-
- Understanding the Dual Nature of AI in Cybersecurity
- Traditional Cybersecurity vs. AI-Enhanced Cybersecurity
- Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
- Risks and Challenges of AI in Cybersecurity
- Mitigating Risks and Maximizing Benefits: Strategic Implementation
- The Future Outlook: Adapting to the Evolving AI Landscape
- Risk and Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity FAQs
Table of Contents
-
Why Does Machine Learning Matter in Cybersecurity?
-
What Are the Predictions of AI In Cybersecurity?
- Predictions of AI in Cybersecurity Explained
- The New Cyber Arms Race: AI as an Offensive Force Multiplier
- Autonomous Defense: Predictions for Security Operations
- New Attack Surfaces and Governance Challenges
- The Future of the Security Workforce and AI
- Industry-Specific AI Applications and Case Studies
- Historical Context and AI Evolution
- Predictions of AI in Cybersecurity FAQs
-
10 Things to Know About Machine Learning
What are the Risks and Benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity?
3 min. read
Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence, through machine learning and advanced algorithms, significantly enhances cybersecurity by strengthening threat detection, response, and prevention capabilities. While offering transformative advantages in analyzing vast datasets and automating defenses, AI also introduces new, complex risks. These include the potential for AI-powered attacks and challenges related to the ethical deployment of AI.
Key Points
-
Significant Benefits for Cybersecurity Operations
AI enhances threat detection, automates incident responses, and improves vulnerability management. -
Key Advantages of AI Integration in Cybersecurity
AI offers real-time anomaly detection, predictive threat intelligence, and rapid containment of attacks. -
Risks of AI in Cybersecurity
New AI-powered attack vectors are emerging, like adversarial AI, automated malicious campaigns, and deepfake social engineering. -
Ethical Concerns and Trust Issues with AI
Algorithmic bias and the "black box" nature of AI models pose significant challenges to the responsible deployment of AI. -
Effective AI Implementation in Cybersecurity
Successful AI implementation requires a comprehensive security framework, continuous model monitoring, and a balanced approach to human oversight.

Understanding the Dual Nature of AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence is profoundly reshaping the cybersecurity landscape, presenting both powerful defensive capabilities and novel attack vectors. Its integration into security operations has become critical, allowing organizations to combat the scale and sophistication of modern cyber threats with unprecedented efficiency.
However, this transformative technology also arms malicious actors, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its inherent risks. Recognizing the dual nature of AI—as both a shield and a potential weapon—is paramount for security leaders.
AI's significance in cybersecurity stems from its ability to process and analyze vast volumes of data more efficiently and accurately than human capabilities allow. This enables enhanced threat intelligence, automated response mechanisms, and proactive vulnerability identification.
Simultaneously, the very power that makes AI a formidable defense can be weaponized, leading to more sophisticated and evasive attacks, as well as new ethical dilemmas and operational challenges. A balanced perspective, acknowledging both the immense benefits and the complex risks, is essential for strategizing effective, future-proof cybersecurity solutions.
Traditional Cybersecurity vs. AI-Enhanced Cybersecurity
| Criteria | Traditional Cybersecurity | AI-Enhanced Cybersecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Detection Speed | Often manual and reactive, leading to slower detection. | Real-time to near real-time, detecting threats instantly. |
| Data Analysis Volume | Limited by human capacity, processes smaller datasets. | Massive scale, analyzes petabytes of data continuously. |
| Incident Response Time | Manual processes result in slower containment and remediation. | Automated and orchestrated, enabling rapid response. |
| Human Effort Required | High, requiring extensive manual investigation and triage. | Reduced, with AI automating routine tasks and flagging critical alerts. |
| Predictive Capability | Minimal, primarily relies on known signatures and past events. | High: predicts emerging threats and attack patterns. |
| Vulnerability Prioritization | Often manual and based on generalized risk scores. | Intelligent, prioritizes based on context, exploitability, and asset criticality. |
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence offers substantial advantages in enhancing an organization’s cybersecurity posture. Its analytical power transforms how security teams identify, respond to, and prevent cyber threats.
Enhanced Threat Detection and Analysis
AI excels at sifting through vast quantities of data to uncover subtle indicators of compromise that human analysts might miss. This capability enables earlier detection and a more comprehensive understanding of threat landscapes.
Real-time Anomaly Detection
AI algorithms continuously monitor network traffic, system logs, and user behavior for deviations from established baselines. They can pinpoint unusual activities—like unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration—in real time. This immediate flagging allows security teams to investigate and mitigate potential breaches before they escalate.
Predictive Threat Intelligence
Machine learning models analyze historical attack data and current threat intelligence feeds to identify emerging patterns and anticipate future attacks. This predictive capability enables organizations to strengthen their defenses against likely threats proactively. It shifts the security paradigm from reactive to anticipatory, bolstering overall resilience.
Automated Incident Response and Orchestration
Beyond detection, AI plays a pivotal role in automating the complex and time-sensitive tasks involved in incident response. This automation significantly reduces response times and minimizes the impact of cyber attacks.
Rapid Containment and Remediation
AI-driven systems can automatically trigger response actions upon detecting a threat, such as isolating infected endpoints or blocking malicious IP addresses. This immediate containment prevents threats from spreading across the network, limiting damage and accelerating recovery. Automated remediation tasks further streamline the process.
Security Automation and Workflow Optimization
AI integrates with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms to automate repetitive security tasks and workflows. This includes functions like incident triage, data enrichment, and playbook execution. Automating these processes frees security analysts to focus on more complex investigations and strategic initiatives.
Vulnerability Management and Risk Assessment
AI significantly improves an organization’s ability to identify and address vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. It moves beyond traditional scanning to provide more intelligent insights into potential weaknesses.
Proactive Vulnerability Identification
AI algorithms can analyze code, network configurations, and system architectures to identify potential vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. They leverage vast databases of known vulnerabilities and exploit techniques to pinpoint weaknesses proactively. This proactive stance helps prevent attacks by addressing security gaps early.
Prioritized Risk Remediation
AI can assess the context and potential impact of identified vulnerabilities, prioritizing them based on factors like exploitability and asset criticality. This intelligent prioritization ensures that security teams focus their efforts on the most significant risks. It optimizes resource allocation for maximum security improvement.
Improved Behavioral Analytics and UEBA
Understanding normal user and entity behavior is crucial for detecting insider threats and compromised accounts. AI-powered behavioral analytics provide deep insights into these patterns.
Insider Threat Detection
AI-driven User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) solutions establish baselines for individual user and entity behavior. They flag deviations such as unusual access patterns, data downloads, or login times that may indicate malicious insider activity. This enables early detection of potentially harmful actions by employees or trusted partners.
Compromised Account Identification
By continuously analyzing login attempts, access patterns, and resource utilization, AI can identify anomalies indicative of compromised user accounts. For example, logins from unusual geographical locations or multiple failed login attempts followed by a successful one can trigger alerts. These insights enable the quick identification and remediation of hijacked accounts, thereby preventing further damage.
Risks and Challenges of AI in Cybersecurity
While AI offers immense benefits, its adoption in cybersecurity also introduces new complexities and potential vulnerabilities. Security professionals must understand and address these inherent challenges.
Emerging AI-Powered Attack Vectors
The same AI capabilities that enhance defenses can also be weaponized by malicious actors, leading to more sophisticated and evasive attacks. The arms race between offensive and defensive AI is a significant concern.
Adversarial AI and Model Poisoning
Attackers can manipulate AI models by injecting malicious data during training—known as model poisoning—or by crafting inputs that cause a trained model to misclassify data—adversarial attacks. This can lead to AI systems failing to detect threats or, worse, classifying legitimate activity as malicious. Such attacks undermine the reliability of AI-driven security tools.
Automated Malicious Tools and Campaigns
AI can automate the creation and execution of highly personalized and effective cyber attacks. This includes autonomous malware that adapts to defenses, self-propagating worms, and sophisticated scanning tools. The speed and scale of these AI-powered attacks far exceed what human attackers could achieve, making them incredibly difficult to defend against.
Sophisticated Phishing and Deepfake Social Engineering
Generative AI can create highly convincing deepfakes—realistic but fake images, audio, or video—for use in advanced phishing and social engineering campaigns. These AI-generated fakes can convincingly impersonate executives or trusted individuals, making it nearly impossible for humans to discern their authenticity. This significantly increases the success rate of such deceptive attacks.
Ethical and Trust Concerns
The pervasive nature of AI raises significant ethical considerations, particularly regarding fairness, privacy, and accountability. Ensuring the ethical deployment of AI is critical for maintaining trust and avoiding unintended negative consequences.
Algorithmic Bias and Discriminatory Outcomes
AI models learn from the data they are trained on. If this data contains biases—intentional or unintentional—the AI system can perpetuate or even amplify those biases. In a cybersecurity context, this could result in certain user groups being unfairly flagged or legitimate activities being misidentified as threats due to biased historical data. Addressing data bias is essential for equitable security.
Accountability, Transparency, and "Black Box" Issues
The complex, "black box" nature of some advanced AI models can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific decisions. This lack of transparency poses challenges for auditing, explaining security incidents, and establishing accountability when AI systems make errors or contribute to breaches. Ensuring explainable AI (XAI) is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring legal compliance.
Operational and Human Capital Challenges
An excessive reliance on AI without adequate human oversight or expertise can create new vulnerabilities. The human element remains indispensable for effective cybersecurity.
Over-Reliance and Reduced Human Oversight
Over-automation can lead to a reduction in human vigilance and critical thinking. If security teams become too dependent on AI to identify all threats, they may miss novel or subtle attack methods that the AI has not been trained to recognize. Maintaining human oversight and the ability to intervene are crucial for comprehensive security.
Talent Shortages and Skill Gaps
The rapid advancement of AI technology has created a significant demand for cybersecurity professionals with expertise in AI, machine learning, and data science. A shortage of skilled personnel capable of developing, deploying, and managing AI-driven security solutions creates a critical gap. This shortage hinders the effective adoption and management of AI.
Data Privacy and Compliance Implications
AI systems often require access to vast amounts of sensitive data. This data consumption introduces significant privacy and compliance challenges.
Handling Sensitive Data at Scale
AI models analyzing network traffic, user behavior, and threat intelligence often process sensitive personal and organizational data. Ensuring the secure handling, storage, and anonymization of this data is paramount to prevent privacy breaches. Organizations must implement resilient data governance strategies.
Navigating Evolving Regulatory Landscapes
The rapid evolution of AI technology often outpaces the development of regulatory frameworks. Organizations deploying AI in cybersecurity must navigate a complex and evolving landscape of data protection laws and industry-specific regulations. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and reputational damage.
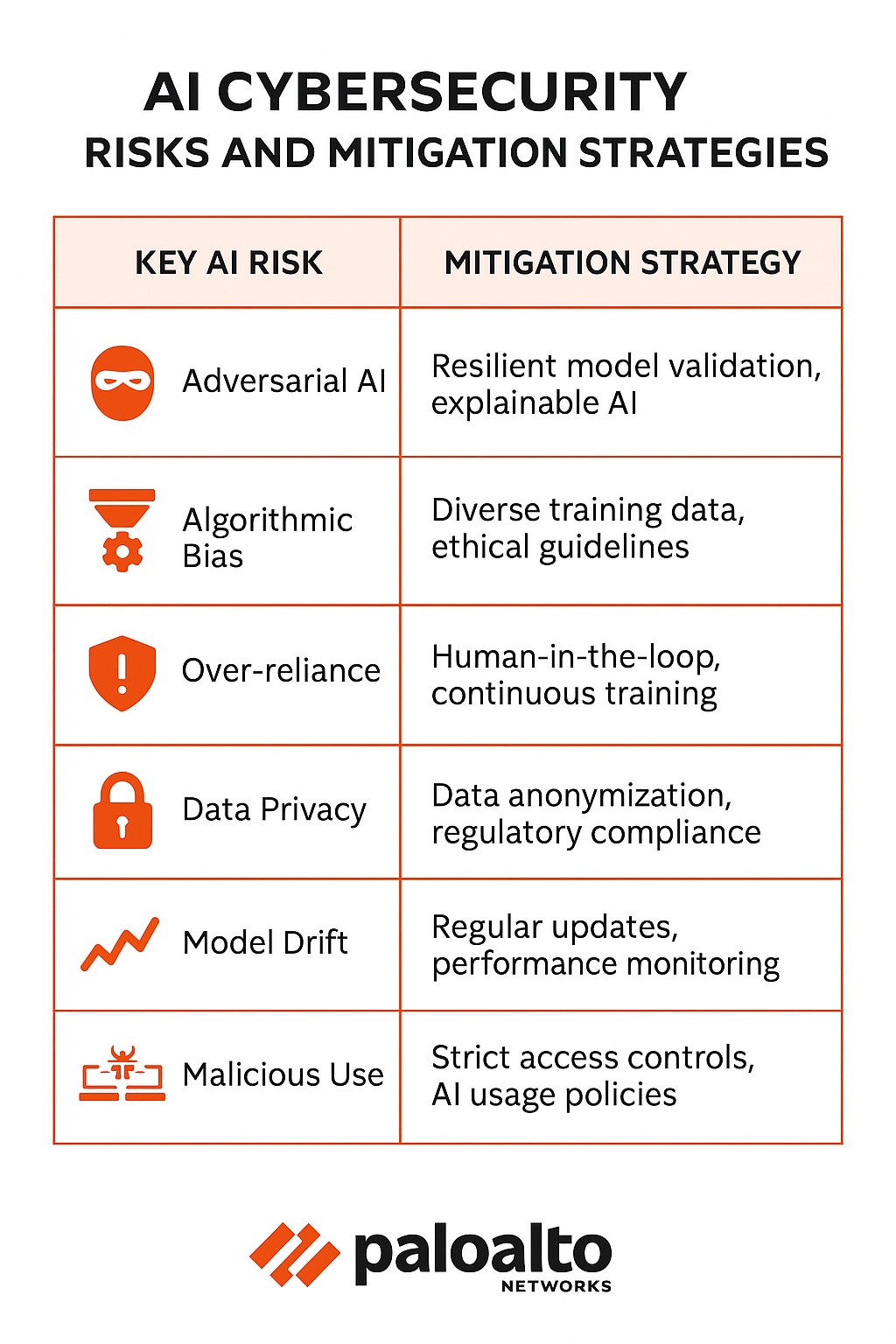
Mitigating Risks and Maximizing Benefits: Strategic Implementation
Successfully integrating AI into a cybersecurity framework requires careful planning, strong development practices, and a commitment to responsible deployment. This involves both technical implementation and strategic oversight.
Developing a Secure AI Framework
A comprehensive framework is essential to ensure that AI systems themselves are secure and contribute effectively to overall security. This framework must cover the entire lifecycle of AI models.
Integrating Security into the AI Development Lifecycle
Integrating security practices throughout the AI development lifecycle—from data collection and model training to deployment and maintenance—is critical. This involves implementing secure coding practices, conducting vulnerability testing of AI models, and adhering to security-by-design principles. Applying DevOps principles to AI development, often referred to as MLOps, helps ensure continuous security integration.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation of AI Models
Deployed AI models require continuous monitoring to ensure their ongoing effectiveness and to detect any signs of compromise or degradation. This includes monitoring for data drift, concept drift, and adversarial attacks. Regular evaluations help maintain model integrity and performance in a dynamic threat environment.
Best Practices for Responsible AI Adoption
Responsible AI adoption means maximizing benefits while mitigating risks, emphasizing human collaboration, and adhering to ethical principles. This involves thoughtful deployment and continuous learning.
Prioritizing Human-AI Collaboration and Augmentation
AI should augment human capabilities rather than replace them. Security teams must retain ultimate oversight, using AI as a powerful tool to enhance their decision-making and efficiency. Human analysts provide critical contextual understanding and intuition that AI systems currently lack.
Establishing Clear Ethical Guidelines and Policies
Organizations must develop and adhere to clear ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI in cybersecurity. These guidelines should address issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability. Ethical frameworks ensure that AI is used in a manner that aligns with an organization's values and societal expectations.
Integrating AI with Existing Security Ecosystems
AI solutions should not operate in isolation but instead seamlessly integrate with an organization's broader security ecosystem. This creates a more cohesive and powerful defensive posture.
AI should augment existing security tools, including Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms. This integration allows AI to enrich data, automate responses, and provide deeper insights across the entire security stack. A unified approach maximizes the value of AI investments.
The Future Outlook: Adapting to the Evolving AI Landscape
The landscape of AI in cybersecurity is continually evolving, driven by rapid technological advancements and the changing nature of cyber threats. Staying ahead requires foresight and adaptability.
Continuous Evolution of AI in Offense and Defense
The ongoing AI arms race between attackers and defenders will lead to increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks and defense mechanisms. Organizations must anticipate these developments and invest in research and development to maintain a competitive edge. The threat landscape will continue to be characterized by rapid innovation.
Importance of Collaborative Defense and Information Sharing
As AI becomes more prevalent, collaborative defense initiatives and information sharing among organizations and security vendors will become even more critical. Sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and insights into AI-powered attacks can strengthen collective resilience. A unified front is essential against a globally connected adversary.
Risk and Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity FAQs
Measuring the return on investment for AI in cybersecurity involves assessing reductions in incident response times, decreased breach costs, improved threat detection rates, and the reallocation of human resources to higher-value tasks. Quantifying these improvements through metrics like mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR) provides tangible evidence of AI’s impact.
Security professionals need training that blends traditional cybersecurity knowledge with skills in data science, machine learning fundamentals, and AI ethics. This includes understanding AI model behavior, interpreting AI-generated insights, and the ability to identify and mitigate adversarial AI attacks. Specialized certifications in AI and machine learning for security are also emerging.
Yes, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can leverage AI in cybersecurity through cloud-based security solutions and managed security service providers (MSSPs) that integrate AI capabilities. These services offer access to advanced AI tools without requiring significant in-house expertise or infrastructure investment. Focusing on specific AI-powered features, such as advanced threat detection or automated patching, can be highly beneficial.
AI helps defend against ransomware by identifying anomalous file encryption patterns, detecting unusual network communication indicative of command-and-control activity, and analyzing file access behaviors to prevent unauthorized access. It can also predict potential ransomware targets by assessing system vulnerabilities and user behavior, allowing for proactive isolation and containment.
Several rules and frameworks are emerging globally to address the ethical use of AI, including the EU’s Artificial Intelligence Act and NIST's AI Risk Management Framework. These initiatives focus on principles such as transparency, accountability, fairness, and human oversight, providing guidelines for the responsible development and deployment of AI in sensitive areas, including cybersecurity.