- 1. What is 5G?
- 2. What is SD-WAN?
- 3. What is the state of the 5G market?
- 4. What is the state of the SD-WAN market?
- 5. What are the potential use cases for SD-WAN and 5G?
- 6. What are the potential challenges of combining 5G and SD-WAN?
- 7. What does the future hold for 5G and SD-WAN?
- 8. SD-WAN and 5G FAQs
How Do 5G and SD-WAN Work Together?
The prospect of combining SD-WAN and 5G is still uncertain as both technologies continue to develop.
SD-WAN may facilitate the integration of various connection types, including 5G, into a unified network architecture. Additionally, SD-WAN's capabilities in managing and optimizing network traffic could enhance the performance and reliability of 5G networks.
However, the full potential and practical implementation of this combination are not yet clear.
What is 5G?
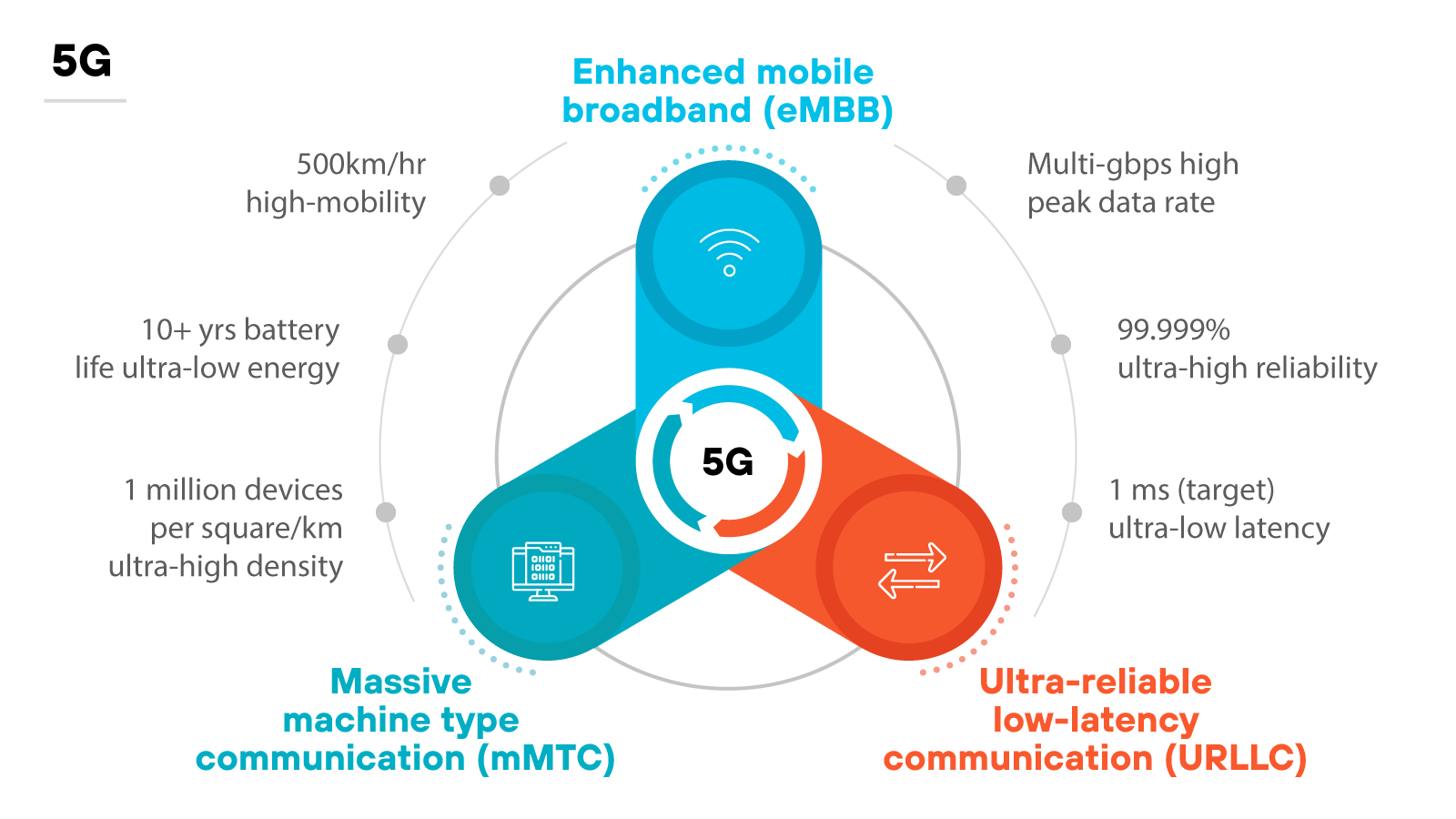
5G, the fifth generation of cellular networks, represents a significant evolution in telecommunications.
Launched in 2019 by various companies and telecom operators, 5G majorly improves speed, latency, and bandwidth compared to its predecessors. It provides faster download and upload times, stronger connectivity, and better reliability. The advancement of 5G marks a major upgrade from 4G technology.
The technology behind 5G relies on cellular infrastructure that divides service areas into smaller regions called cells. Devices within the cells connect to the network via radio waves, base stations, and antennas.
5G uses higher frequency bands, including millimeter waves, which provide substantial data transfer rates. This is what results in enhanced network speed and capacity.
It’s worth noting, though, that high-frequency signals do have a limited range. Which means they require closer proximity to cell stations.
Maintaining coverage and performance of high-frequency 5G networks requires extensive infrastructure development—including installing numerous cell stations.
What is SD-WAN?
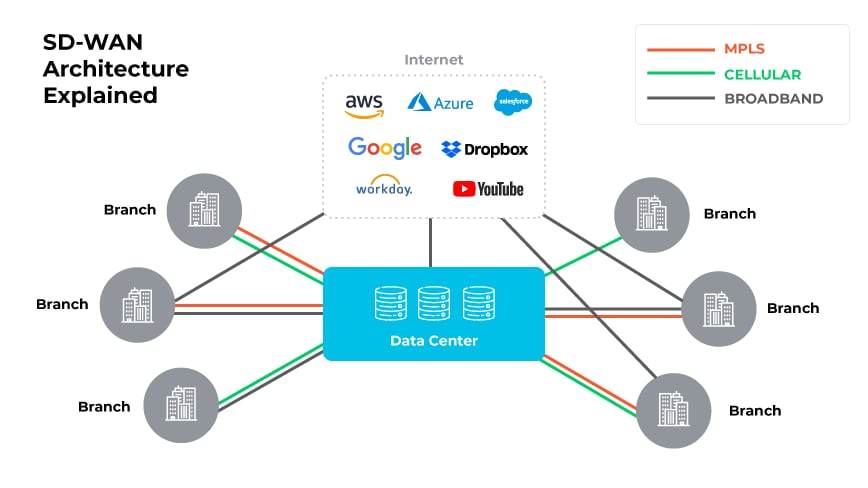
SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) is a networking technology that applies software-defined networking principles to manage and optimize the performance of wide area networks (WANs).
It allows organizations to securely connect users, applications, and data across multiple locations, improving performance, reliability, and scalability.
How?
By providing centralized control and visibility over the entire network.
SD-WAN simplifies WAN management. It works by virtualizing the WAN service to connect and extend enterprise networks over large geographical distances. SD-WAN uses various links, like MPLS, wireless, broadband, VPNs, and the internet, to provide access to corporate applications and resources regardless of location.
SD-WAN monitors WAN connection performance and manages traffic to maintain high speeds and optimize connectivity, offering better security and reliability than traditional WANs.
What is the state of the 5G market?
"In the United States alone, telcos spent roughly $100 billion to purchase 5G spectrum at auction in 2021. Despite these substantial infrastructure investments, the adoption and monetization of 5G are still in their infancy."
-McKinsey & Company, Navigating the three horizons of 5G business building
While there’s no shortage of enthusiasm for 5G, the reality is that deployment is still in progress. Plus, the COVID-19 pandemic and supply chain disruptions postponed carrier rollout plans.
- GSMA Intelligence forecasts that there will be 5 billion 5G connections by 2030.
- 5G Americas has higher expectations, predicting 7 billion 5G connections by 2028.
- On the other hand, McKinsey & Company estimated that only one-quarter of the world's population will have access to high-band 5G coverage by 2030. McKinsey also reported that telecommunication providers are expected to invest around $600 billion in 5G infrastructure from 2022 to 2025.
In any case, one thing is for sure:
The growth of 5G will come with significant costs.
It’s true that 5G coverage will expand substantially, but the fact is that it will primarily extend to the periphery.
Basically, coverage is increasing—but for now, most of it’s concentrated in major metropolitan areas. Carriers are only just beginning to offer more affordable data plans with unlimited access.
Also, 5G network slicing, which provides guaranteed QoS and dynamic resource allocation, is currently available only in select U.S. cities.
From an enterprise perspective, adoption of 5G technology is varied. The industry is still exploring use cases and business opportunities that use the advanced specifications of the technology.
In fact, the prospect of pairing SD-WAN with 5G is an evident example of this.
What is the state of the SD-WAN market?
"By 2026, 60% of new SD-WAN purchases will be part of a single-vendor secure access service edge (SASE) offering, up from 15% in 2023. By 2026, generative AI technology embedded in SD-WAN offerings will be used for 20% of initial network configuration, up from near zero in 2023.”
-Gartner, Inc., 2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SD-WAN
The SD-WAN market is experiencing rapid growth and maturation due to the increasing demand for flexible, cloud-based networking solutions.
According to the 2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SD-WAN, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% is projected from 2022 through 2027.
Multiple factors are driving the growth, including:
- Existing branch office router equipment refreshes
- Network service provider (NSP) or managed service contracts renewals
- The shift in traffic patterns resulting from the growing use of cloud and multicloud resources
A significant trend in the SD-WAN market is its convergence with secure access service edge (SASE) offerings. It’s anticipated that by 2026, 60% of new SD-WAN purchases will be part of a single-vendor SASE offering, up from 15% in 2023 (Gartner).
The shift highlights the growing importance of combining networking and security capabilities to meet the needs of modern enterprises.
Also, the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into SD-WAN solutions is expected to enhance network management, uptime, and performance. Generative AI technology is projected to be used for 20% of initial network configurations by 2026 (Gartner).
High-end SD-WAN solutions now offer dynamic path selection, centralized orchestration, and secure connections across multiple WAN links. They’re replacing traditional branch routers and shifting from MPLS-centric to public internet-centric models.
The transition is crucial as enterprises increasingly shift traffic from private data centers to public cloud and SaaS environments.
The future of SD-WAN technology is more certain than that of 5G. It remains a growing market because organizations across virtually all industries need efficient, scalable, and secure networking solutions in cloud and hybrid environments.
Further reading:
- SD-WAN vs. SASE: What’s the Difference?
- Why ML and AI Are Key Technologies for SD-WAN
- What Is Next-Generation SD-WAN?
- Securing Branch Locations with SD-WAN
What are the potential use cases for SD-WAN and 5G?
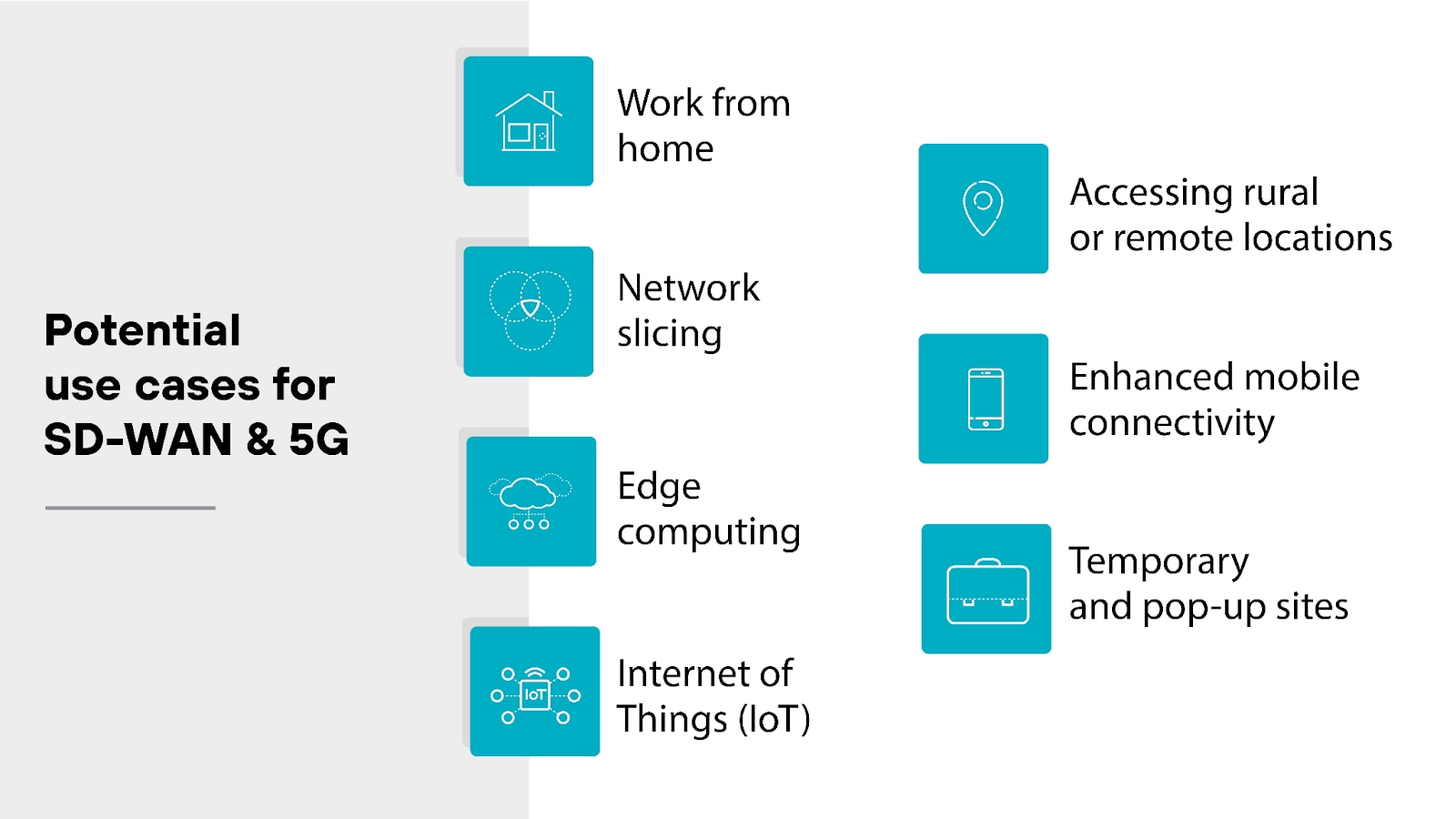
Both SD-WAN and 5G offer worthwhile applications to organizations on their own. Given that 5G is largely still in development, for now we can make educated speculations as to how the two might pair well together.
Overall, the convergence of SD-WAN and 5G technology may have the potential to significantly impact the landscape of network connectivity.
Here are some of the key use cases where SD-WAN and 5G might make an impact:
Work from home
With the rise of remote work, SD-WAN and 5G can create a robust network infrastructure for home offices. SD-WAN ensures secure and efficient traffic management, while 5G provides high-speed connectivity. The combination could support seamless network access to corporate resources, ultra low latency, and reliable performance.
Accessing rural or remote locations
Industries like farms, mining operations, and oil fields often need to monitor and manage remote or rural sites. Combining SD-WAN with 5G could provide connectivity in areas where traditional wired networks aren’t practical.
This setup would make it possible to transmit data in real time, control machinery remotely, and improve safety by reducing the need for on-site personnel.
Edge computing
Since edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to its source, combining it with SD-WAN and 5G could further enhance performance.
SD-WAN optimizes traffic routing, while 5G provides high-speed, low-latency connectivity. So this setup could potentially benefit scenarios that need real-time data analysis.
Autonomous vehicles and industrial automation could see improved performance and responsiveness, for instance.
Network slicing
Network slicing involves creating multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, each optimized for different types of traffic.
SD-WAN could manage these slices effectively in a 5G environment, ensuring critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and performance. This capability would be important for industries like healthcare and manufacturing, where different applications have varying requirements.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of SD-WAN and 5G could very well be pivotal for IoT applications.
Here’s why: IoT applications require reliable, low-latency connectivity for a vast number of devices. SD-WAN can dynamically manage network traffic to make sure that IoT devices operate efficiently. 5G's role in this is to provide the high-speed, low-latency connectivity necessary for the vast number of IoT devices, ensuring efficient operation and communication.
For example, in smart cities, this combination supports connected infrastructure like traffic lights, environmental sensors, and public safety systems.
Temporary and pop-up sites
Events, pop-up stores, and temporary sites require quick and reliable network setup. Together, SD-WAN and 5G can offer fast deployment of high-speed internet connectivity—and without the need for extensive infrastructure.
This kind of flexibility would be especially useful for retail, entertainment, and emergency services. Operations could theoretically work efficiently in temporary locations.
Enhanced mobile connectivity
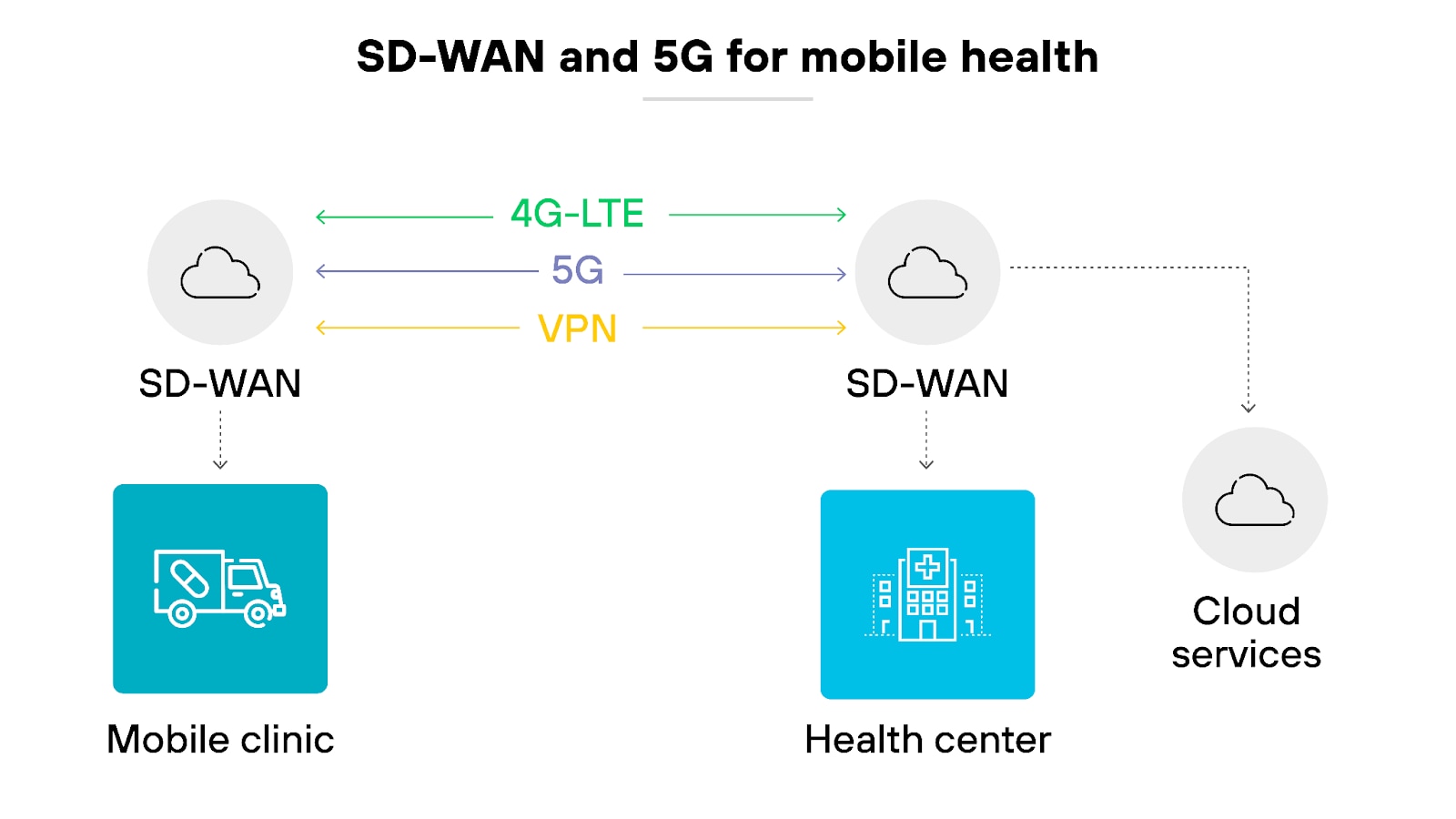
For mobile users, SD-WAN combined with 5G can provide improved connectivity by dynamically selecting the best available network.
This capability would be essential for scenarios where consistent connectivity is crucial, like healthcare units or disaster response teams. Users would benefit from uninterrupted access to critical applications and data, regardless of location.
Further reading: How SD-WAN Benefits IoT
What are the potential challenges of combining 5G and SD-WAN?
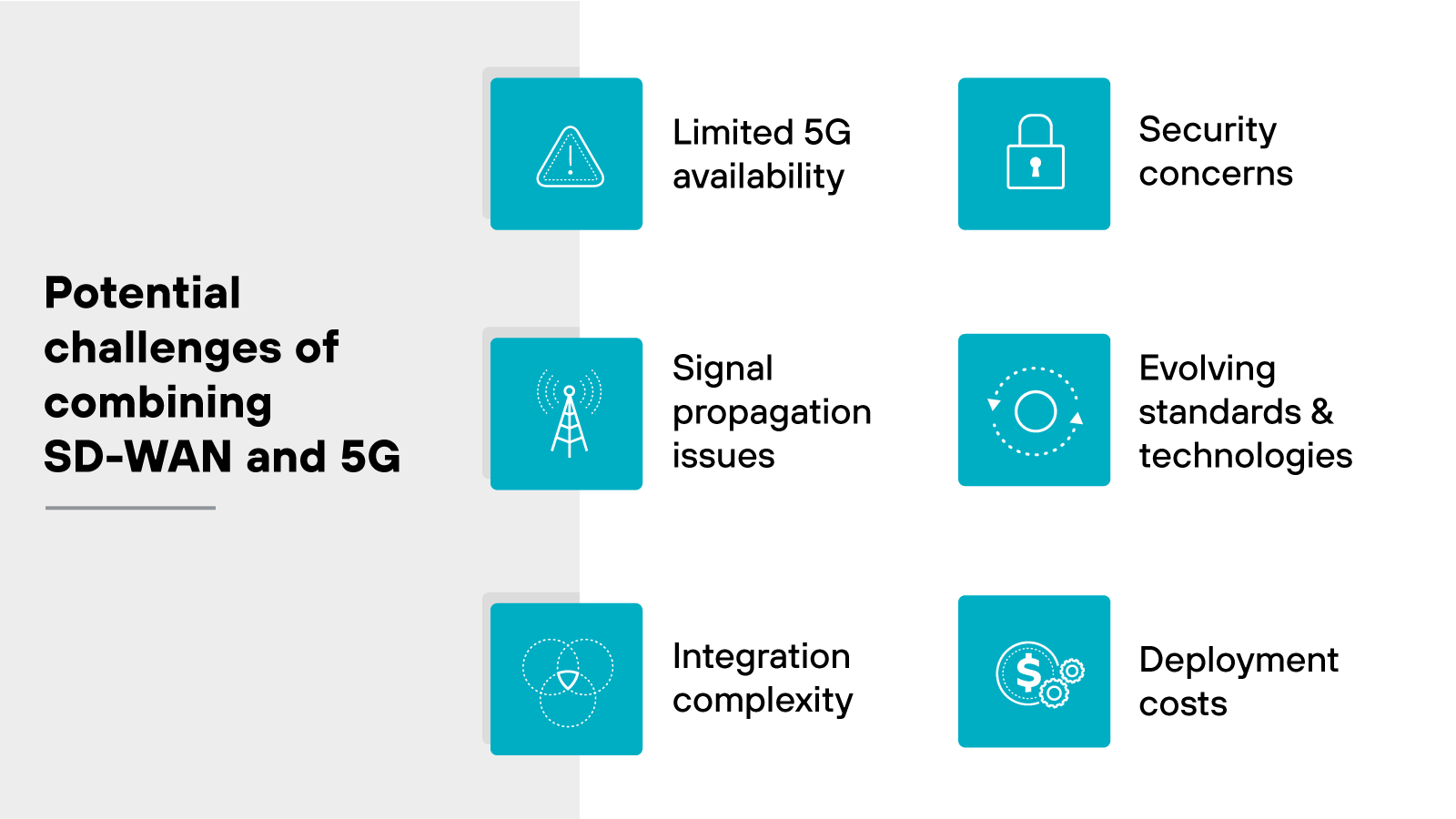
Combining 5G and SD-WAN may eventually offer some worthwhile use cases and benefits, but it also presents several challenges we don’t yet have answers for. These challenges stem from the current state of 5G infrastructure, integration complexities, and evolving technologies.
Here are some of the key issues to consider:
Limited 5G availability
One of the primary challenges of combining 5G and SD-WAN is the limited availability of 5G networks.
5G promises high-speed connectivity, but its rollout is still in progress. Plus, coverage isn’t ubiquitous. Which means that organizations in areas without robust 5G infrastructure cannot use 5G-enhanced SD-WAN.
Integration complexity
Integrating 5G with existing SD-WAN infrastructure can be complex and resource-intensive.
Organizations first have to ensure compatibility between current network components and the new 5G technology. The integration process can require significant time and expertise that may not be worth investing in given the current maturity stage of 5G.
Signal propagation issues
5G signals, especially those in the higher frequency bands, have difficulty propagating through physical obstacles like walls and buildings. The limitation of signal strength can lead to inconsistent connectivity and reduced performance in indoor environments.
SD-WAN can complement 5G by allowing organizations to use multiple types of connections to maintain connectivity. But SD-WAN alone does not solve 5G signal propagation issues.
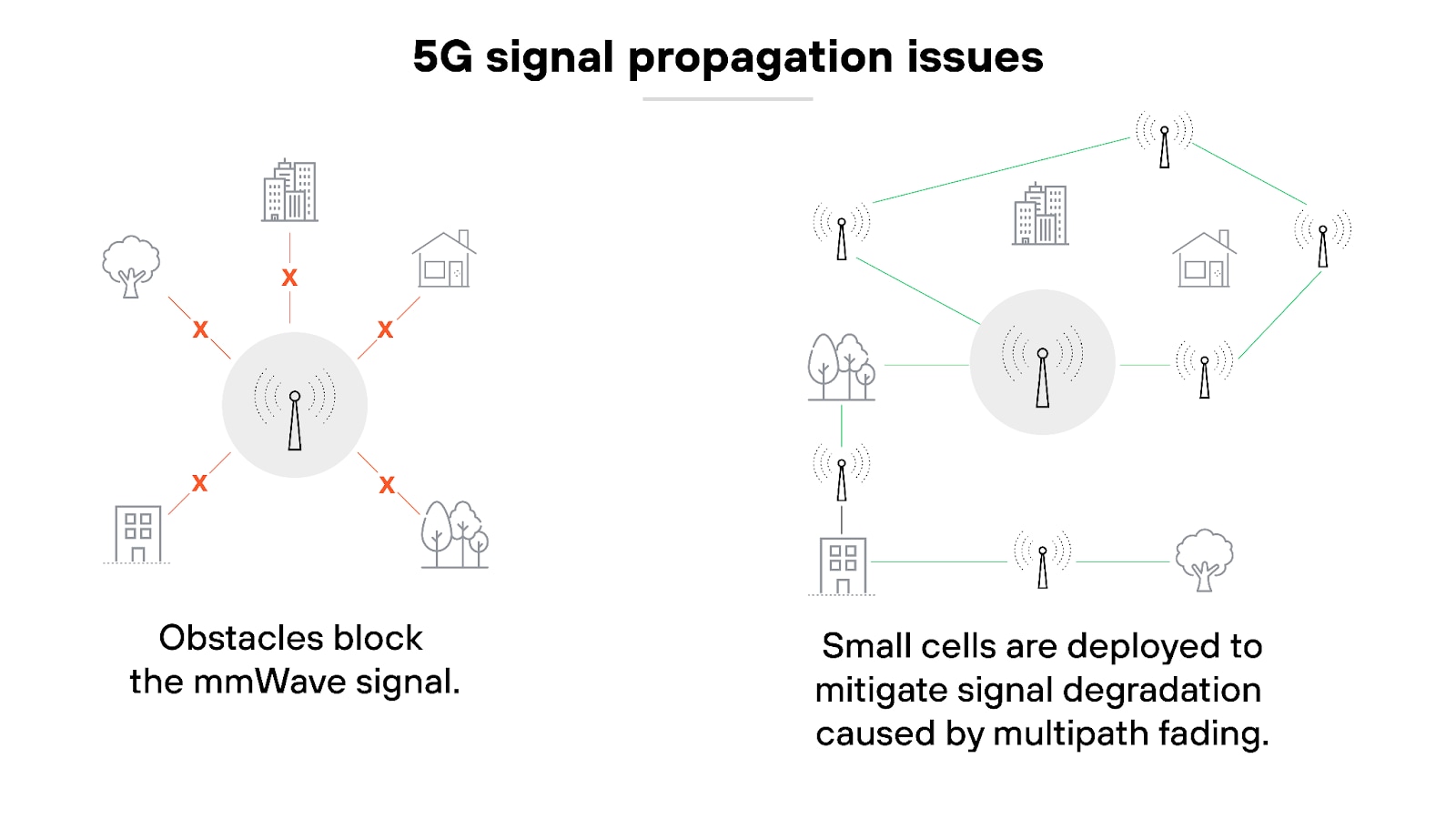
To mitigate this, organizations usually need to invest in additional infrastructure, such as deploying small cells or external antennas—and that increases costs and complexity. This is difficult to justify when there are already proven, durable solutions that do the same thing effectively, and for less.
Security concerns
While SD-WAN enhances network security, introducing 5G can bring a whole new set of vulnerabilities.
A 5G network’s broader attack surface and the complexity of managing multiple connection types can make it challenging to maintain effective security protocols.
Organizations need to implement additional security measures to protect against potential threats in a 5G-enabled SD-WAN environment.
Deployment costs
Deploying 5G infrastructure can be expensive, especially in the early stages of adoption.
The cost of 5G equipment, installation, and maintenance can be higher than traditional wired solutions. Plus, the pricing of 5G services may not yet be competitive with established broadband options.
These factors may make 5G a less attractive financial proposition for some organizations.
Evolving standards and technologies
The rapid evolution of 5G standards and technologies can pose a challenge for organizations looking to implement a stable, future-proof network solution.
As new standards emerge, businesses may need to upgrade their equipment and adjust their network configurations to stay current. Not to mention, the ongoing need for updates can lead to additional costs and operational disruptions.
What does the future hold for 5G and SD-WAN?
The fact of the matter is that we don’t know yet exactly what the future holds for 5G, let alone 5G and SD-WAN.
The promise of 5G hasn’t quite materialized, yet. Yes, it offers undeniably fast speeds and ultra low latency. But the reality is that while 5G appears on our phones in public networks, most private networks continue to rely on LTE and a converged 3G/4G core network. Industrial devices are generally still using 4G with IMSI identification (as opposed to the more modern, secure SUPI for 5G networks).
As 5G technology matures, its integration with SD-WAN could reveal significant potential for enhanced connectivity and network management. However, whether this combination will become a realistic and widespread solution remains to be seen.