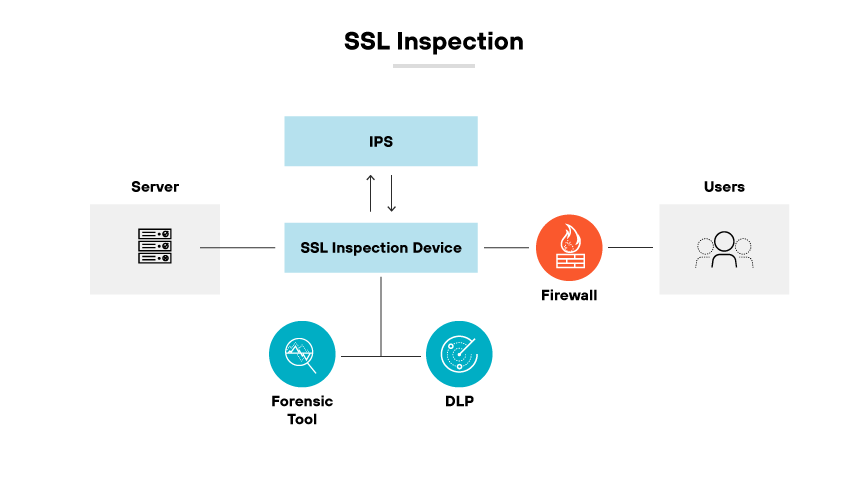
A secure web gateway decrypts encrypted traffic between a client and a server during SSL/TLS inspection to check for security threats. By decrypting the SSL/TLS encrypted data, the SWG can examine the contents for risks such as malware, data exfiltration, or policy violations. After inspection, the data is re-encrypted and sent to its destination, ensuring the integrity of the secure communication channel.
The importance of SSL/TLS inspection as a use case for SWGs stems from the increased prevalence of encrypted web traffic. With more organizations using HTTPS to secure their information, SSL/TLS inspection has become essential for maintaining a robust security posture. It enables organizations to extend their visibility into previously obscured traffic, uphold security policies (even within encrypted sessions) and protect against encrypted threats.
Secure, Flexible Connection Methods
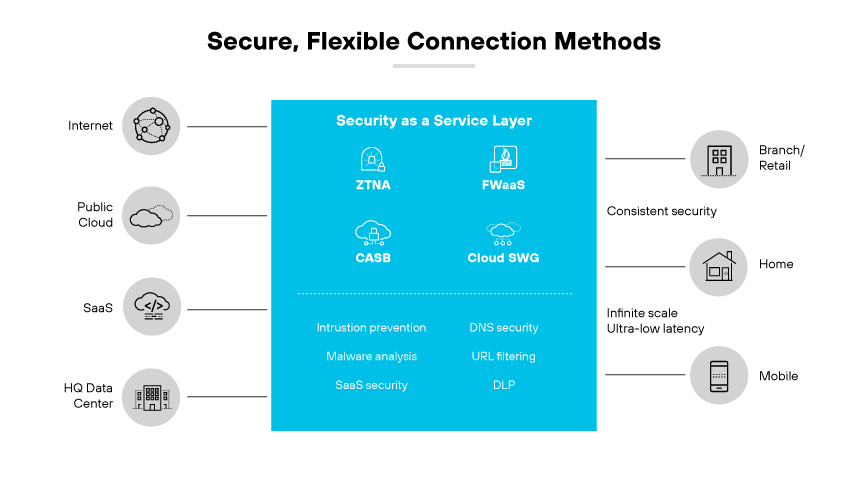
Secure, flexible connection methods address the need for secure internet access that adapts to various networking architectures and user requirements. Secure web gateways facilitate this by offering a range of connection options, including direct-to-internet access, which is particularly essential for remote workers.
Flexible connection methods enable employees to safely connect to the internet and enterprise data centers and resources without the limitations of traditional network infrastructures. Incorporating application control into these connection methods enhances security by ensuring remote works are using approved applications only, which is essential for maintaining policy compliance and mitigating security risks.
Secure, flexible connection methods are crucial in modern secure web gateways as they support the shift from centralized, on premises solutions to cloud based services that cater to a distributed workforce. This adaptability ensures consistent security policy application, regardless of the user's location or device, which maintains high security standards across the organization. The ability to integrate seamlessly with existing network setups minimizes disruption and allows businesses to evolve security infrastructure without extensive overhauls.
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
SWG and SASE Implementation

Deploying SWG functionality can be challenging because most organizations set it up as a stand-alone environment without coordinating workflows, reporting, or logging with other organizational security infrastructure. This often leads to complexity and hindered security operations, as the scattered nature of various security products can create inefficiencies.
At the same time, the security service edge (SSE)/secure access service edge (SASE) model continues to gain traction, integrating multiple security and networking functions into a singular, cloud centric service. SASE architecture combines networking and security services including software defined wide area network (SD-WAN), secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and zero trust network access (ZTNA) into a cohesive offering. SASE is designed to administer a suite of security services from the cloud, offering a streamlined solution for modern businesses.
As a critical element of SASE, SWG is not the only feature. It's part of a larger ensemble that must address the increasing challenges faced by growing organizations. The rise in remote workforces, the widespread use of SaaS platforms, and the varied nature of enterprise applications dispersed across on site and cloud environments make comprehensive coverage essential. The SASE framework propels SWG into the cloud, enhancing security measures and providing a complete view and control of the network's security posture.