Next-gen CASB
- Why are CASBs important for businesses today?
- What are the four components of CASB?
- How does a CASB work?
- What are the benefits of a CASB?
- What are the primary CASB use cases?
- What are the different types of CASB deployment models?
- How to choose a CASB solution and what to look for
- How to implement a CASB in 6 steps
- What is the role of a CASB in SASE architecture?
- Comparing CASBs with other security technologies
- What is the history of CASB?
- CASB FAQs
What Is a CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker)? | 101 Guide
- Why are CASBs important for businesses today?
- What are the four components of CASB?
- How does a CASB work?
- What are the benefits of a CASB?
- What are the primary CASB use cases?
- What are the different types of CASB deployment models?
- How to choose a CASB solution and what to look for
- How to implement a CASB in 6 steps
- What is the role of a CASB in SASE architecture?
- Comparing CASBs with other security technologies
- What is the history of CASB?
- CASB FAQs
- 1. Why are CASBs important for businesses today?
- 2. What are the four components of CASB?
- 3. How does a CASB work?
- 4. What are the benefits of a CASB?
- 5. What are the primary CASB use cases?
- 6. What are the different types of CASB deployment models?
- 7. How to choose a CASB solution and what to look for
- 8. How to implement a CASB in 6 steps
- 9. What is the role of a CASB in SASE architecture?
- 10. Comparing CASBs with other security technologies
- 11. What is the history of CASB?
- 12. CASB FAQs
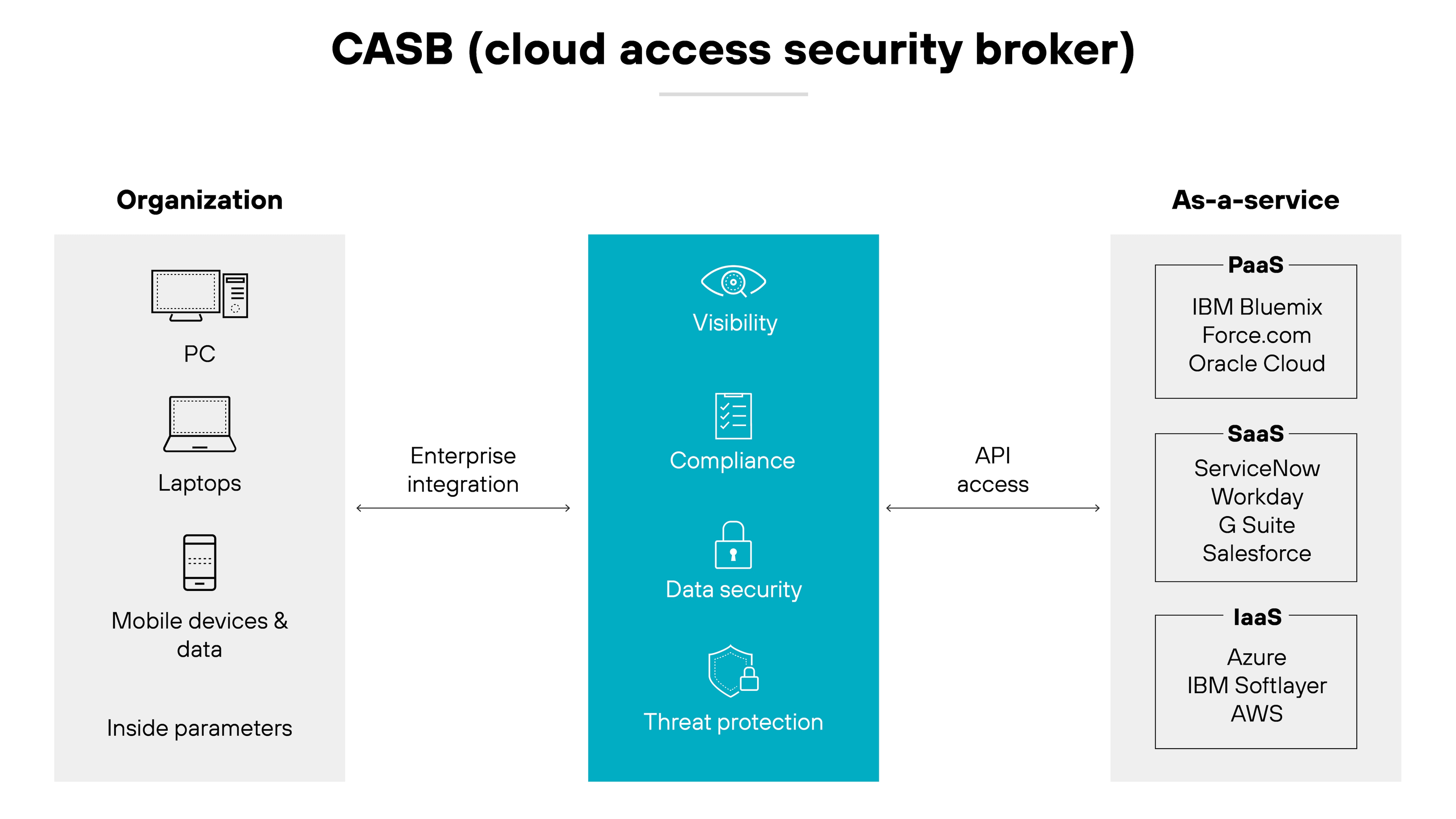
A cloud access security broker (CASB) is a security tool that acts as an intermediary between an organization's on-premises infrastructure and cloud service providers. It extends security measures to the cloud, enforcing policies and providing visibility into cloud application usage.
CASBs operate across various cloud models: software-as-a-service (SaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS).
They protect organizational data by managing security functions like authentication, authorization, and encryption.
Why are CASBs important for businesses today?
CASBs are important for businesses today because with the vast adoption of cloud services, businesses face majorly increased security vulnerabilities.
A little less than one third of cases (29%) in 2024 were cloud-related. This means that our investigation involved collecting logs and images from a cloud environment or touched on externally hosted assets such as SaaS applications.
Those cases don’t necessarily represent the situations in which threat actors are doing damage to cloud assets. We see this in about one in five cases in 2024 (21%), where threat actors adversely impacted cloud environments or assets."
CASBs provide a critical layer of security that ensures enterprise data—whether in transit or at rest—remains secure across cloud platforms and applications.

Here’s why this matters:
Traditional network security measures like firewalls are less effective outside the physical data center.
Plus: The rise of remote work and BYOD policies expands the potential for insecure app usage, AKA shadow IT.

CASBs address these risks by offering features like shadow IT control and cloud data loss prevention (DLP).
This enables businesses to maintain stringent security standards while adopting flexible and mobile working practices.
Not to mention, cloud environments come with the shared responsibility model we all know and love:
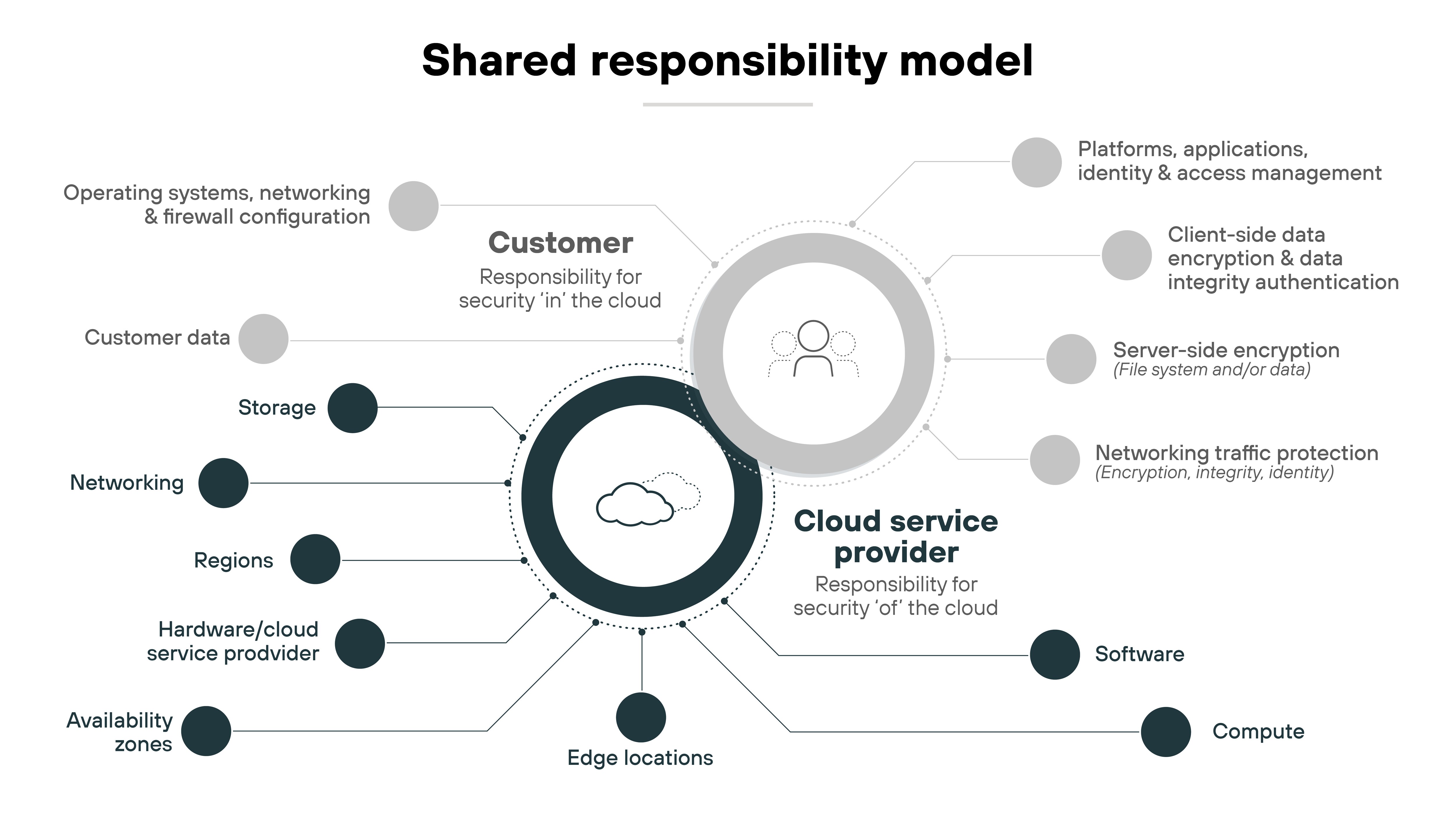
The shared responsibility model leaves certain security obligations to the user.
CASBs help businesses fulfill these responsibilities by enhancing visibility and control over cloud resources.
And that’s important for compliance and protecting against sophisticated cyber threats.
In essence, CASBs matter because they allow businesses to extend the security perimeter to the cloud seamlessly and effectively—which leads to the safe and compliant use of cloud applications.
What are the four components of CASB?
The four components of CASB include:
Visibility
Data security
Threat protection
Compliance
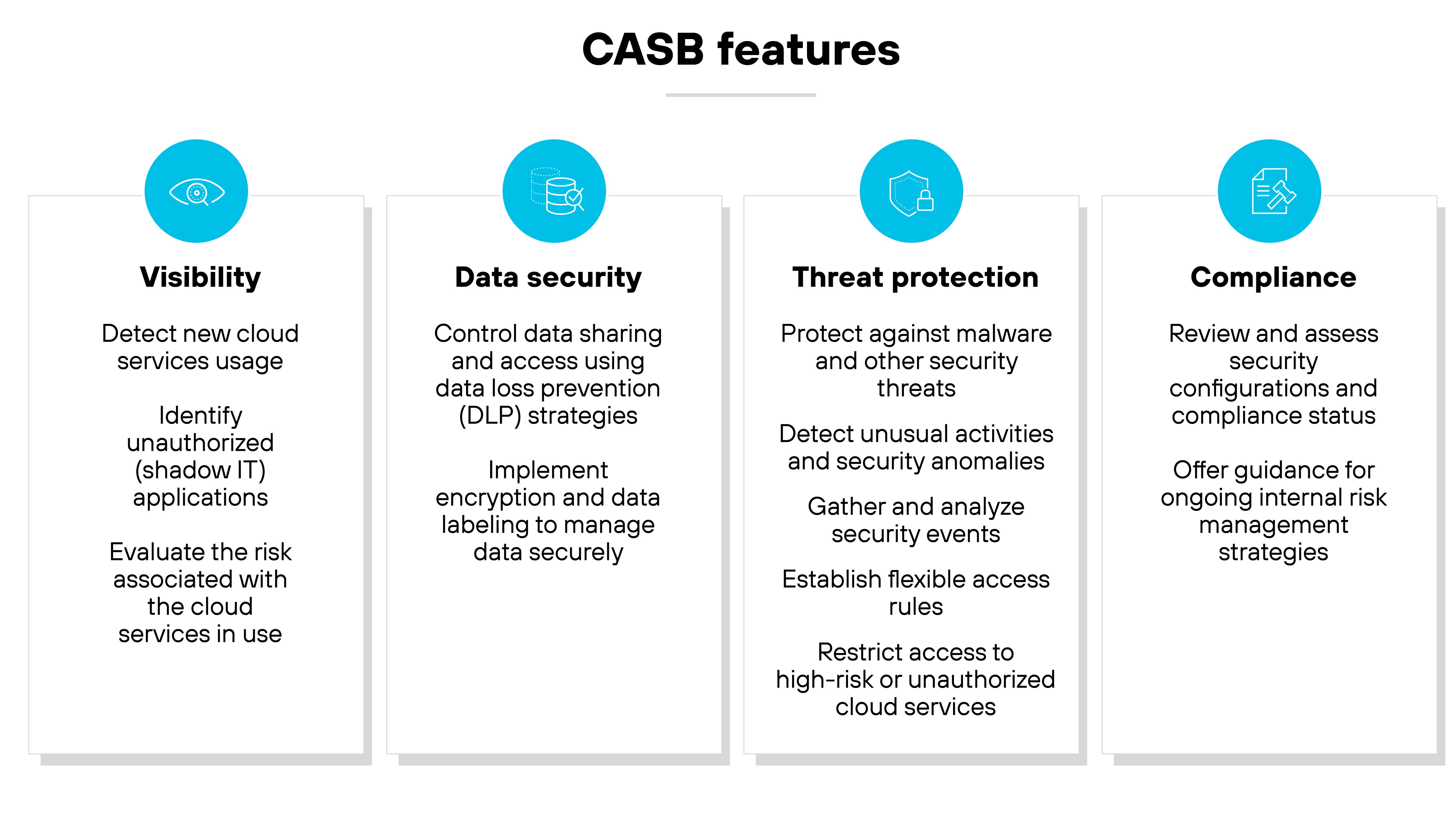
Let’s break down the four main components that make CASBs essential in detail:
Visibility: Visibility is the starting point for effective cloud security. CASBs provide a panoramic view of all cloud services in use within an organization, shedding light on shadow IT. And that allows IT teams to see which cloud applications are being accessed and by whom, which means more informed policy decisions and risk assessments.
Compliance: Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory requirements becomes more manageable with a CASB. A CASB makes it way easier for the security team to be certain that cloud data handling complies with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. CASBs automate compliance tasks, reducing the burden on IT teams and helping prevent costly penalties for non-compliance.
Data security: Protecting sensitive data is a core function of CASBs. They extend traditional security measures into the cloud, implementing controls such as access restrictions and data loss prevention (DLP) to safeguard data in transit and at rest. This not only prevents data leaks but also enhances the overall integrity of data across cloud platforms.
- Threat protection: CASBs are equipped to defend against both internal and external threats. By analyzing usage patterns and detecting anomalies, they can identify potential security incidents before they escalate. This proactive threat management includes everything from malware defense to spotting risky user behaviors, ensuring comprehensive security coverage.
How does a CASB work?
A CASB works through a strategic process to ensure robust security across an organization’s cloud environment.
Here’s a breakdown of how CASBs typically work:
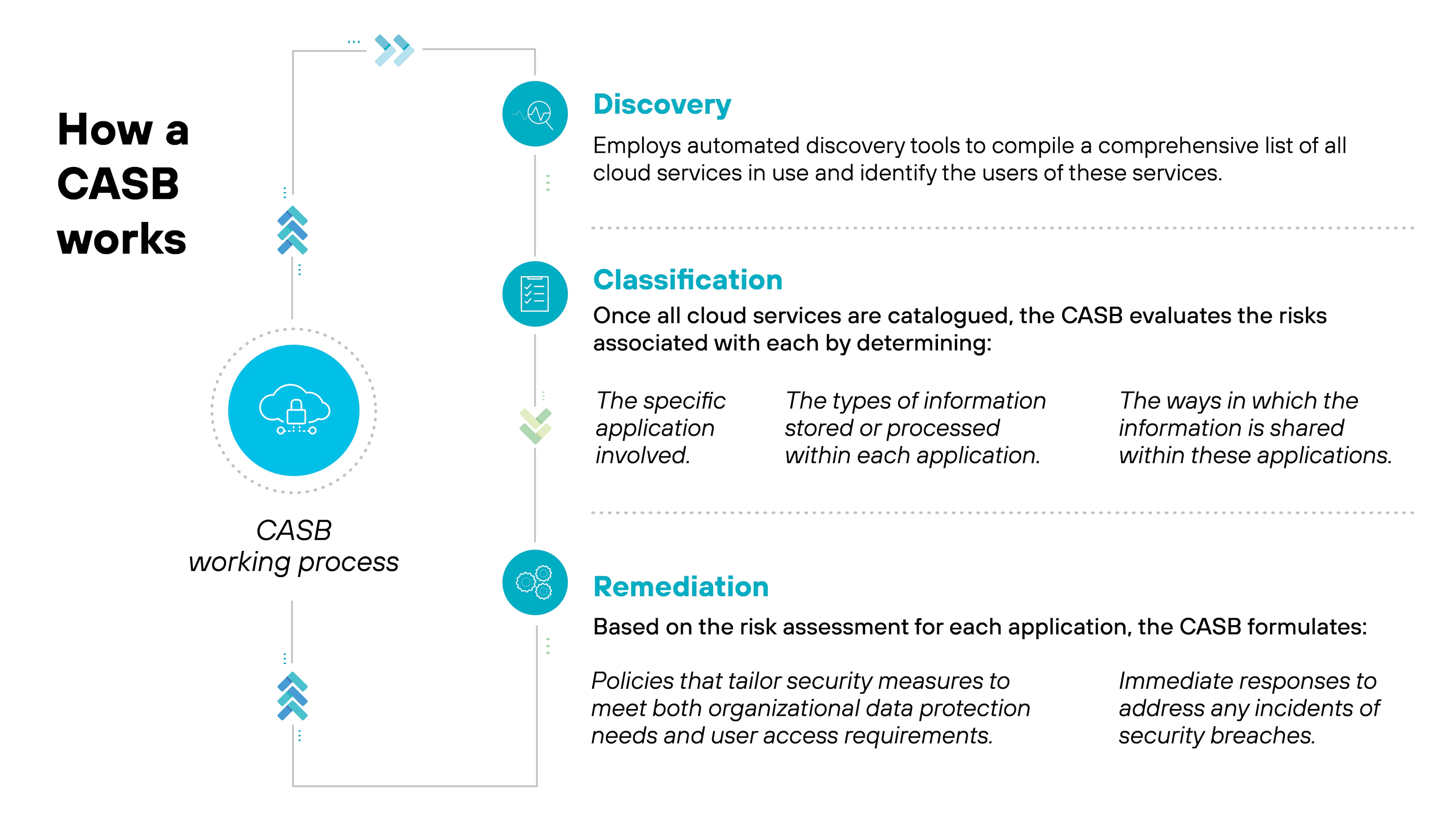
- Discovery: The first step involves identifying all cloud applications being used within the organization. This includes sanctioned apps as well as shadow IT—applications not officially sanctioned by the organization. By employing auto-discovery technologies, a CASB can catalog all cloud services accessed, pinpointing potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Classification: After discovery, the next phase is to assess the risk associated with each identified cloud service. A CASB evaluates the types of data stored and shared within these applications and the security measures they employ. This step helps determine the security posture of each application and how it aligns with the organization's compliance and governance standards.
- - Remediation: Based on the risk assessment, the CASB then enforces appropriate security policies to manage and mitigate risks. This includes implementing access controls, enforcing data protection measures like encryption, and providing real-time threat protection. If any activity or data movement violates the set policies, the CASB can automatically take corrective actions, such as blocking risky transactions or alerting security personnel.
Essentially, CASBs integrate various security functions—such as threat prevention, compliance management, and data security—into a single solution that spans multiple cloud services.
A unified approach simplifies cloud application security management.
It also makes protecting sensitive information and maintaining compliance in a dynamic cloud environment way more reasonably achievable.
What are the benefits of a CASB?
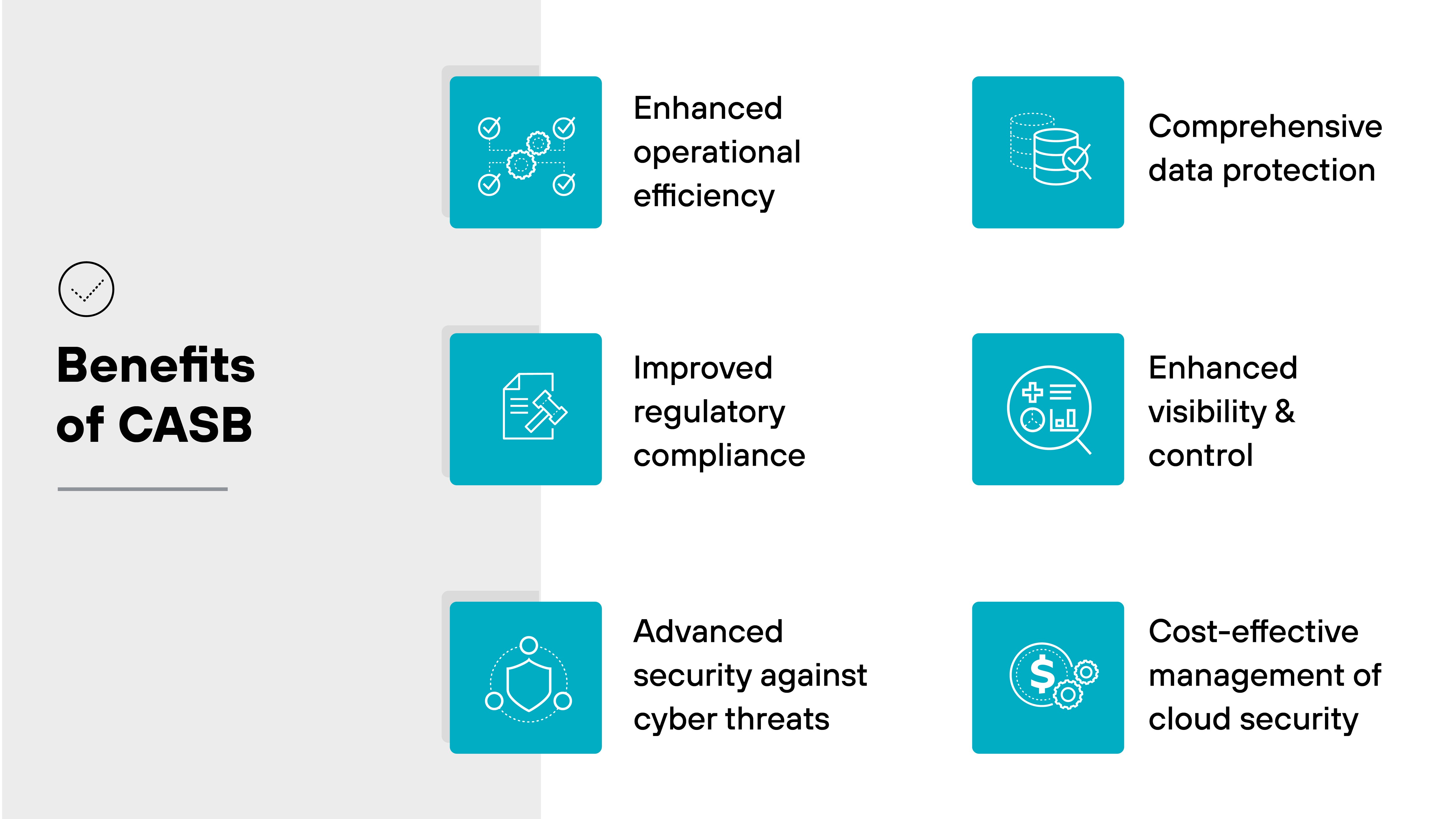
Implementing a cloud access security broker (CASB) brings plenty of advantages to organizations navigating the complexities of cloud security.
Here’s how CASBs benefit businesses:
Enhanced operational efficiency: CASBs integrate multiple security functions into a single platform, which streamlines cloud security management. The consolidation reduces the complexity and costs associated with managing disparate security tools, which simplifies the security management lifecycle.
Improved regulatory compliance: CASBs ensure organizations meet stringent regulatory standards for data protection. By applying uniform security policies across all cloud services, businesses can maintain compliance automatically. And that reduces the risk of costly penalties.
Advanced security against cyber threats: CASBs offer proactive threat protection with sophisticated behavior analytics and anomaly detection. They safeguard against both internal and external threats, preventing unauthorized access and other cyber risks in real-time.
Comprehensive data protection: By extending robust data security measures like encryption and access controls to the cloud, CASBs ensure sensitive data is protected both in transit and at rest. They enforce DLP to prevent data exfiltration and leaks. Which ultimately secures critical data.
Enhanced visibility and control: CASBs provide deep visibility into cloud application usage within an organization, including the detection and management of shadow IT. This way, security teams can better manage security risks by enforcing consistent security policies across all cloud resources.
Cost-effective management of cloud security: By consolidating security measures into a unified platform, CASBs reduce the overhead and complexity associated with multiple security solutions. And that cuts costs and improves the effectiveness of security measures across cloud environments.
What are the primary CASB use cases?
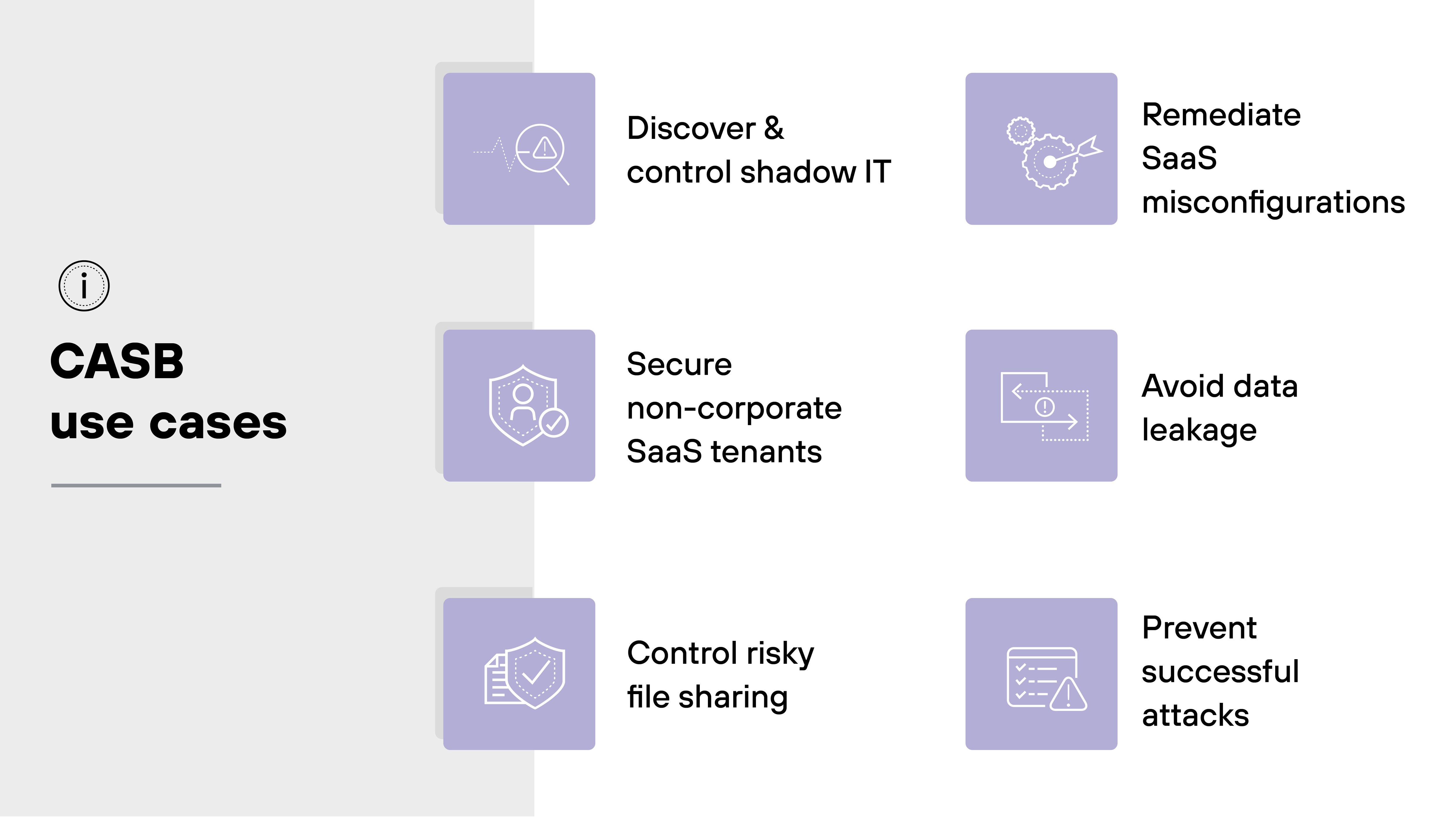
A CASB is a critical tool when it comes to managing and securing an organization's use of cloud services.
Below are some of the primary use cases where CASBs provide the biggest benefits:
Discover and control shadow IT
Secure non-corporate SaaS tenants
Control risky file sharing
Remediate SaaS misconfigurations
Prevent data leakage
Prevent successful attacks
Discover and control shadow IT
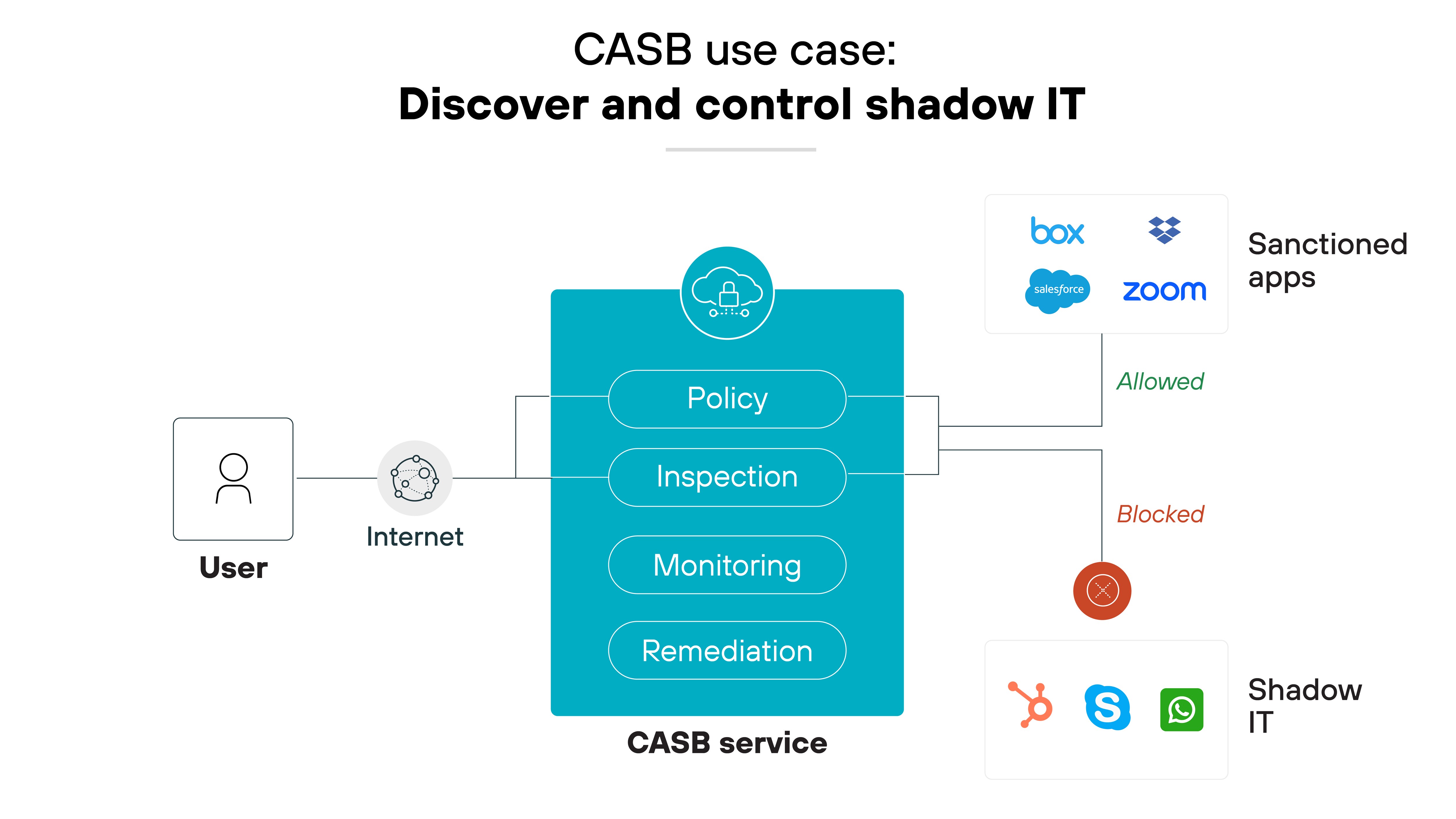
Again: CASBs are instrumental in identifying and managing shadow IT.
By automatically discovering these apps, CASBs help IT teams understand and secure cloud usage by applying policies that can allow, block, or restrict activities based on the organization’s security protocols.
This not only enhances visibility but also mitigates the risks associated with unauthorized app usage.
Secure non-corporate SaaS tenants
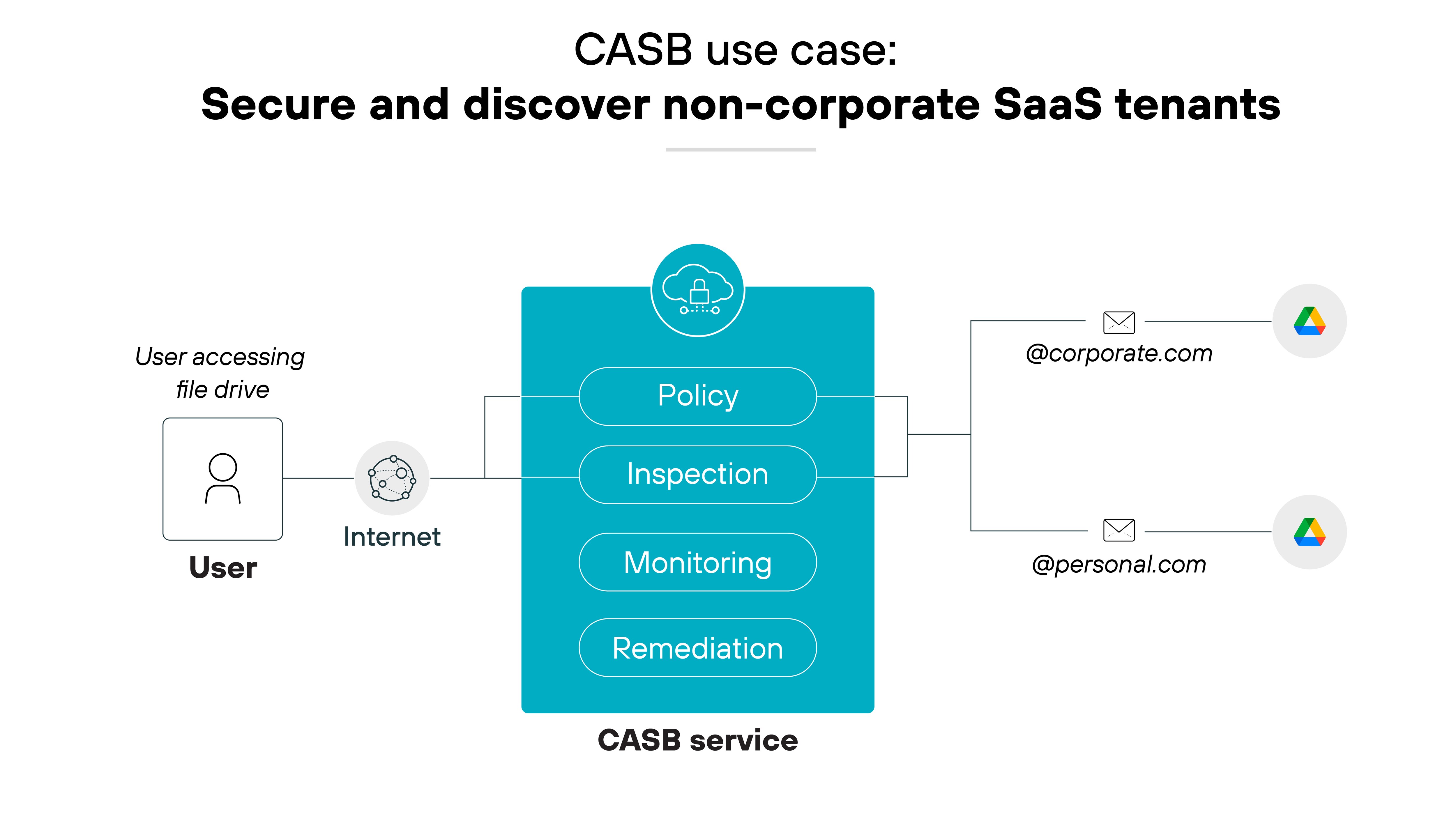
In environments where users may access both sanctioned and unsanctioned instances of applications like Google Drive, CASBs distinguish between these instances and apply appropriate security measures.
This capability allows security teams to protect organizational data without hindering productivity. Which leads to a balanced approach to cloud application security.
Control risky file sharing
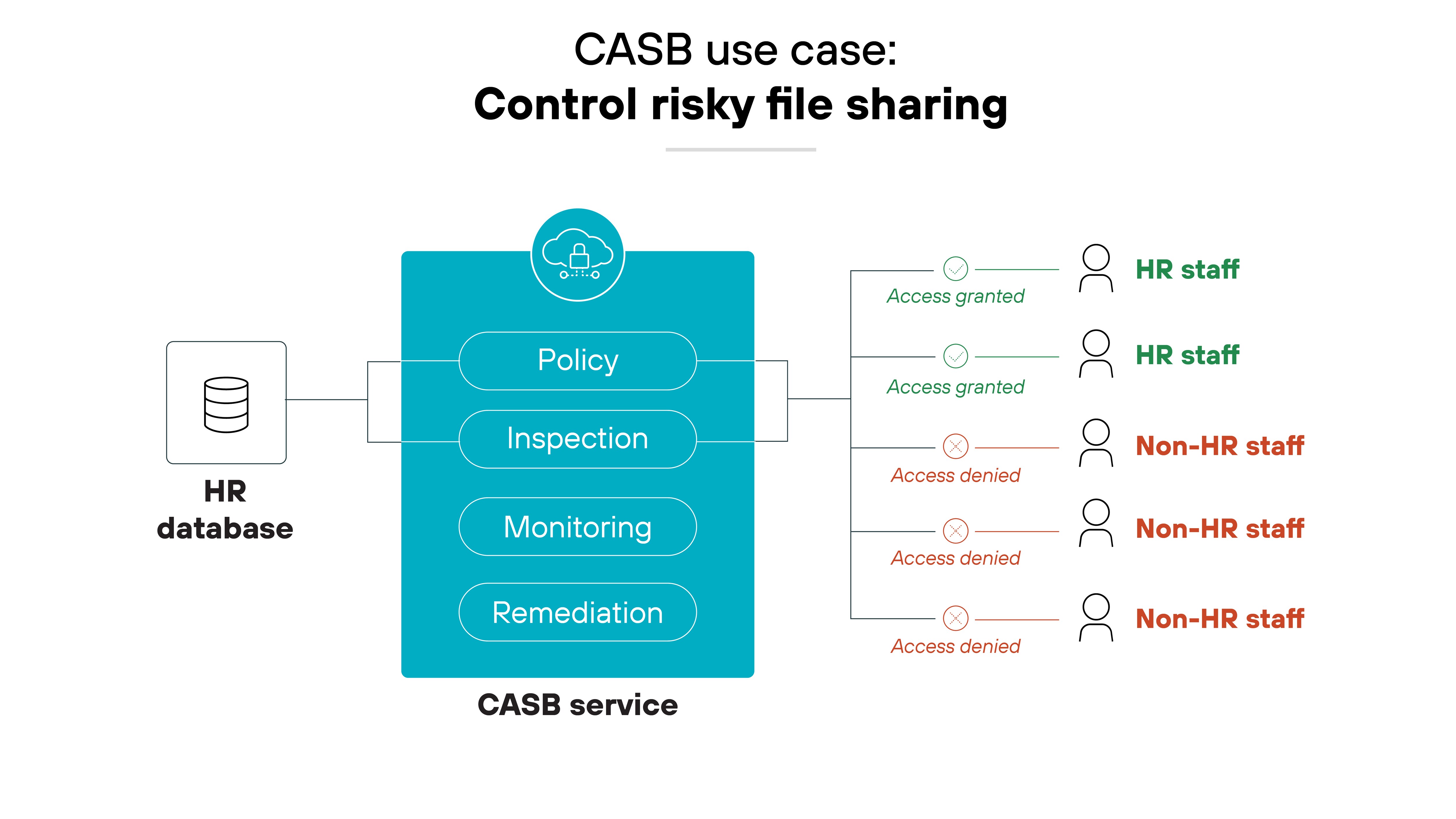
Cloud applications enable unprecedented levels of sharing and collaboration.
CASBs manage this by monitoring who is sharing what within sanctioned applications and reacting to any shares that pose a risk.
This particular control is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and for maintaining compliance with data protection regulations.
Remediate SaaS misconfigurations
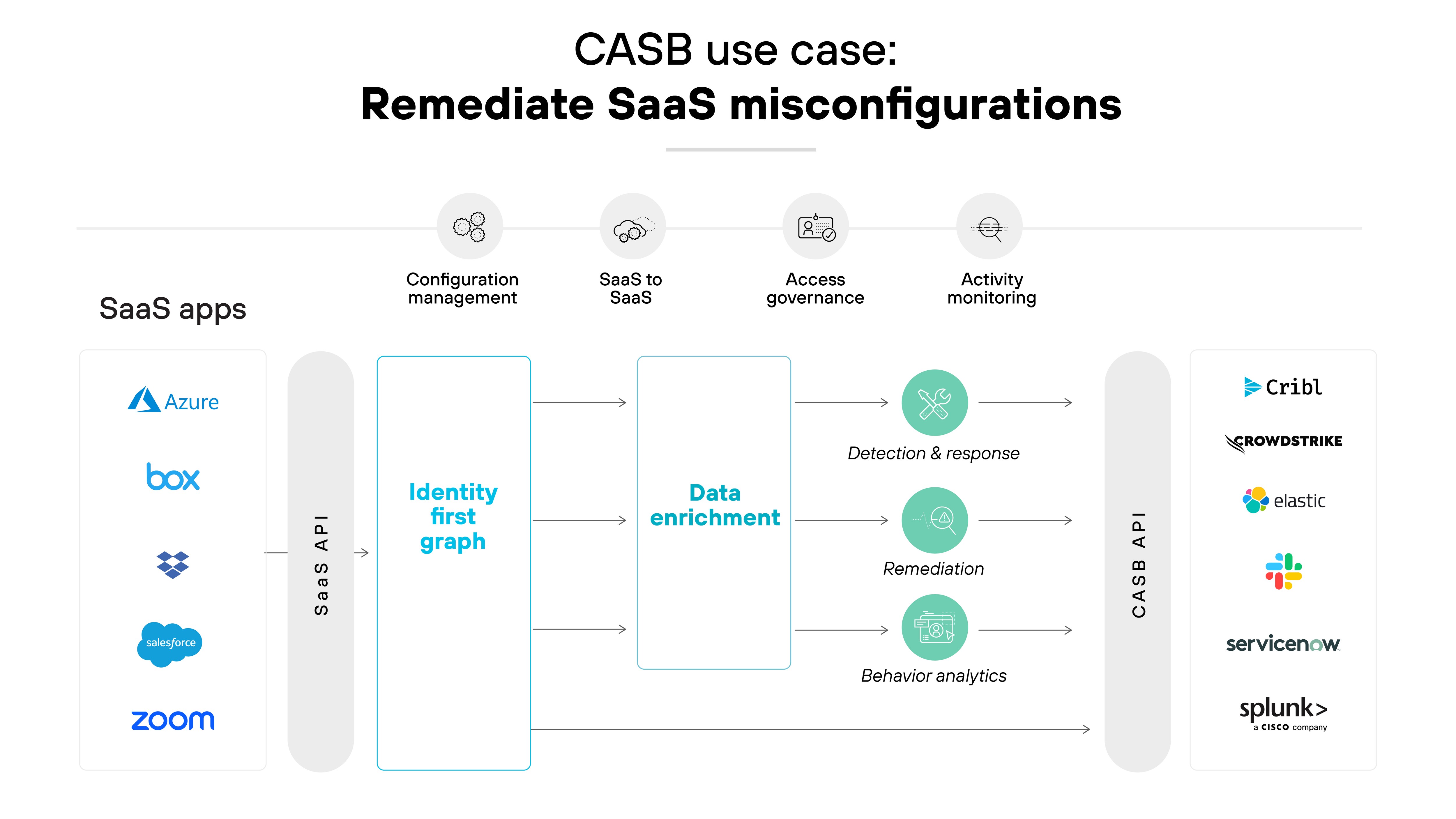
Misconfigurations in cloud applications can lead to significant security risks.
CASBs provide continuous monitoring and automatic remediation of such misconfigurations. Which means that cloud services are not correctly configured and compliant.
Prevent data leakage
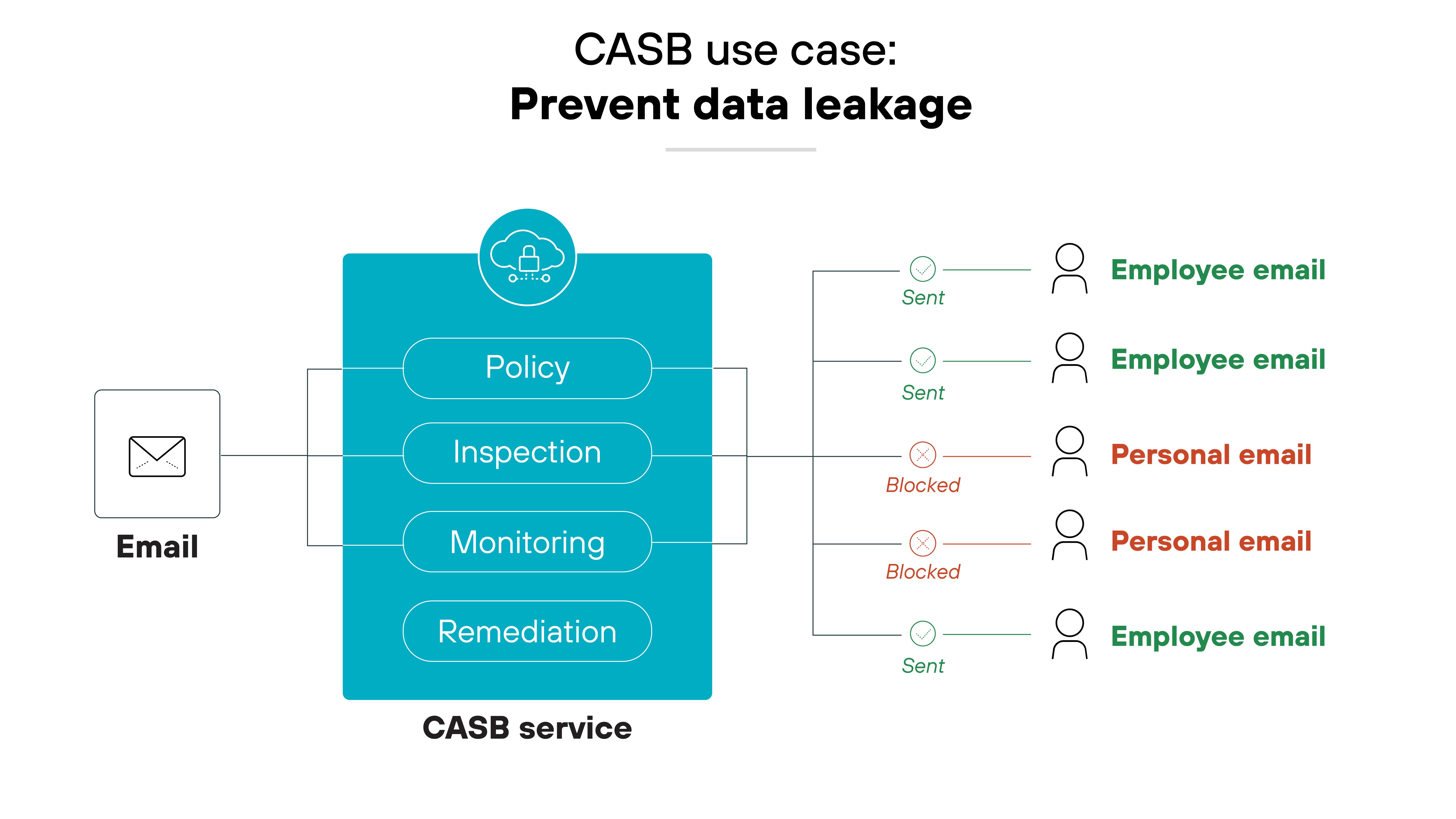
By integrating with cloud services, CASBs enforce DLP policies that monitor and control sensitive data patterns in the cloud.
This function is essential in preventing data breaches and adhering to compliance regulations.
Prevent successful attacks
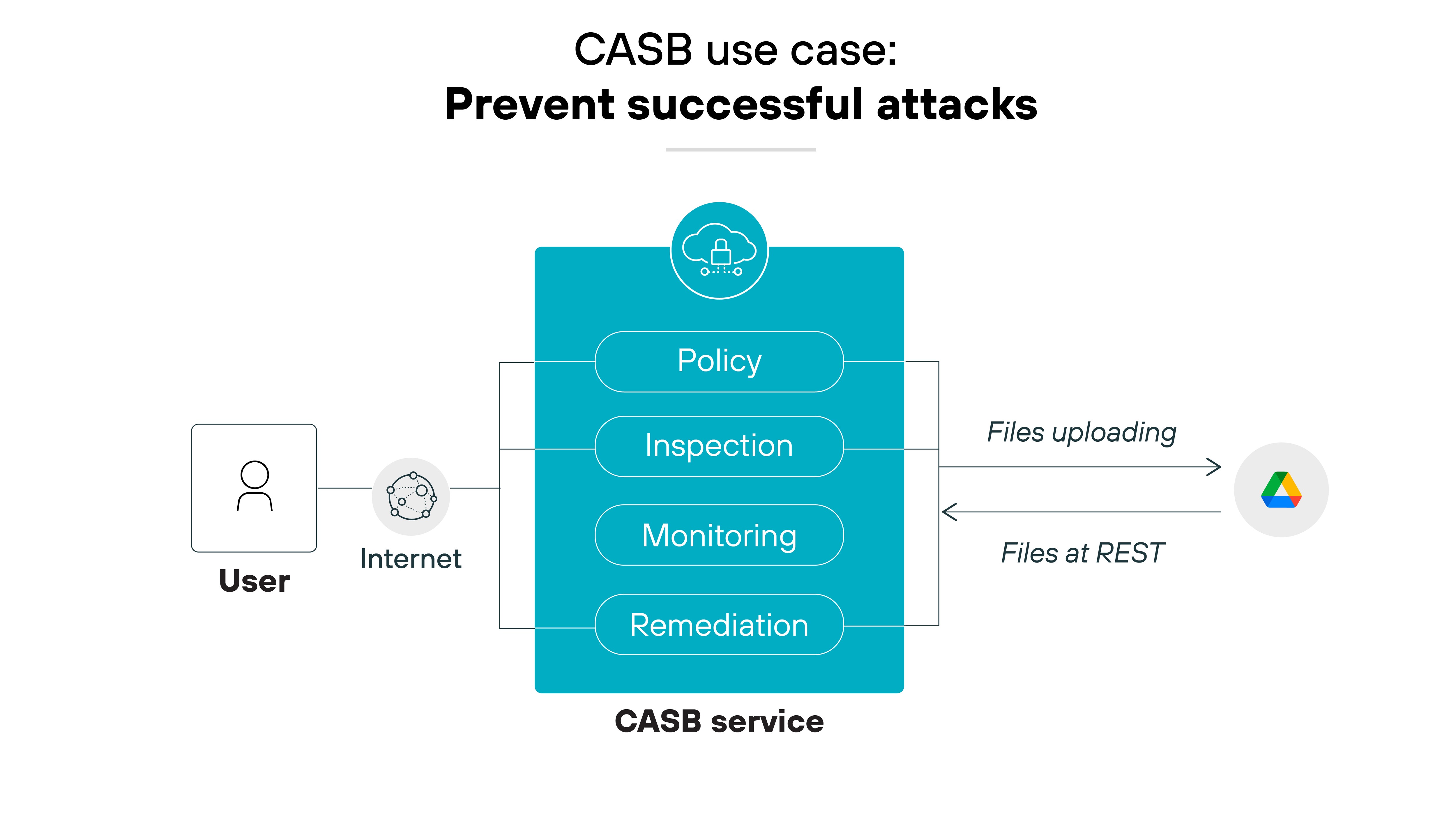
CASBs protect against malware and other cyber threats in real time by scanning files at upload and at rest. They do this with advanced threat protection mechanisms.
This includes real-time and out-of-band scanning, cloud sandboxing, and isolating browsing sessions from unmanaged endpoints to secure access and prevent data breaches.
What are the different types of CASB deployment models?
CASBs offer various deployment models to fit the diverse security needs and architectural preferences of organizations.
Each CASB model has distinct features that cater to specific security, compliance, and performance requirements, including:
API-based CASB deployment
Proxy-based CASB deployment
Hybrid CASB deployment
API-based deployment
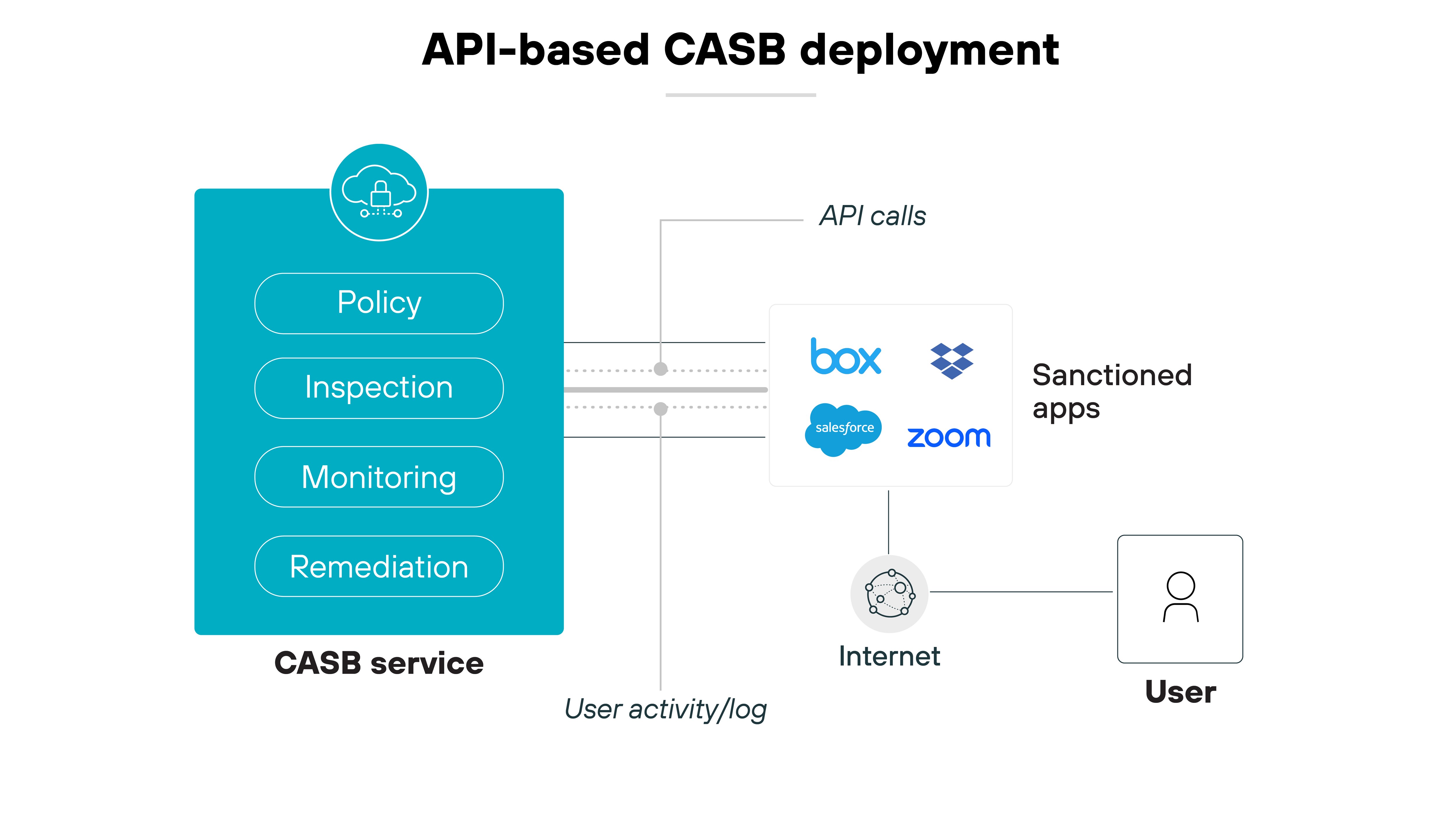
API-based CASBs integrate directly with cloud service providers (CSPs) using their application programming interfaces (APIs).
This method allows the CASB to monitor and control interactions between users and cloud services seamlessly. It's effective for continuous monitoring and retroactive adjustments in cloud environments.
Organizations tend to prefer this model for its minimal impact on user experience and its ability to enforce security policies and compliance without redirecting web traffic.
However: It may not provide real-time data protection or threat mitigation.
Proxy-based deployment
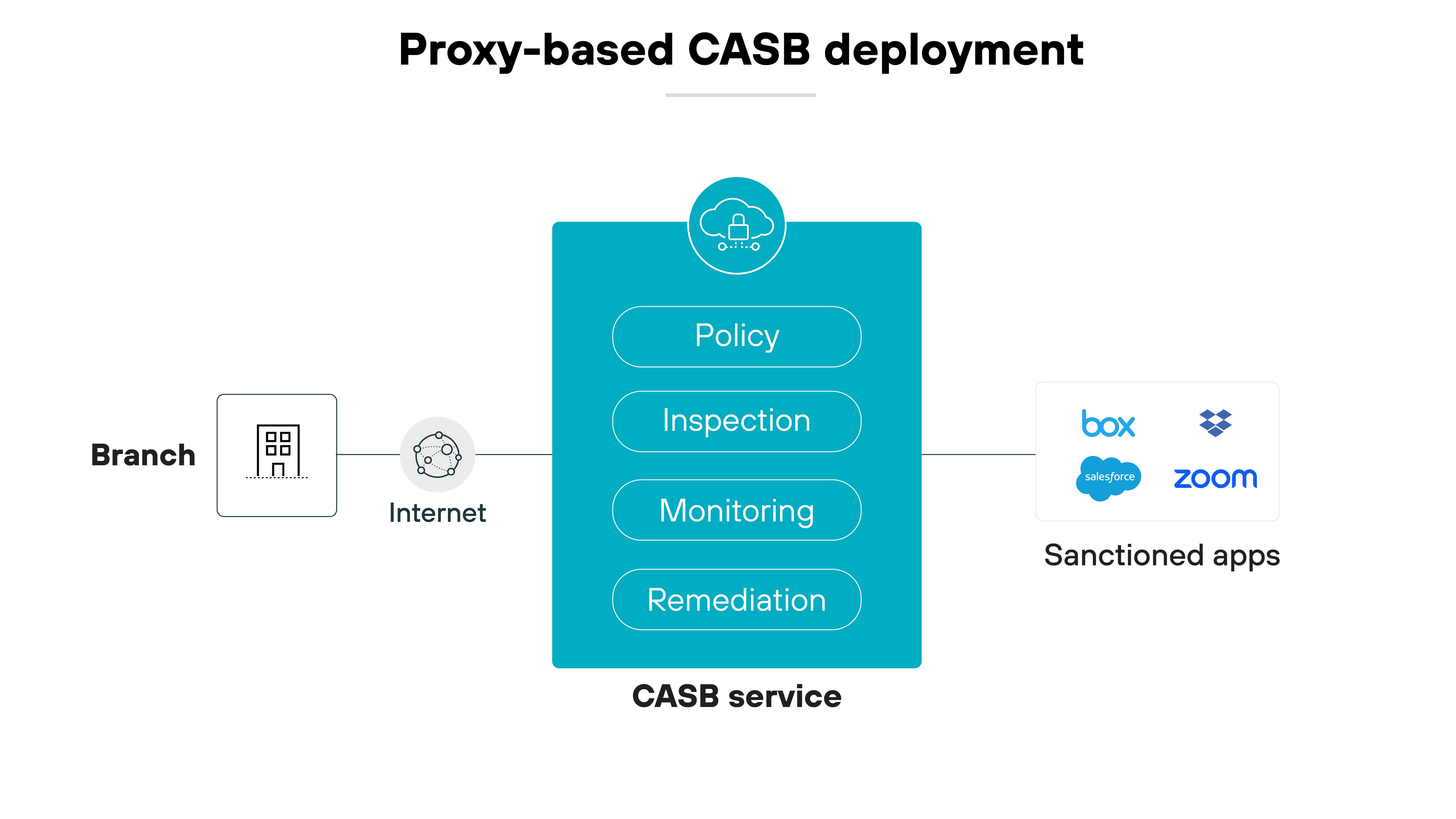
Proxy-based CASBs route user traffic through the CASB to enforce security policies in real time.
This can be set up as either a forward proxy—which directs outbound traffic from users to the cloud—or as a reverse proxy—which manages requests coming from the internet to the cloud service.
This model offers immediate threat prevention and deep visibility into data in transit.
On the other hand: It can introduce latency and requires significant network configuration to ensure seamless user experiences.
Hybrid deployment

The hybrid model combines API and proxy-based approaches, offering a balance of real-time data protection and post-event compliance enforcement.
This model provides comprehensive security coverage. So organizations can rely on the instant control of proxy-based methods and the extensive coverage of API-based methods.
Hybrid deployments are particularly valuable for organizations that require robust security without compromising on the flexibility of cloud operations or user experience.
How to choose a CASB solution and what to look for
Choosing a cloud access security broker (CASB) solution requires evaluating its ability to secure cloud applications, enforce policies, and protect data.
CASBs have evolved to address complex cloud security challenges, offering visibility, control, and threat protection across distributed environments.
The right CASB should align with your organization's security priorities while ensuring consistent protection across SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS applications.
Here’s what you should think about when selecting a CASB for your organization:
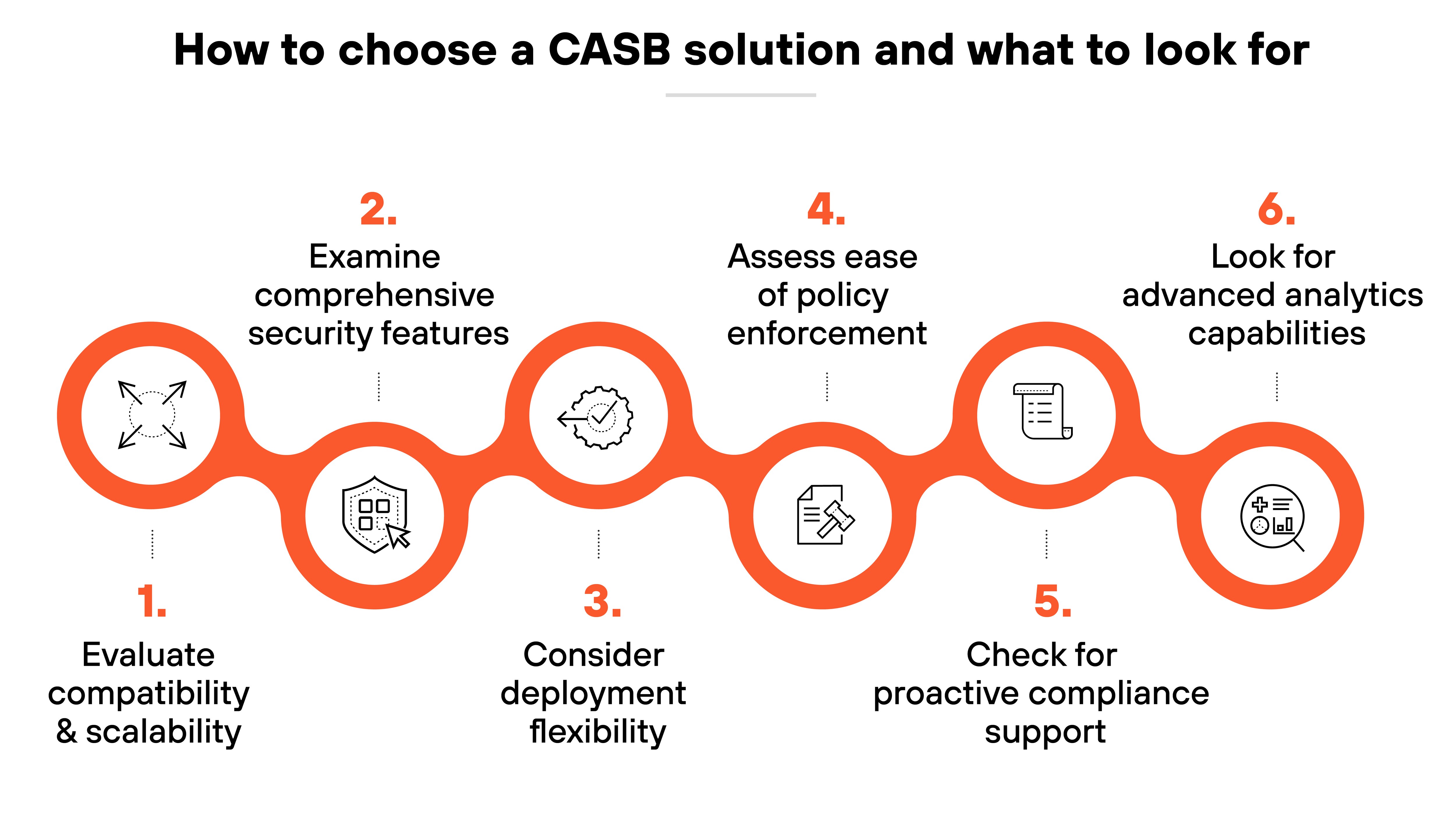
Evaluate compatibility and scalability: Ensure the CASB can integrate seamlessly with your existing security infrastructure and scale as your organization grows. It should support your current and future cloud environments, adapting to changes in your security needs without compromising performance.
Examine comprehensive security features: A good CASB should offer robust security capabilities, including real-time threat detection, data protection, and compliance management. Look for solutions that provide detailed visibility and control over both sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud applications, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Consider deployment flexibility: Choose a CASB that offers flexible deployment options that suit your specific operational requirements. Whether it's on-premises, cloud, or hybrid models, the right CASB should enhance your security without necessitating major changes to your existing workflows.
Assess ease of policy enforcement: The CASB you choose should facilitate straightforward policy management and enforcement. This includes automating compliance tasks and simplifying the creation and maintenance of security policies across various cloud services and applications.
Check for proactive compliance support: Select a CASB that proactively updates and manages your cloud security and compliance policies. It should keep pace with the latest regulatory changes and ensure your organization remains compliant with industry standards.
- Look for advanced analytics capabilities: Opt for a CASB that offers advanced analytical tools to monitor and evaluate user behaviors and activities across cloud services. This helps in identifying potential security threats and mitigating risks before they escalate.
How to implement a CASB in 6 steps
Now that we’ve established why implementing a CASB effectively enhances your organization's cloud security posture through a structured approach, let’s talk about how to do it.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the implementation steps involved in deploying a CASB:
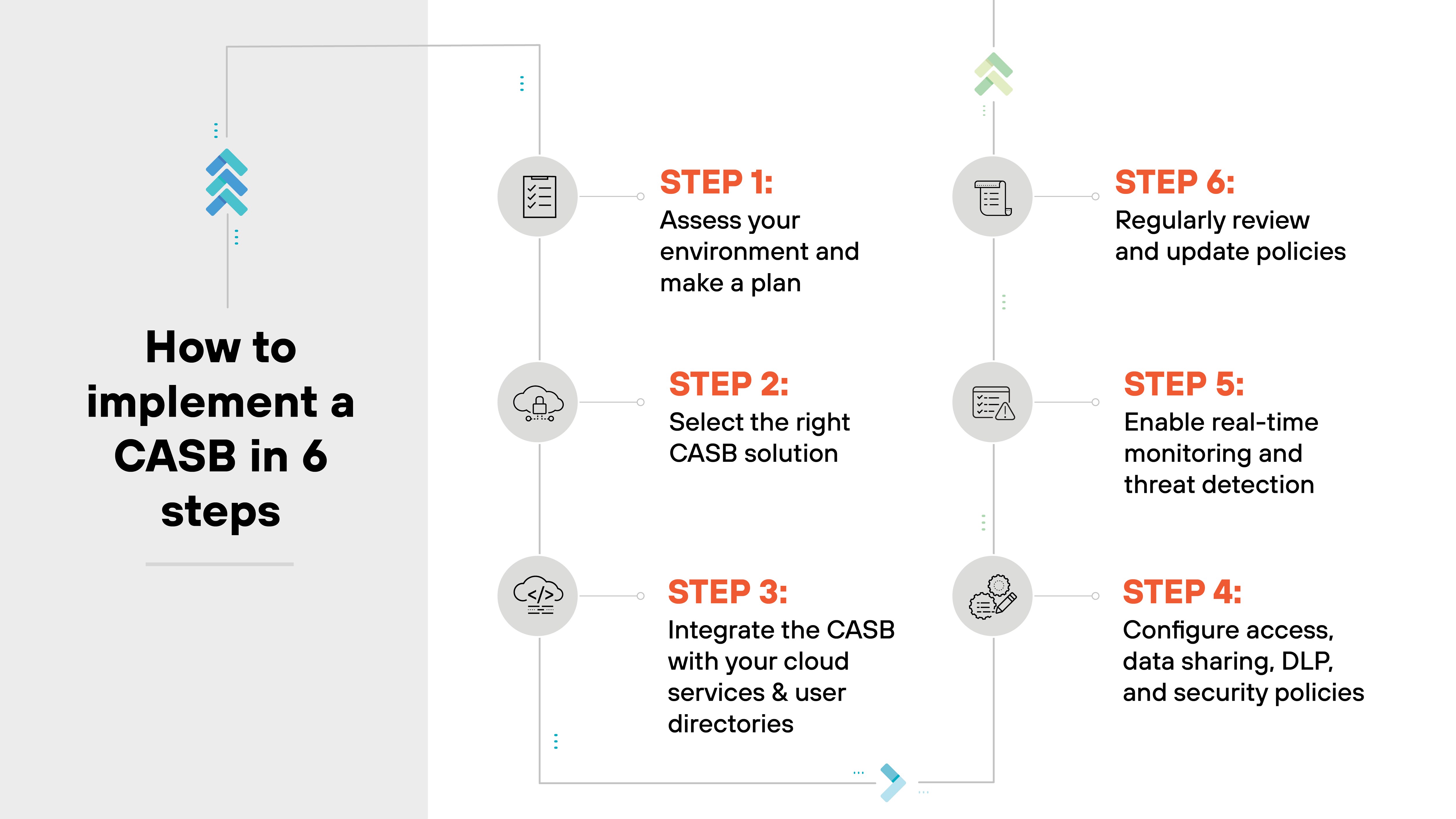
Step 1: Assess your environment and make a plan
The first step is to conduct a thorough assessment of your current cloud environment:
Identify all cloud services in use
Understand the data flows
Pinpoint potential security vulnerabilities
Develop a clear understanding of your security and compliance requirements, which will guide the selection and configuration of your CASB solution.
Step 2: Select the right CASB solution
Choosing the appropriate CASB solution is crucial.
Evaluate different CASB offerings based on:
Compatibility with your cloud infrastructure
Security features they offer
Ease of integration with your existing IT environment
Consider factors like real-time threat protection capabilities, compliance support, and the level of granularity in visibility and control.
Step 3: Integrate the CASB with your cloud services and user directories
Integration is key to ensuring that your CASB functions seamlessly with your existing cloud applications and IT policies.
This involves configuring the CASB to work with your cloud service providers and aligning it with your user authentication systems, like single sign-on (SSO) or Active Directory.
Proper integration is what really enables the CASB to accurately monitor traffic and enforce security policies.
Step 4: Configure access, data sharing, DLP, and security policies
With the CASB integrated, the next step is to set up the necessary security policies.
This includes configuring access controls to manage who can use cloud services and what data they can access.
Implement DLP policies to protect sensitive information and configure sharing settings to prevent unauthorized data exposure.
Step 5: Enable real-time monitoring and threat detection
Activate the CASB’s monitoring and threat detection capabilities to continuously oversee and protect your cloud environment. This includes setting up alerts for unusual activities and potential security breaches.
Regularly review and adjust the CASB’s settings based on evolving security needs and emerging threats to maintain robust cloud security.
Step 6: Regularly review and update policies
Cloud environments are dynamic, with new services being adopted and existing ones being updated frequently.
Regularly review your CASB settings and policies to ensure they remain effective against new threats and compliant with updated regulations. The ongoing evaluation helps in adapting to the changing cloud landscape and maintaining a strong security posture.
What is the role of a CASB in SASE architecture?
In SASE architecture, a cloud access security broker is essential for extending security policies beyond the traditional perimeter to cloud applications.
It ensures consistent security across both on-premises and cloud environments. The integration is critical as organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid IT infrastructures.
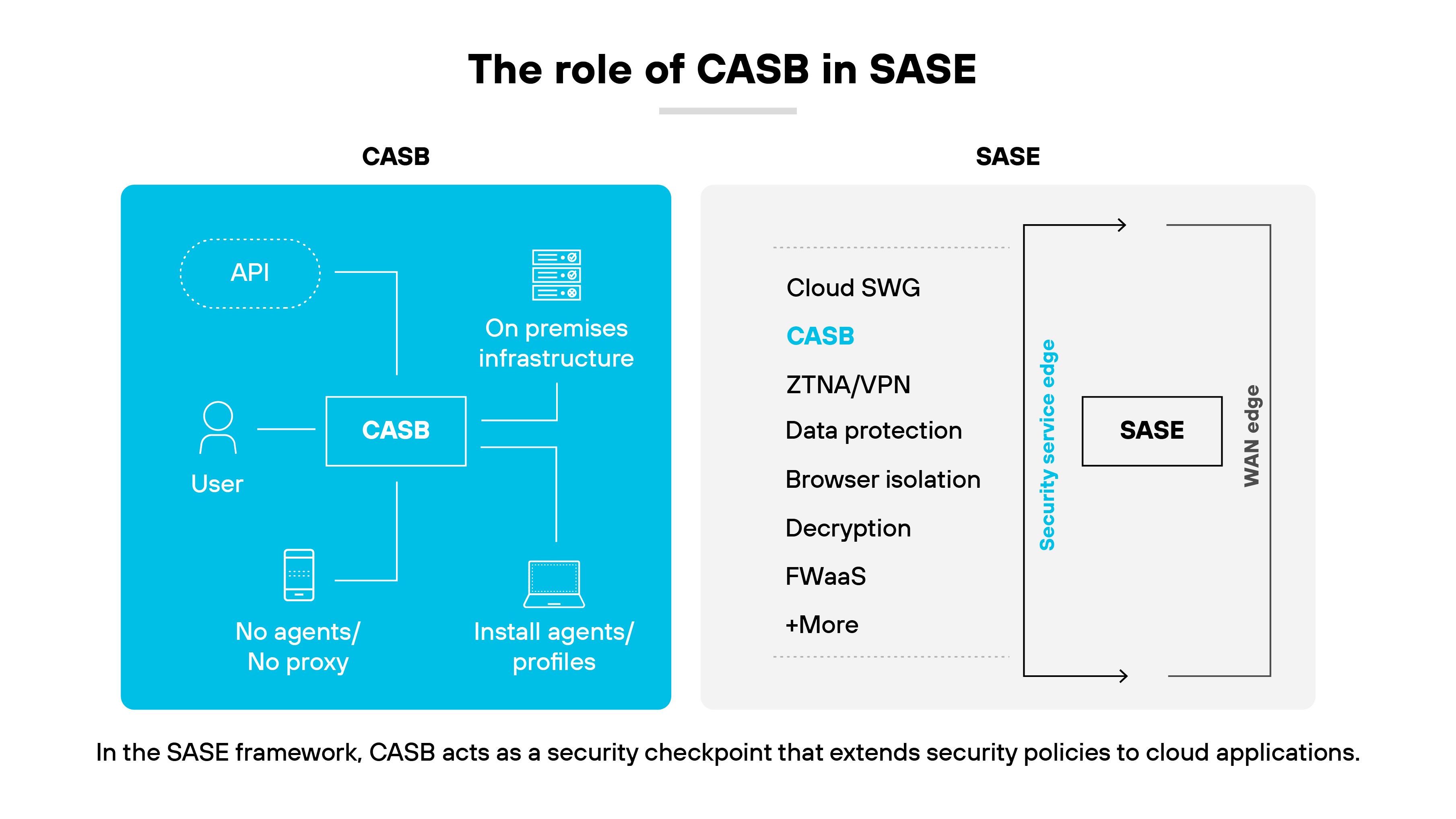
A CASB's primary function within SASE is to monitor and control access to cloud applications.
It checks that only authorized users can handle sensitive data, crucial for compliance with strict regulatory standards. This role is particularly important for companies using multiple SaaS applications accessed from various, sometimes insecure, locations.
As part of SASE, the CASB helps ensure cloud security is not isolated but integrated into the overall network security strategy.
Comparing CASBs with other security technologies
| Feature | Cloud access security broker (CASB) | Security service edge (SSE) | Security information and event management (SIEM) | Data loss prevention (DLP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | Secures cloud applications by monitoring and controlling data traffic between users and cloud services. | Provides comprehensive security features across network environments including CASB, SWG, and ZTNA within SASE. | Aggregates and analyzes security information and events across IT infrastructure. | Detects and prevents data breaches, leaks, and exposure of sensitive information. |
| Security coverage | Targets cloud-based environments and services, managing data access and security. | Covers data security both in transit and at rest across all network environments. | Focused on monitoring and managing on-premises environments; offers broad security event logging and incident management. | Operates across network, endpoint, and storage to safeguard sensitive data wherever it is processed, stored, or transmitted. |
| Implementation area | Cloud environments, particularly for SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS applications. | Integrated within SASE architecture to provide secure access to cloud services and network security. | On-premises environments; suitable for monitoring network hardware and applications. | On-premises and cloud environments; covers data across all domains. |
| Specific capabilities | Data security, threat protection, compliance, and visibility within cloud applications. | Unified security management with nuanced control over cloud interactions and data protection. | Real-time analysis of security alerts, event correlation, incident management, and compliance reporting. | Ensures data protection with policies that prevent unauthorized access and data exfiltration, focusing on data at rest and in motion. |
CASB vs. SSE
Security service edge (SSE) encompasses broader security features, including CASB, SWG, and ZTNA, within the SASE framework to enhance secure access to cloud services.
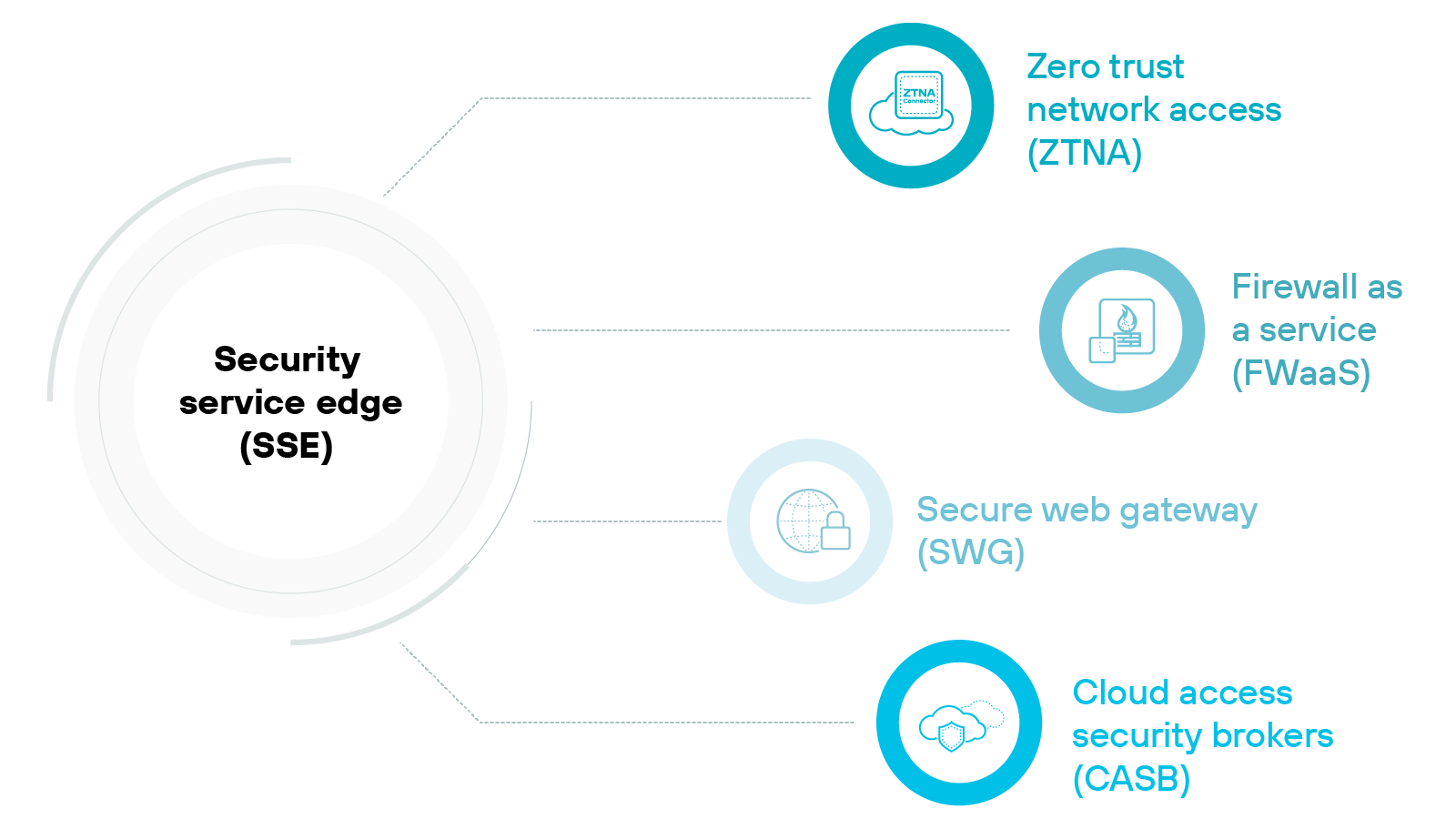
Unlike CASB, which specifically secures cloud applications by monitoring and controlling data traffic between users and cloud services, SSE provides a comprehensive suite of security capabilities designed to protect data in transit and at rest, across all network environments.
The integration of CASB within SSE frameworks ensures nuanced control and visibility over cloud interactions.
CASB vs. SIEM
Security information and event management (SIEM) systems aggregate and analyze activity from various resources across your IT infrastructure.
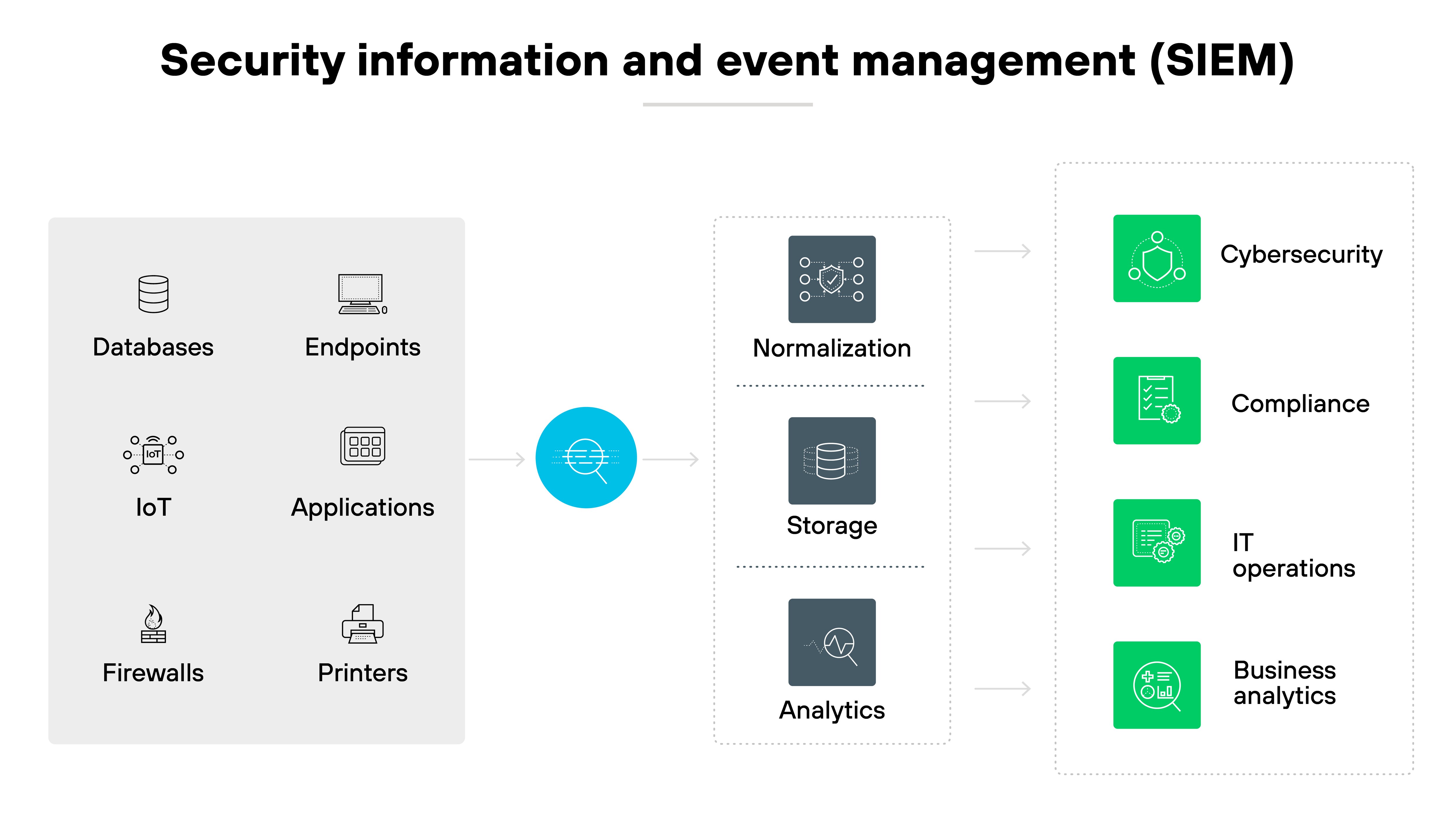
SIEM is used primarily for monitoring and managing on-premises environments, providing real-time analysis of security alerts generated by network hardware and applications.
CASB, on the other hand, focuses specifically on cloud environments, managing and securing data access across cloud services.
While SIEM provides a broad scope of security event logging and incident management, CASB offers targeted cloud application security policies and controls.
CASB vs. DLP
Data loss prevention solutions focus primarily on detecting and preventing data breaches, data leaks, and the exposure of sensitive information across the network and at rest.
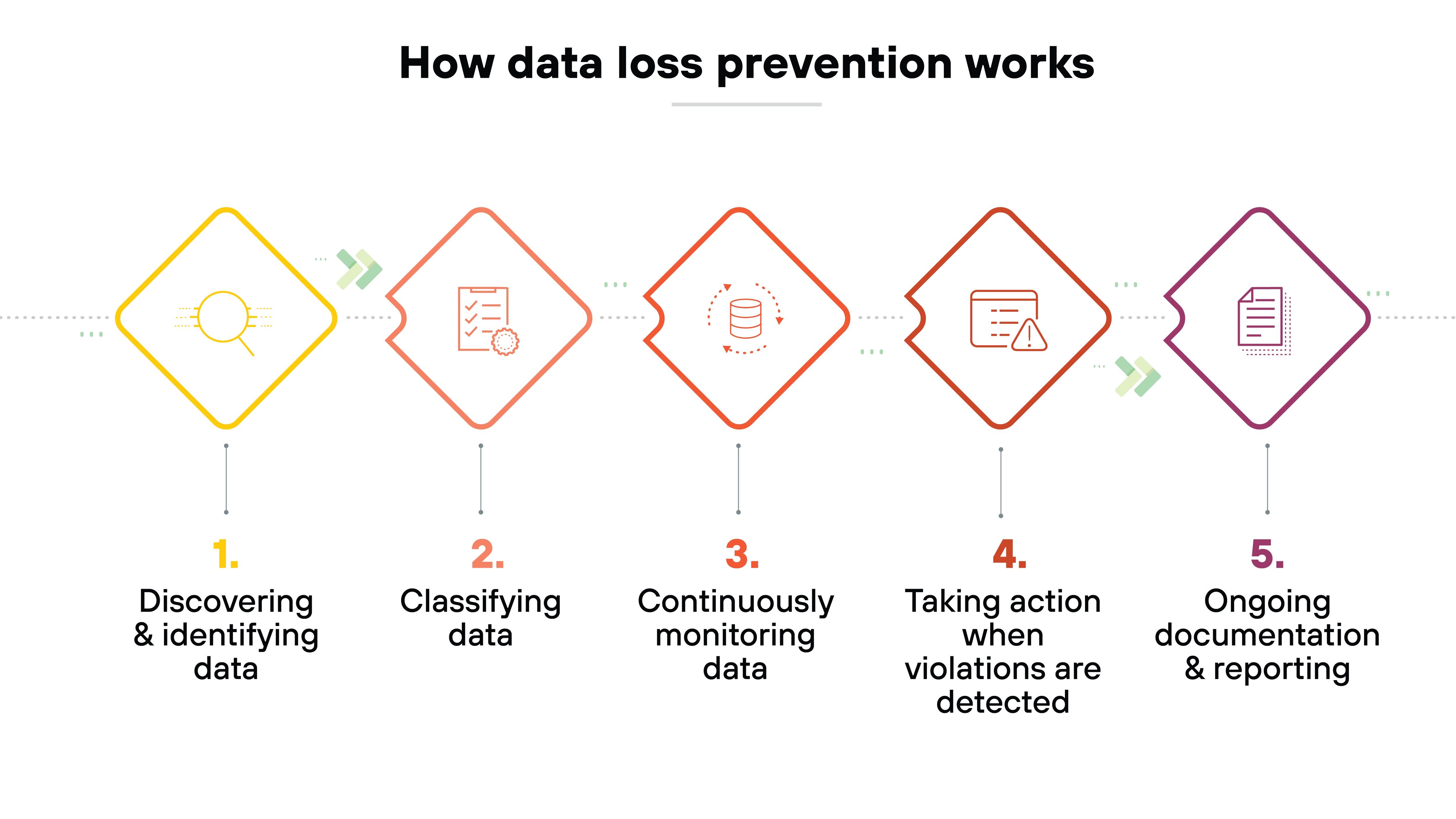
CASB integrates these capabilities within cloud environments, applying DLP policies specifically to cloud-based resources and services.
While traditional DLP covers data across endpoints, networks, and storage, CASB ensures these DLP controls extend into the cloud, offering specialized protections for cloud applications and storage solutions.
This allows for a unified approach to data protection that spans both on-premises and cloud-based environments.
What is the history of CASB?
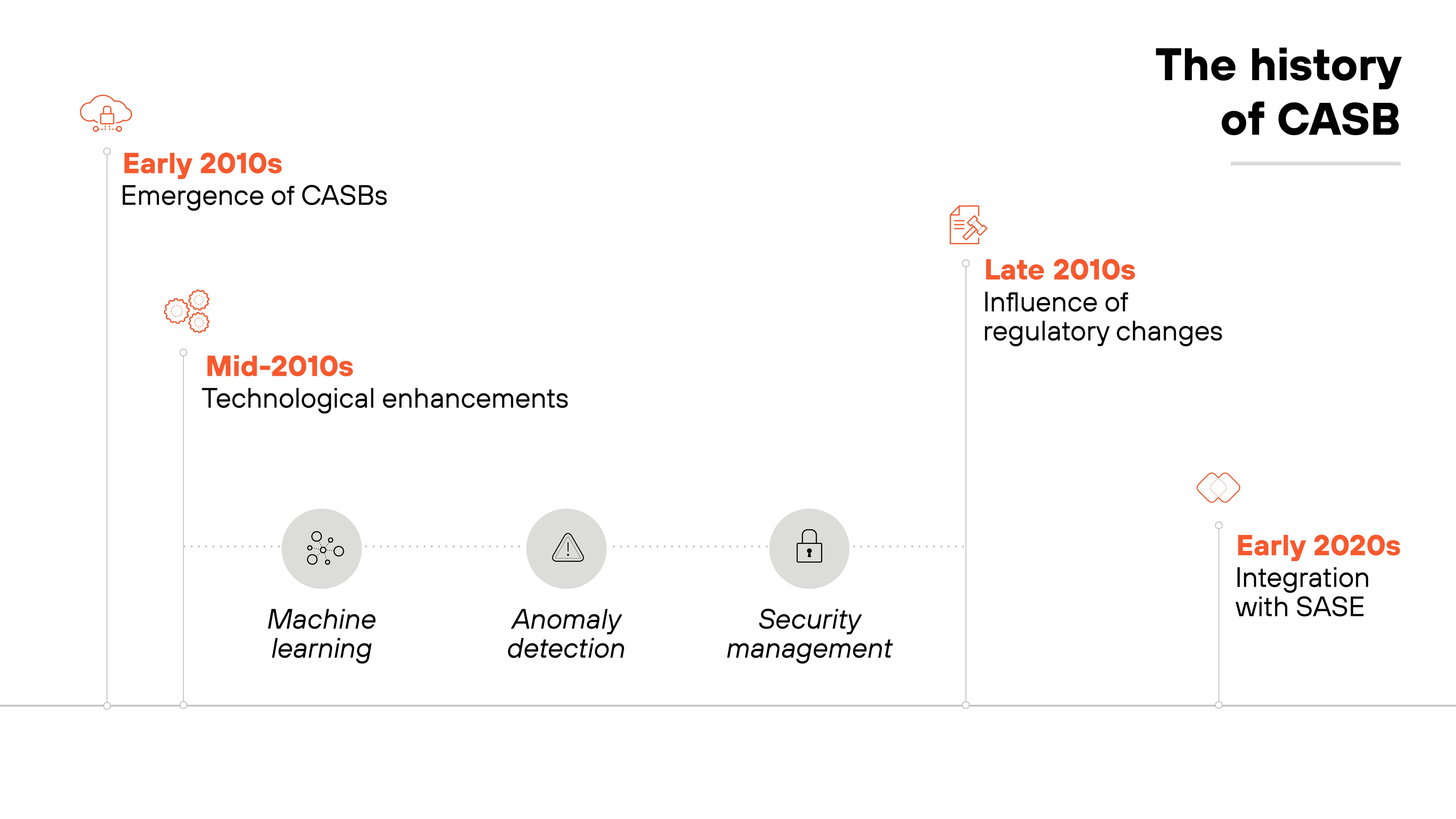
Cloud access security brokers emerged in the early 2010s.
Their arrival coincided with the rapid shift of enterprise data to the cloud. Initially, CASBs were developed to manage the security challenges of SaaS applications. A CASB was focused on extending traditional security measures beyond the confines of on-premises infrastructure.
As cloud adoption grew, so did the functionality of CASBs.
They began incorporating advanced technologies like machine learning—an enhancement that was crucial for improving anomaly detection and managing complex security incidents more effectively.
The regulatory environment also heavily influenced CASB evolution.
Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA called for better data protection strategies, especially for cloud-stored information. CASBs responded by enhancing their compliance features, becoming vital for organizations to meet stringent data protection standards.
Today, CASBs are integral to comprehensive security frameworks, especially with the rise of SASE.