What Is Data Security? [Definition, Overview, & Why It Matters]
Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss. It involves implementing technologies, tools, and policies to ensure data remains safe throughout its lifecycle.
Data security includes methods like encryption, access controls, and regular auditing to prevent breaches and ensure compliance with regulations.
Why does data security matter?
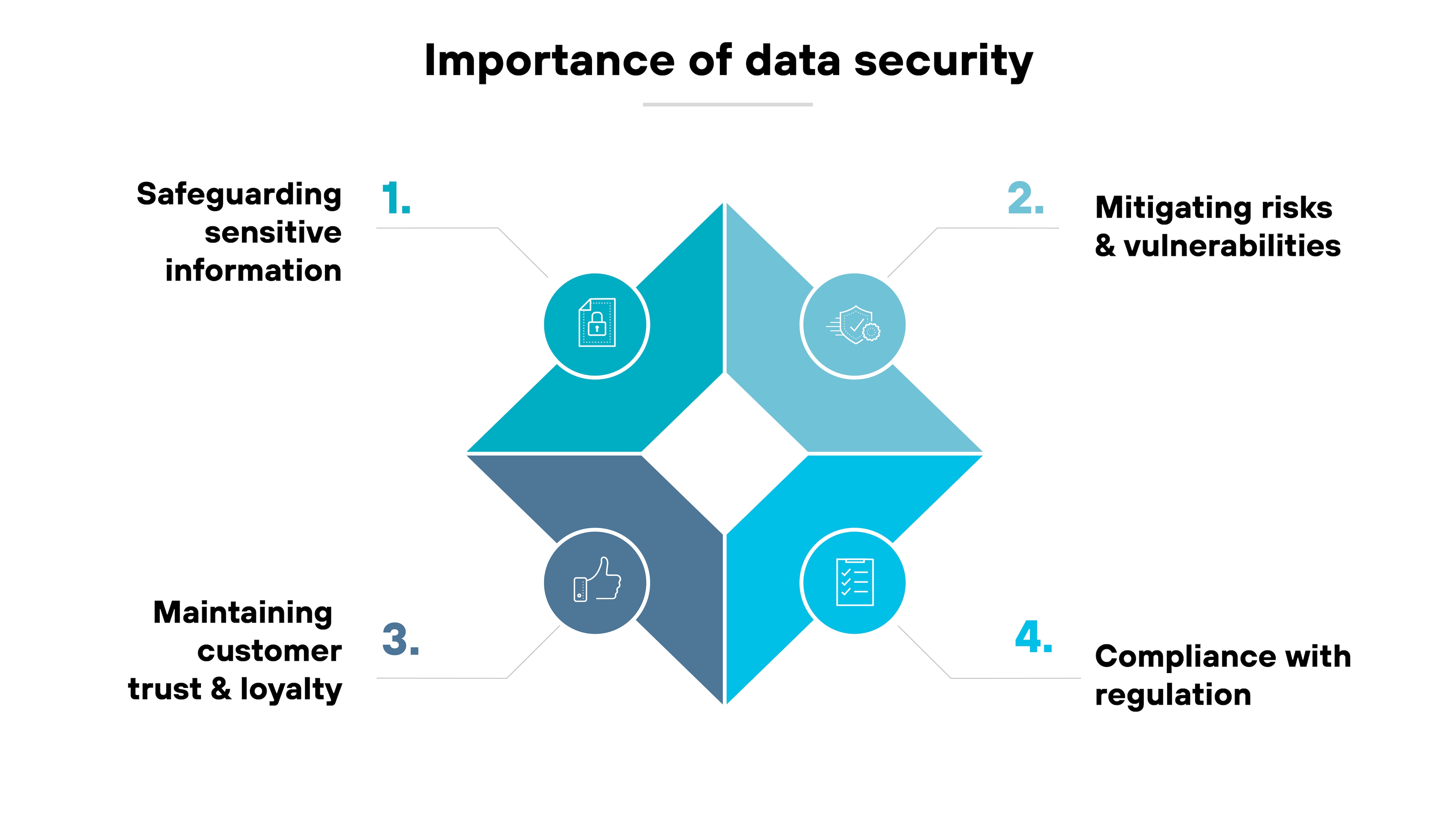
Data security matters because it protects sensitive information from theft, corruption, or unauthorized access. Organizations rely on it to safeguard customer data, intellectual property, and other business-critical assets.
The financial stakes are high. Data breaches are becoming more frequent. And the costs continue to rise.
Regulations add another layer. Laws such as GDPR and HIPAA require organizations to follow strict requirements for protecting data. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and legal exposure.
AI has also raised the bar. These systems depend on massive datasets for training and operation. If the data is tampered with, exposed, or otherwise insecure, it can corrupt the model. That can result in biased, unreliable, or even harmful outputs.
- 86% of incidents Unit 42 responded to in 2024 involved business disruption, ranging from downtime to reputational damage.
- Speed of data theft: In one in five cases (19%), attackers exfiltrated data in less than one hour of compromise. Median time to exfiltration is about two days — far faster than many organizations' detection timelines.
Essentially:
Data security protects against immediate risks like breaches and fines. But it also creates the conditions for long-term trust and safe use of technologies like AI.
So, what are the benefits of data security?
Here's what strong data security practices provide:
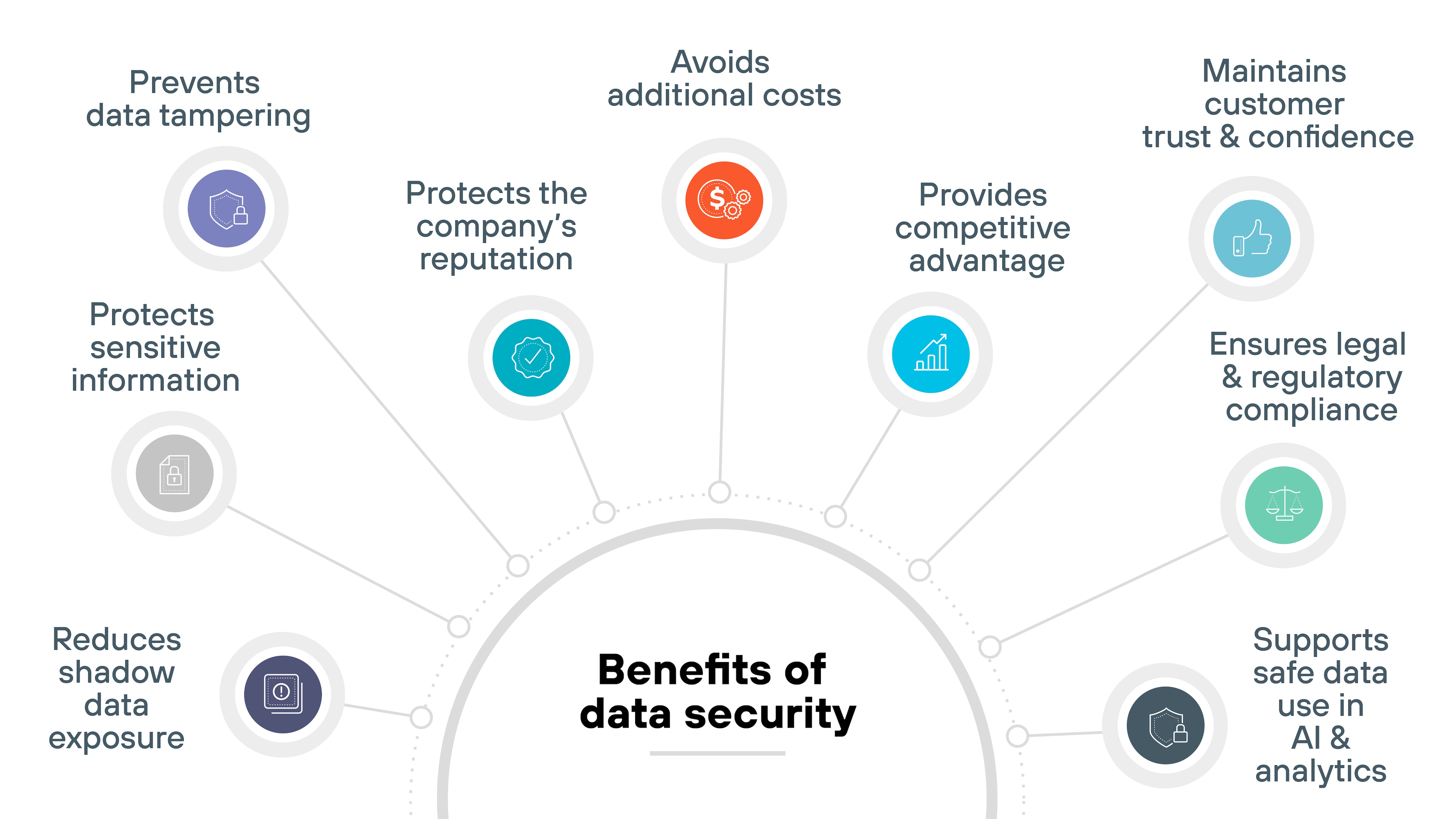
- Protects sensitive information
- Prevents data tampering
- Protects the company's reputation
- Ensures legal and regulatory compliance
- Maintains customer trust and confidence
- Provides competitive advantage
- Avoids additional costs
- Supports safe data use in AI and analytics
- Reduces shadow data exposure
Ultimately, data security isn't only about preventing breaches. It's about staying compliant, protecting trust, and keeping pace with how fast data is created and exploited today.
What makes data security complex in practice?
On paper, the controls look simple. Encrypt data. Set access rules. Back it up.
In practice, keeping data secure across a modern environment is harder than it seems.
Here's why.
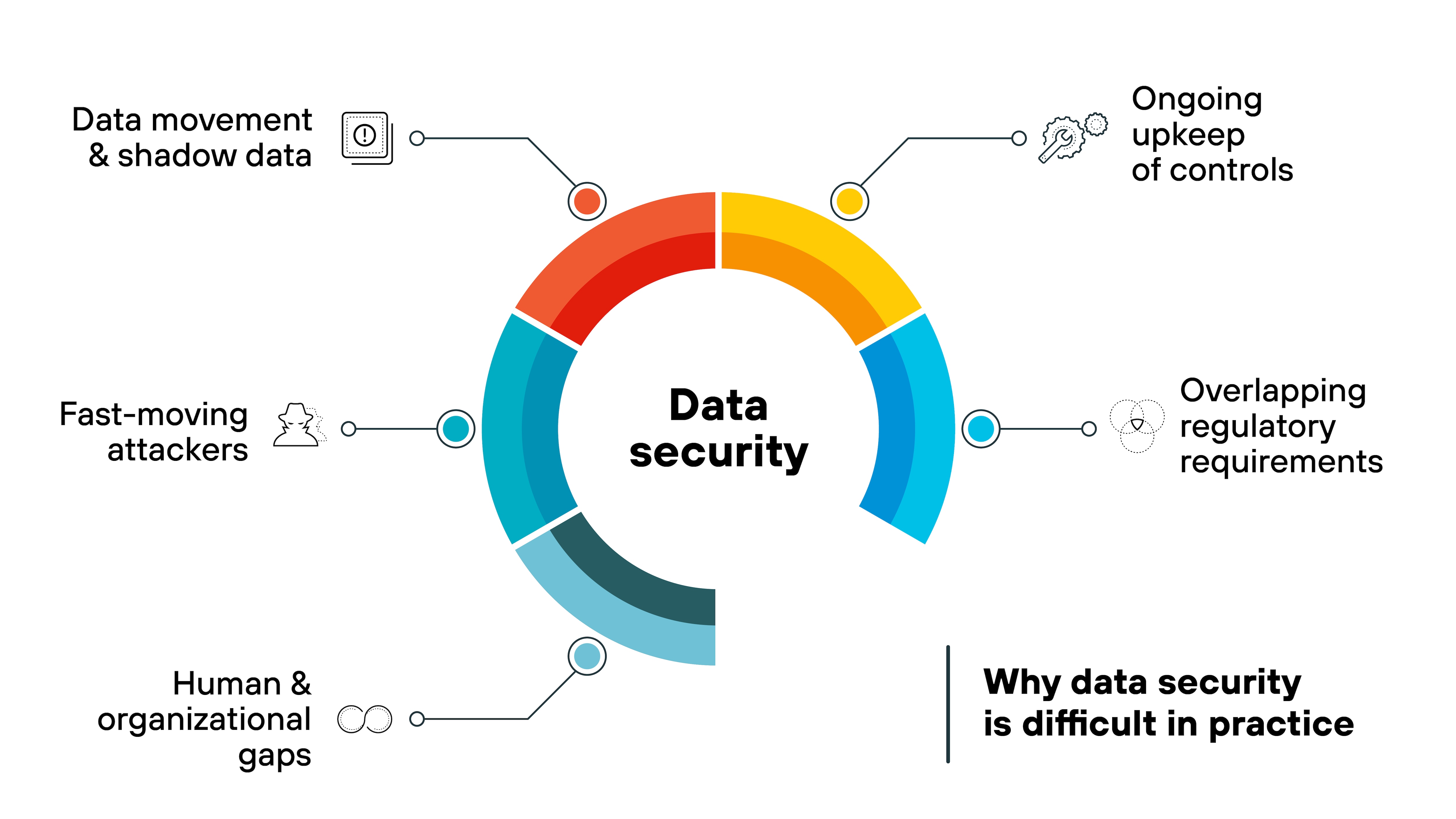
Data doesn't sit still.
It moves across SaaS apps, cloud storage, developer sandboxes, laptops, and vendor systems. New copies appear as teams export, transform, and test. Which means inventories drift.
Discovery tools help. But they lag when data is duplicated outside official workflows. That's where “shadow data” creeps in and breaks assumptions about coverage.
Controls depend on upkeep.
Encryption is only as strong as key handling. IAM only works if privileges match the job someone does today, not last quarter. Backups only help if they restore cleanly and within the window the business expects.
None of that is a one-time project. It's ongoing hygiene. And as systems and teams change, the effort compounds.
Requirements overlap.
Different data sets trigger different obligations. Customer records. Payment data. Health information. Each carries its own handling, retention, and reporting rules.
So organizations layer controls to satisfy multiple frameworks at once. The result can be operational friction: more policies to enforce, more audits to pass, more places a small gap can matter.
Attackers move fast.
Incidents aren't always slow burns. In a material share of cases, data is exfiltrated within hours of initial compromise. The median time to theft is often days, not weeks.
Which means detection and response timelines matter as much as preventive controls. If a control is misconfigured, there isn't much slack before it shows.
People create edges.
Real work happens in spreadsheets, exports, notebook snapshots, and test databases. Contractors need access. BYOD devices connect from anywhere.
Each exception adds a little risk. None looks dramatic on its own. Together they create blind spots that policy alone won't close.
In other words: the hard part isn't knowing what to do. It's keeping the right controls aligned with where the data actually lives, who can reach it, and how quickly things can go wrong.
What are the main approaches to data security?
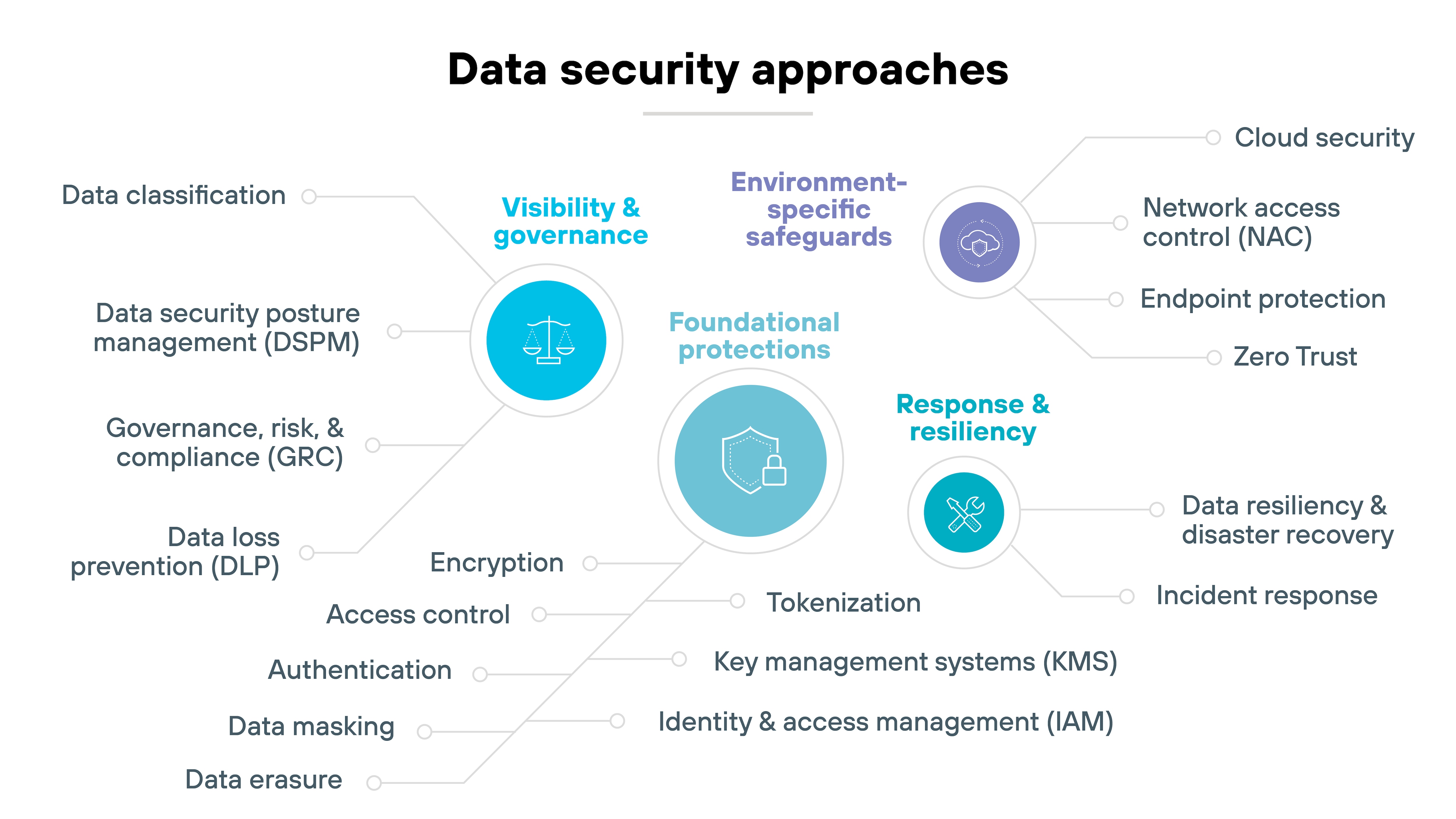
Foundational protections (basic controls every environment needs)
Foundational protections are the baseline of any data security program. They include methods like encryption, access rules, and authentication — along with the systems that keep those methods consistent at scale.
Encryption keeps information unreadable if stolen, but only works if keys are created and managed properly. Access control and authentication decide who can see or change data, while IAM ties those decisions to roles and reviews them over time.
Other measures, like masking or tokenization, reduce exposure when real data isn't needed, and secure erasure ensures information is gone when it's no longer required.
In short, these are the essential safeguards every environment needs before higher-level controls can be effective.
Visibility and governance (knowing where data is and how it's handled)
Visibility and governance make sure you actually know what data exists and how it's being used. Without that, protections are guesswork.
It starts with classification. Label information based on sensitivity and criticality, then tie those labels to policies so they mean something in practice.
From there, DLP monitors how data moves and blocks risky transfers. DSPM fills the cloud and SaaS gap, mapping shadow data that older tools can't see.
Finally, GRC frameworks connect all of this to regulations and internal rules so oversight stays consistent and defensible.
- What Is Data Discovery?
- What Is Data Classification?
- What Is Data Governance?
- What Is Data Access Governance?
- What Is DSPM?
- What Is DLP (Data Loss Prevention)? | Guide to DLP Security
Environment-specific safeguards (securing different layers of the enterprise)
Foundational protections aren't enough once data starts moving. Every device, network, and cloud platform adds new risks and new entry points for attackers.
Endpoints are the first line — laptops, phones, and servers need protection against malware and ransomware. NAC builds on that by deciding which devices can connect in the first place, though it can be tricky in BYOD or hybrid setups.
In the cloud, security focuses on stopping misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and data leaks.
And across everything, Zero Trust applies the rule of “never trust, always verify,” requiring constant checks to prevent lateral movement.
Together, these safeguards extend protection into the places where data actually lives and moves.
Response and resiliency (what to do when things go wrong)
Even strong defenses can't stop every incident. Data may still be lost, stolen, or corrupted. Response and resiliency measures limit the damage and get operations back on track.
Backups and disaster recovery ensure critical data can be restored after an outage or breach, but only if they're tested and reliable.
Incident response adds structure when something goes wrong — defining clear roles, coordinating technical and business teams, and guiding containment and remediation.
The goal is simple: Keep downtime and disruption to a minimum.
What regulations, standards, and frameworks guide data security?
Data security isn't guided by a single rulebook. Organizations are accountable to a mix of laws, standards, and frameworks that define how to protect sensitive information.
The specifics vary by industry and region. But the objectives are consistent:
- Safeguard business-critical and personal data.
- Ensure accountability in how data is collected, stored, and shared.
- Minimize the risk of breaches and other security incidents.
Compliance is more than meeting a checklist. It requires implementing technical and administrative safeguards — like encryption, access controls, and auditing — and maintaining them over time. Done well, compliance not only helps avoid penalties but also builds trust with customers and partners.
Below, we'll dive into the details of some of the most common data security regulations and frameworks:
| Data security regulations, standards, and frameworks |
|---|
| Category | Name | Description | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Law | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Protects personal data of EU citizens, requires consent for data processing, and enforces strict security measures. Violations can lead to fines of up to 4% of annual revenue or €20 million. | Organizations processing personal data of EU residents. |
| Law | California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) | Gives California residents control over their personal data, mandates transparency on data practices, and allows opt-out of third-party data sharing. | Businesses handling personal data of California residents. |
| Law | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) | Protects patient health data, ensures secure medical records, with penalties for non-compliance reaching up to $50,000 per violation. | U.S. healthcare providers, insurers, and business associates handling protected health information. |
| Law | Sarbanes–Oxley Act (SOX) | Mandates strict controls and audits for publicly traded companies over financial reporting systems to ensure data accuracy and security. | U.S. publicly traded companies responsible for financial reporting. |
| Standard | Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) | Sets security standards for organizations handling credit card transactions, requiring the protection of cardholder data and strong security against breaches and fraud. | Organizations processing, storing, or transmitting cardholder data. |
| Standard | ISO/IEC 27001 | Provides guidelines for implementing an information security management system (ISMS) to help reduce risks and protect sensitive information through best practices. | Organizations worldwide implementing an ISMS or seeking certification. |
| Framework | NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 | Defines risk-based outcomes across identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. Helps organizations prioritize and manage data security activities. | Organizations across industries aligning programs with risk-based outcomes. |
| Framework | NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 | Provides a detailed catalog of security and privacy controls to protect information systems and data. Supports confidentiality, integrity, and availability objectives. | U.S. federal agencies and organizations adopting NIST-based controls. |
| Framework | COBIT 2019 | Offers governance guidance linking enterprise goals with IT and data security objectives. Includes control objectives, performance monitoring, and compliance alignment. | Enterprises aligning IT governance with business and compliance requirements. |
| Framework | CIS Controls v8 | Provides prioritized, implementation-focused safeguards for securing data across endpoints, networks, and users. Offers a tactical roadmap for enforcing policy. | Organizations of all sizes adopting prioritized safeguards for practical data security. |
- What Is Data Compliance?
- What Is Data Privacy Compliance?
- What Is Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Compliance?
Comparing data security with related security domains
Data security is only one piece of a bigger puzzle. It overlaps with—but isn't the same as—privacy, protection, or broader security disciplines.
These terms are often used interchangeably, which creates confusion about scope and responsibility. Clarifying the differences makes it easier to see where data security fits and how it connects to adjacent domains.
The table below highlights where each domain starts, where it overlaps, and how they reinforce one another.
| Comparing data security with related security domains |
|---|
| Domain | Definition | Primary focus | Tools & methods | Overlap with data security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data security | Protects digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss throughout its lifecycle. | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. | Encryption, access control, DLP, key management. | Core subject — overlaps with all other domains where data is in scope. |
| Data privacy | Governs who can access and share personal or sensitive data, emphasizing user rights and consent. | Control over personal data handling and third-party use. | Consent management, anonymization, privacy impact assessments. | Privacy depends on security to enforce access and safeguard data. |
| Application security | Secures software applications by preventing vulnerabilities and attacks at the code, runtime, or API level. | Reducing exploitable flaws in apps that handle data. | Secure coding, code reviews, penetration testing, WAFs. | Protects the environments where data is processed and stored. |
| Cybersecurity | Broad discipline covering protection of systems, networks, and digital assets against cyber threats. | Defense of entire IT ecosystem against external and internal threats. | Firewalls, IDS/IPS, SIEM, threat intelligence. | Data security is one component of overall cybersecurity. |
| Data protection | Combines security and recovery practices to keep data safe, intact, and available. | Preventing unauthorized access and ensuring recoverability. | Encryption, backup, redundancy, compliance programs. | Data security is part of protection; protection adds availability and recovery. |
| Information security (InfoSec) | High-level discipline that governs security of all information assets, digital and physical. | Policies, governance, and controls across people, processes, and technology. | ISMS, security policies, audits, risk management frameworks. | Data security is a subset, focusing specifically on digital data. |