- What Is Observability?
- What is AIOps
- What Is Threat Hunting?
-
4 Ways Cybersecurity Automation Should Be Used
- Cybersecurity Automation Explained
- Cybersecurity Automation Use Cases: Four Key Areas
- How Cybersecurity Automation Works
- Benefits of Automating Your Security Operations
- The Critical Role of Human Oversight
- Challenges and Best Practices for Implementation
- How Automation Stops the Attack Lifecycle
- Cybersecurity Automation FAQs
-
What is UEBA (User and Entity Behavior Analytics)?
- How UEBA works
- Benefits of Implementing UEBA
- Examples of UEBA
- Common Use Cases for UEBA
- Challenges and Considerations in UEBA Deployment
- Diverse Threats Addressed by UEBA
- Integrating UEBA and XDR
- UEBA vs NTA
- UEBA vs SIEM
- UEBA vs IAM
- Future Trends and Developments in UEBA
- Choosing the Right UEBA Solution
- UEBA FAQs
- What is Security Analytics?
- What Is Security Event Management (SEM)?
- What is Security Automation?
- What is Cortex XSIAM?
-
How Do I Deploy SecOps Automation?
- Preparing for SecOps Automation
- Start Simple with High-Impact Tasks
- Automation Benefits for Organizations of All Sizes
- Peer Review and Approval
- Secure a Champion for Automation
- Defining Automation Use Cases
- Example Use Cases: Phishing and Malware
- Selecting the Right SOAR Platform
- SOAR Deployment and Use Cases FAQs
- What is an internet operations management program?
- What is AIOps for NGFW?
What Is DEM (Digital Experience Monitoring)?
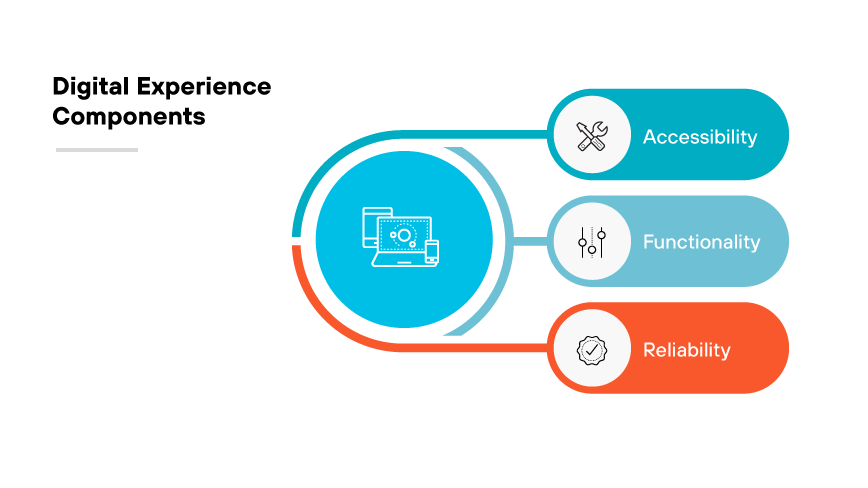
Digital experience is the collective impact of digital interactions between a user and technology based systems.
The accessibility, functionality, and reliability of digital platforms such as websites and mobile applications shape these interactions. The ease with which users can accomplish their objectives on technology platforms determines the quality of the digital experience. Successful digital experiences include intuitive navigation, speedy transactions, and minimal errors.
Continuous monitoring and optimization of these interactions are essential for organizations to address user needs effectively and maintain relevance in the digital marketplace.
Digital Experience Monitoring Components
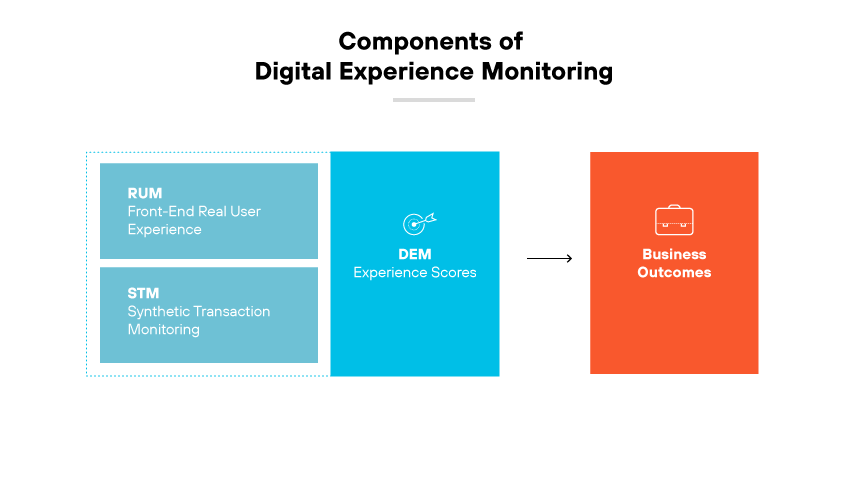
Real User Monitoring (RUM)
Real user monitoring (RUM) is a technology that captures and analyzes every transaction of users interacting with applications. It collects data directly from the user’s device, providing insights into performance from the user’s perspective. RUM helps determine user behavior and application performance. It also pinpoints issues users face in real time.
Synthetic Transaction Monitoring (STM)
Synthetic transaction monitoring (STM) uses scripted sequences to emulate the path a customer or user would take through a website or application. It allows for consistent transaction and application performance testing, regardless of actual user traffic. STM is essential for identifying issues before they impact users, and for understanding performance across different locations and times.
End User Experience Scores
End user experience scores are the quantitative measure of user satisfaction based on the performance and usability of digital services. They derive from analyzing data collected from RUM and STM. End user experience metrics reflect the overall health of digital platforms and guide improvements to elevate the user experience.
How Does Digital Experience Monitoring Work?
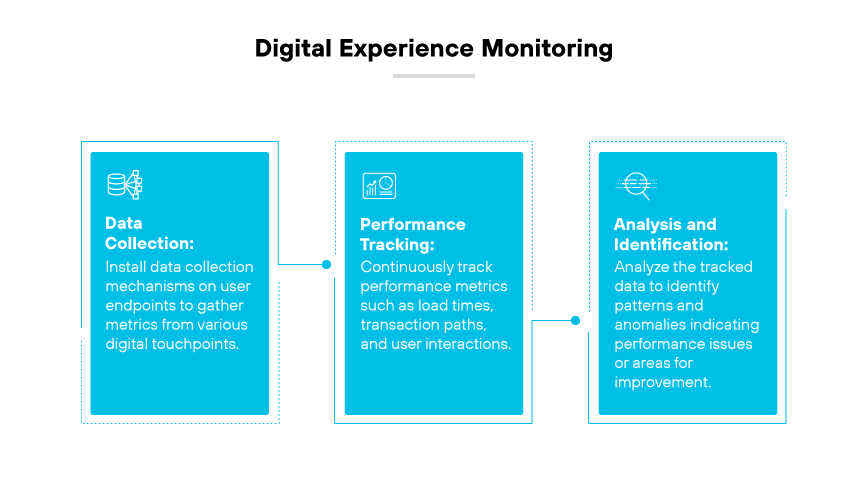
Digital experience monitoring (DEM) operates on a framework that prioritizes the end user's interaction with digital platforms. At its core, DEM tools assess the performance and availability of applications and services. These tools track a variety of metrics such as load times, transaction paths, and user interactions within applications. The goal is to pinpoint areas that impede optimum user experience.
The process begins with data collection across various touchpoints within the digital environment. This includes monitoring web applications, application programming interfaces (APIs), and mobile applications. Tools designed for DEM capture real time performance indicators which are crucial for assessing the digital health of an organization. Then, metrics analysis identifies patterns and anomalies that could signal potential or existing issues.
DEM uses technologies such as synthetic transaction monitoring and real user monitoring to test performance and collect data from actual user interactions. This combination provides a comprehensive view by identifying potential issues before they affect users and uncovering real time experiences. Network visibility is also key, ensuring the digital infrastructure supporting user interactions is functioning as intended.
Why Is Digital Experience Monitoring Important?

Digital experience monitoring is critical because it enables organizations to measure and optimize the performance of their digital services from the user's perspective. It plays a vital role in detecting and resolving issues before they affect the user. DEM allows organizations to maintain a high level of service availability and performance. This proactive approach to monitoring ensures users have a consistently positive experience with the organization's digital platforms, which is crucial for sustaining engagement and satisfaction.
DEM provides insights that allow organizations to understand the complexity of digital interactions and user journeys. Businesses use DEM tools to track application and infrastructure performance in isolation and as part of the broader digital ecosystem, including cloud services and external APIs. By analyzing this data, organizations can identify trends, anticipate issues, and make informed decisions to improve the overall digital experience.
”Digital experience monitoring (DEM) is a performance analysis discipline that supports the optimization of the operational experience and behavior of a digital agent, human or machine, with the application and service portfolio of enterprises. These users, human or digital, can be a mix of external users outside the firewall and inside it. This discipline also seeks to observe and model the behavior of users as a flow of interactions in the form of a customer journey."
— Gartner, Market Guide for Digital Experience Monitoring1
The importance of DEM extends beyond maintaining operational efficiency. It also directly impacts business outcomes. A seamless digital experience can lead to increased productivity, higher customer retention, and ultimately, better financial performance. In a competitive digital landscape, the ability to rapidly respond to and resolve user experience issues translates into a significant competitive advantage. DEM is not just an IT tool but a business imperative that supports strategic goals and drives continuous improvement.
Types of Digital Experience Monitoring Tools
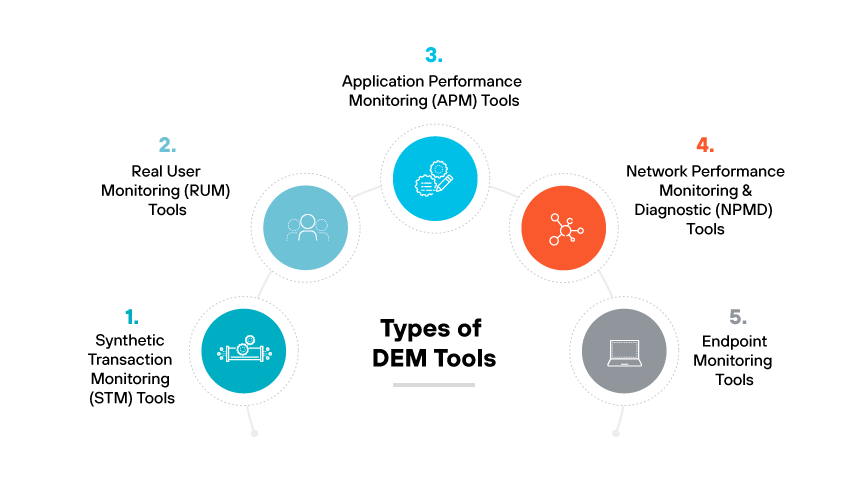
Synthetic Monitoring and Synthetic Transaction Monitoring (STM) Tools
Synthetic monitoring tools are scripts or agents designed to emulate the actions of users on applications, websites, or services. They perform scheduled tasks to test and ensure systems are operating correctly from various global locations. These tools can detect outages and performance issues before they affect actual users.
Real User Monitoring (RUM) Tools
Real user monitoring tools gather and analyze data from interactions that real users have with digital services. By capturing real time information on page load times, clicks, and transaction paths, RUM tools provide an accurate picture of user experience and satisfaction. They are essential for pinpointing problem areas and improving the overall user journey.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) Tools
Application performance monitoring (APM) tools focus on the software application layer, tracking response times, system health, and error rates. APM tools are vital for identifying bottlenecks in the application stack and ensuring application infrastructure supports a superior user experience.
Network Performance Monitoring and Diagnostics (NPMD) Tools
Network performance monitoring and diagnostics tools analyze the network performance aspects that influence the user experience, such as latency and packet loss. NPMD tools are important for maintaining the reliability and speed of the network that supports digital interactions.
Endpoint Monitoring Tools
Endpoint monitoring tools observe and assess the performance of user devices, including desktops, mobile phones, and tablets. They check for hardware or software issues that could impact user experience, ensuring endpoints are not a barrier to efficient digital service delivery.
DEM Benefits
Improved User Experience
The most direct benefit of DEM is user experience enhancement. DEM tools ensure users enjoy a smooth, satisfying interaction with digital platforms. They achieve this by continuously monitoring digital services and identifying and resolving issues in real time. A high quality user experience generally fosters user loyalty and retention.
Efficient Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution
DEM enables organizations to shift from a reactive to a proactive stance in problem solving. It detects potential issues before they escalate, allowing for preemptive action. By doing so, DEM minimizes downtime and maintains seamless digital services operation, which is critical in today’s fast paced digital landscape.
By integrating various monitoring functions into a cohesive DEM strategy, organizations can streamline operations. Integration often leads to reduced IT related costs because it improves the efficiency of identifying and addressing issues.
Data Driven Insights
DEM provides valuable insights into the functioning of various digital touchpoints through performance data analysis and collection. This data is crucial for making informed decisions about improvements and enhancements to digital platforms. It also facilitates a better understanding of user behavior, which can drive strategy in product development and service provision.
Enhanced Business Outcomes
The goal of any business initiative is to achieve better outcomes, which DEM contributes to directly. By ensuring optimal digital platforms performance, DEM helps businesses to improve their service offering. Better service offerings lead to increased customer satisfaction, higher sales, and stronger financial performance.
DEM Challenges
Complexity of Digital Ecosystems
The intricate web of modern digital ecosystems can complicate digital experience monitoring. Organizations must navigate various platforms, devices, and network environments. The diversity creates the need for versatile DEM tools capable of monitoring and synthesizing data across all these elements. This can make it challenging to achieve comprehensive coverage.
Data Management and Accuracy
Accurate data collection is fundamental to DEM. However, ensuring the precision of this data, especially given the volume and variety, is challenging. Organizations must finely tune monitoring tools to filter out noise and irrelevant data. Precision makes it easier to avoid inaccurate reporting that could lead to misguided decisions.
Integration with Existing Systems
Organizations need to be able to integrate DEM tools with existing IT infrastructure. The challenge is ensuring integrations are seamless and do not disrupt operations. It requires careful planning and execution, often requiring a specialized skillset within the IT team.
Disparate Technologies in DEM Solutions
Choosing a DEM solution can be challenging due to the diverse technologies different vendors use, including but not limited to:
- Real user monitoring (RUM) or browser telemetry using JavaScript injection
- Synthetic transaction monitoring (STM) for simulating user actions on web and mobile interfaces
- Synthetic monitoring for applications and network path analysis
- End user experience monitoring (EUEM)
- Monitoring of endpoints and user behavior via desktop and mobile agents
- APM agents and NPMD probes
A comprehensive DEM approach must effectively integrate these disparate technologies to provide a cohesive understanding of user experience across all platforms.
Real Time Monitoring and Response
A core component of DEM is the ability to monitor and respond to issues in real time. However, this can be resource intensive and may lead to alert fatigue if not managed properly. Balancing the need for immediate action with efficient resource allocation is a common challenge in DEM implementation.
Privacy and Compliance
With the increase in data privacy regulations, DEM solutions must not only be effective but also compliant with legal standards. Adhering to these regulations while still gaining meaningful insights from user data can be a delicate balance for some organizations.
How to Establish a Digital Experience Monitoring Strategy
To establish an effective digital experience monitoring (DEM) strategy, organizations need a comprehensive plan that addresses both technical and business considerations. Initially, it is essential to set clear objectives that align with the organization’s broader goals. Identify the key digital touchpoints and user journeys that are critical to the business and the intended customer experience. To capture a complete view of the digital experience, the identification process should include input from stakeholders across various departments.
With the goals and key journeys established, the next step is selecting the appropriate DEM tools. These tools should monitor performance metrics and provide actionable insights. Establish KPIs that resonate with business objectives, and ensure prospective DEM tools can track these KPIs effectively. It is important to integrate these tools seamlessly with current systems to avoid any disruption and ensure they can scale with the digital environment.
The final phase involves ongoing analysis and optimization. Monitor collected data to identify trends and areas for improvement. Use these insights to refine digital platforms continually and address any issues proactively. Regularly review KPIs and adjust the strategy as needed to stay aligned with evolving business goals and user expectations. Effective communication of these insights to all relevant teams will ensure the DEM strategy translates into an enhanced digital experience for users.
How to Choose a DEM Solution
A wide variety of DEM tools are available on the market. Choosing the right solution requires careful evaluation of organizational needs and the capabilities of available tools. Start by assessing the digital channels most critical to business operations, as well as those that customers interact with most. This will help determine the features required for a DEM solution.
Integration and Compatibility
The chosen DEM tool must integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure. It should support compatibility across various platforms and systems currently in use. This ensures implementation will not disrupt established workflows. Compatibility will also make it easier to use existing data for more comprehensive insights.
Real Time Analytics
A valuable DEM solution provides real time analytics, which make it possible to immediately identify and resolve issues. This capability ensures consistent user experience monitoring and management.
Scalability
Consider the DEM tool’s scalability to ensure it can accommodate user base growth, data volume, and increased complexity of digital services. A scalable solution will serve an organization in the long term, adapting to evolving requirements without the need for frequent replacements.
User Centric Insights
Choose a DEM tool that offers user centric insights, giving a clear view of the end user experience. This should include metrics and data points that reflect actual user interactions, pain points, and behavior patterns, which are critical for improving and personalizing the user experience.
Support and Service
Assess the level of support and service the vendor provides. Reliable customer support is crucial for resolving potential issues with the DEM tool. The vendor should offer ample resources for training, assistance, and maximizing the tool’s potential.
The Role of DEM in Security
As many organizations shift network and security architectures to the cloud, such as through SASE, balancing seamless digital experience with security enforcement tends to be a struggle.
When security impacts user experience by rendering applications inaccessible or introducing inconveniences like latency and streaming downtime, users often find ways to bypass security enforcement. This can involve using unsanctioned applications or transferring sensitive data to personally owned devices.
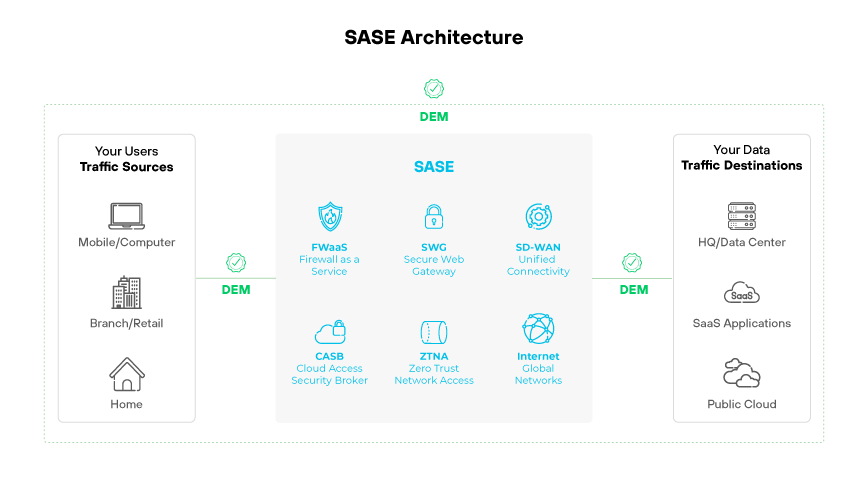
When remote connectivity is seamless, user friendly, and improves overall digital experience, employees will use it. Keeping users on sanctioned devices and services the organization can control improves overall security posture. SASE solutions with native DEM capabilities can bridge the gap between network and security teams by addressing both challenges through a single solution.
Comparing DEM with Other Technologies
DEM vs. Network Monitoring
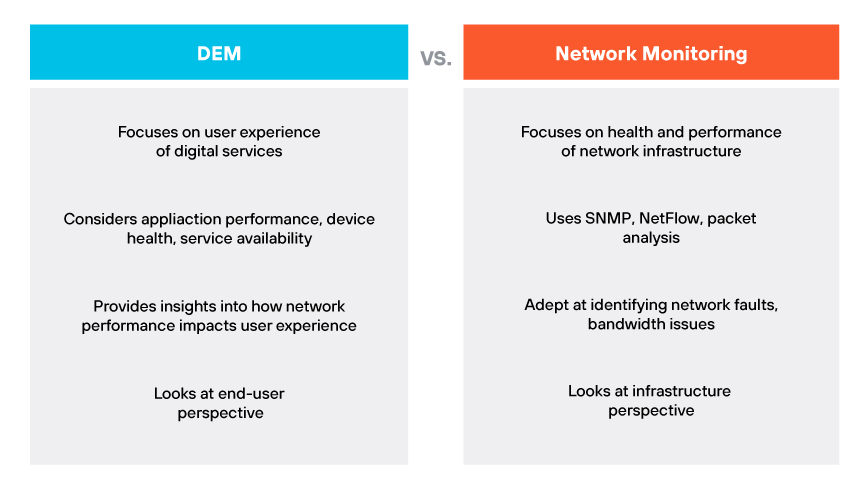
Digital experience monitoring (DEM) and network monitoring serve different but complementary functions. Network monitoring focuses primarily on the health and performance of an organization's network infrastructure. It uses technologies such as SNMP, NetFlow, and packet analysis to ensure network devices are functioning correctly and efficiently. These tools are adept at pinpointing network faults and bandwidth issues but do not extend to the user experience level.
In contrast, DEM goes beyond connectivity and bandwidth metrics to understand the actual experience of a user engaging with digital services. It considers factors such as application performance, device health, and service availability from the end user perspective. DEM tools provide insights into how network performance impacts the overall user experience, which network monitoring alone cannot provide.
DEM vs. APM
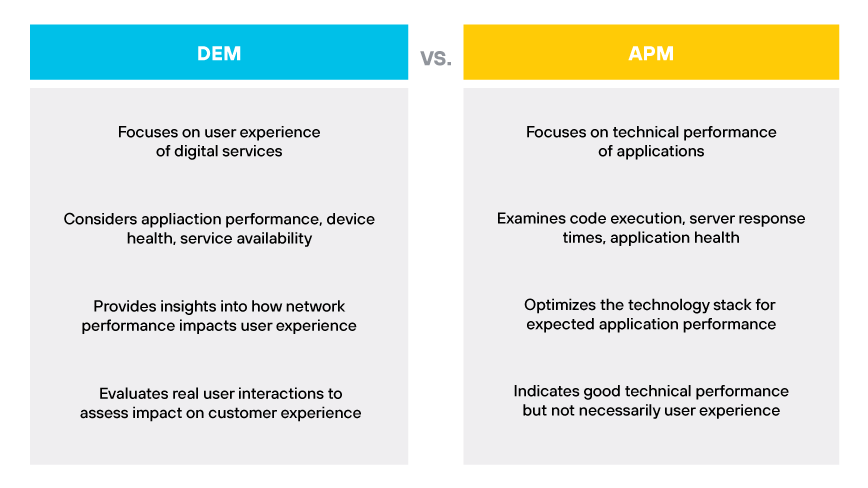
Application performance monitoring (APM) and digital experience monitoring both aim to optimize digital services, but they approach it from different angles. APM examines application performance from a technical standpoint, focusing on code execution, server response times, and application health. It seeks to optimize the technology stack to ensure applications perform as expected.
DEM, on the other hand, measures the impact of application performance on the user. It evaluates real user interactions with applications to determine if performance issues are detracting from the overall digital customer experience. While APM may indicate that an application is performing well technically, DEM could reveal that users are experiencing slow page loads or transaction delays. DEM provides a layer of insight that complements the detailed analysis provided by APM.
DEM vs. DEX
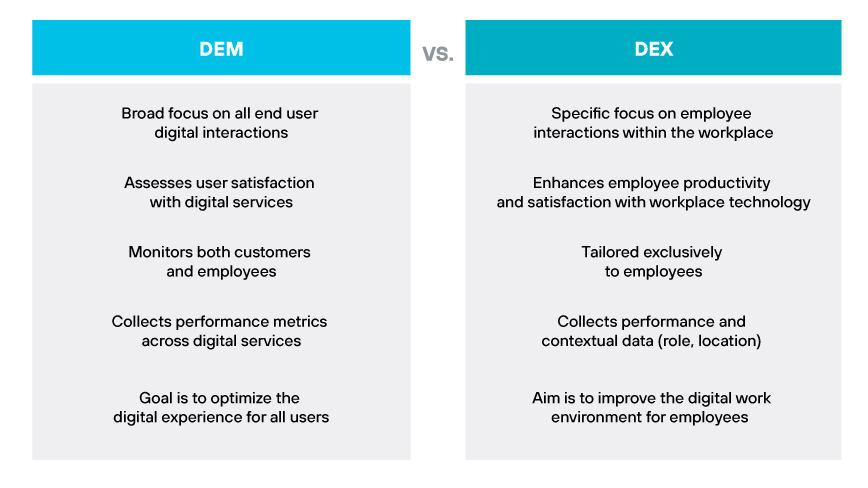
DEM is often compared to digital employee experience (DEX) because they both focus on the digital interactions of users. However, DEM has a broader scope that encompasses any end user's digital interactions, whether they are customers or employees. It assesses user satisfaction with digital services across the board.
DEX narrows this focus specifically to employee interactions with technology within the workplace. It incorporates performance and contextual data about employees, such as role and location, and may even collect feedback on sentiments toward the tools they use. DEX aims to enhance employee productivity and satisfaction with workplace technology by addressing both the technical and human sides of digital interactions.
The Evolution of Digital Experience Monitoring
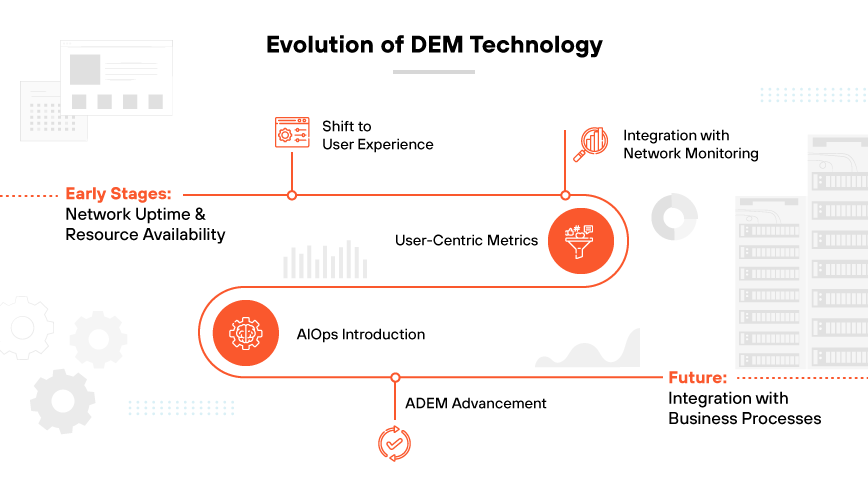
In the early stages of digital experience monitoring, the primary focus was network uptime and resource availability. The growth of ecommerce and digital services provoked a shift towards understanding and improving the end user experience. The evolution of DEM reflects a deeper integration of technology with customer centric strategies, emphasizing the importance of user satisfaction in digital interactions.
Initially, DEM aligned closely with network monitoring. DEM emphasized ensuring that servers, databases, and infrastructure were operational. This approach, however, often overlooked the actual experience of users interacting with digital platforms. As businesses recognized the direct correlation between user satisfaction and success metrics like conversion rates and retention, DEM began to incorporate more user focused metrics.
The incorporation of artificial intelligence operations (AIOps) marked a significant development in DEM evolution. AIOps utilizes artificial intelligence to automate the identification and resolution of common IT issues. The technology can anticipate user behavior, predict potential disruptions, and offer actionable insights to optimize the digital experience proactively.
Autonomous digital experience management (ADEM) represents a further advancement in this field. ADEM integrates the capabilities of DEM into a comprehensive, cloud native approach, extending its reach beyond performance monitoring to include insights across the entire service delivery path. This allows for real time visibility and proactive issue resolution, catering to the modern demand for seamless digital interactions anywhere and anytime.
Integration with business processes is likely to continue to an even greater extent as the future of DEM unfolds. User experience data will probably inform not only IT operations but also marketing, product development, and customer service strategies.
As enterprises continue to navigate the path of digital transformation, DEM stands as part of the journey, supporting superior user experiences, operational excellence, and strategic innovation.
DEM FAQs
Digital experience includes all user interactions with digital interfaces, like websites and applications.
1Gartner: Create Powerful Customer Experiences2Gartner 2023 Market Guide for Digital Experience Monitoring
