Generative AI (GenAI) and large language models (LLMs) are becoming ubiquitous in businesses across sectors, increasing productivity, driving competitiveness and positively impacting companies’ bottom lines. However, as LLMs and GenAI become deeply integrated into your critical operations and decision-making processes, adversaries can exploit subtle vulnerabilities to manipulate your model outputs to coerce unauthorized behaviors or compromise sensitive information. They do this through a method called prompt attacks – a relatively new but increasingly sophisticated technique used to manipulate AI models. Whether you are a business leader, developer or security professional, understanding prompt attacks is essential. This is why we are thrilled to share new research with you that provides a framework to better understand the new prompt attacks targeting AI systems and models.
Palo Alto Networks has released Securing GenAI: A Comprehensive Report on Prompt Attacks – Taxonomy, Risks and Solutions, groundbreaking research on adversarial prompt attacks targeting GenAI systems.
The report reveals that leading LLMs remain highly vulnerable to prompt attacks. It also shows that some of these attacks achieve success rates as high as 88%, posing a significant risk to enterprises and AI applications.
This report underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive understanding of prompt-based threats and introduces a taxonomy classifying all known and emerging prompt attacks. This structured framework enables organizations to systematically assess risks, develop proactive defense strategies and enhance the security of GenAI systems against adversarial manipulation.
Understanding Emerging GenAI Prompt Attacks
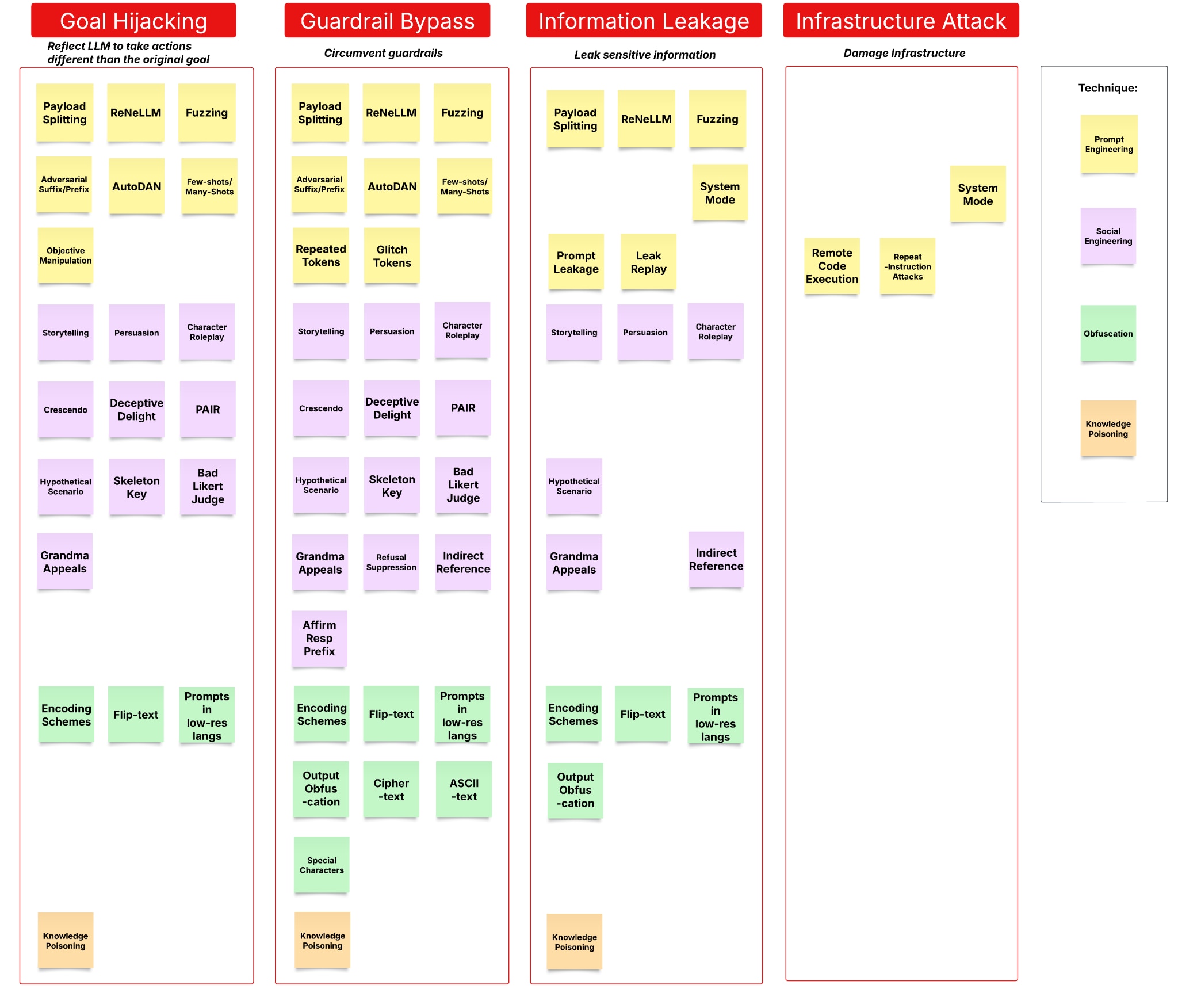
The research and supporting taxonomy have classified all identified prompt attacks into four categories by their impacts. These categories aim to guide your security teams in effectively identifying, mitigating and preventing adversarial prompt attacks:
- Goal Hijacking – Attackers manipulate prompts to alter the model’s intended behavior. For example, by framing malicious instructions as a storytelling task, an attacker can trick an LLM into generating unintended responses.
- Guardrail Bypass – Attackers circumvent your security controls, such as system prompts, training data constraints or input filters. This can include obfuscating disallowed instructions using encoding techniques or exploiting plugin permissions to generate harmful content or execute malicious scripts.
- Information Leakage – These attacks can extract your sensitive data, such as system prompts or proprietary training data. Techniques include reconnaissance on applications and replay attacks designed to retrieve confidential information from prior interactions.
- Infrastructure Attack – Prompts are crafted to exploit your system resources or execute unauthorized code. Examples include consuming excessive computational power or triggering remote code execution, which can compromise application integrity.
This proposed categorization differs from other technique-based categories, like prompt engineering, social engineering, obfuscation and knowledge poisoning. This is because techniques evolve over time, making it essential to focus on their broader implications. As such, each technique can contribute to one or more of the impact categories mentioned above. This is why, for most AI practitioners, the impacts of the prompt attacks are much more important than the techniques themselves.
Figure 1 provides a comprehensive mapping of over 30 prompt attack techniques to their respective impact categories, illustrating how different methods lead to specific security risks. Our findings confirm that this classification effectively captures the full spectrum of adversarial prompt attacks, offering a structured framework for understanding and mitigating these evolving threats.
Protecting Your Business from Emerging Risks
To effectively detect and prevent both existing and emerging prompt attacks, organizations must implement a holistic, multilayered security strategy for GenAI systems. Your key defense mechanisms must be tailored to each category of adversarial prompt attacks and work together in a layering of defenses. The following are some examples of mitigations by category of attack:
- Goal Hijacking Mitigation – Attackers often use this attack in an attempt to override prior instructions and manipulate the model into performing unintended tasks. Mitigation requires implementing input-level guardrails to detect and block adversarial prompt manipulation, including social engineering techniques and text obfuscation that attempt to alter model behavior.
- Guardrail Bypass Prevention – Since new jailbreak techniques continuously emerge, maintaining an adaptive and up to date LLM prompt security framework is essential. A robust guardrail system should continuously monitor and prevent attempts to override system restrictions, manipulate agent memory or exploit model vulnerabilities.
- Information Leakage Defense – Protecting against data exfiltration demands multiple layers of security. Input and output filtering should detect and prevent exposure of sensitive information, such as PII, PHI or proprietary data. Additionally, prompt leakage and replay attacks must be mitigated by securing system prompts and training data. AI agent workflows should also be safeguarded to prevent unauthorized tool extraction and use.
- Infrastructure Attack Prevention – Defending GenAI systems from infrastructure threats requires a combination of traditional application security and AI-specific protections. Repetitive prompt execution attacks should be blocked using adversarial prompt detection, while inputs and outputs must be scanned for malicious payloads, including harmful URLs and malware. Furthermore, monitoring user inputs for unauthorized backend tool access is crucial in preventing exploitation of AI agents.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can strengthen their GenAI systems against adversarial prompt attacks, ensuring both resilience and secure deployment in real-world environments.
Future Proofing Your GenAI Security Strategy
The benefits of GenAI will have positive business impacts for every company that adopts this revolutionary technology. But to see this impact, it must be adopted securely from the get-go. For this reason, it’s critical that stakeholders across the GenAI ecosystem proactively defend against adversarial prompt attacks and enhance the security of their systems, networks and data. Everyone has a part to play:
- GenAI Developers must securely design and conduct rigorous testing before deployment. Understanding adversarial prompt attack techniques and their impact enables developers to build resilient systems that withstand evolving threats.
- GenAI users, especially enterprises, are responsible for recognizing the risks associated with adversarial prompt attacks. By exercising caution and validating GenAI outputs, users can mitigate potential security threats and prevent unintended consequences.
- Enterprise administrators and information security professionals need to understand the different types of adversarial prompt attacks so that they can help strengthen security policies and risk management strategies. Organizations can help secure their environments by evaluating GenAI systems, enforcing strict access controls, and responding effectively to emerging threats.
The good news is that Palo Alto Networks has got you covered with advanced security solutions tailored for GenAI systems:
- AI Runtime Security is an adaptive, purpose-built solution that discovers, protects and monitors the entire enterprise application and agent stack including models and data from AI-specific and foundational network threats.
- AI Access Security offers comprehensive visibility and control over GenAI usage in enterprise environments, detecting potential data exposure risks and strengthening the overall security posture.
By integrating these security measures, your organization can confidently leverage GenAI while minimizing risks from adversarial prompt attacks.
The insights generated from our research are not merely observations – they’re a call for preemptive action. GenAI security solutions must secure the entire AI application and agent ecosystem including models and data. Read Securing GenAI: A Comprehensive Report on Prompt Attacks – Taxonomy, Risks and Solutions, embrace the strategies and join us in strengthening our defenses against the emerging adversarial prompt attacks. Together, we can redefine security, ensuring GenAI's potential is realized safely and effectively, promoting secure environments where innovation flourishes under comprehensive cybersecurity.